|
| His Majesty's Naval Service of the British Armed Forces |
|---|
| Components |
|
| History and future |
| Operations |
| Equipment |
| Personnel |
| Auxiliary services |
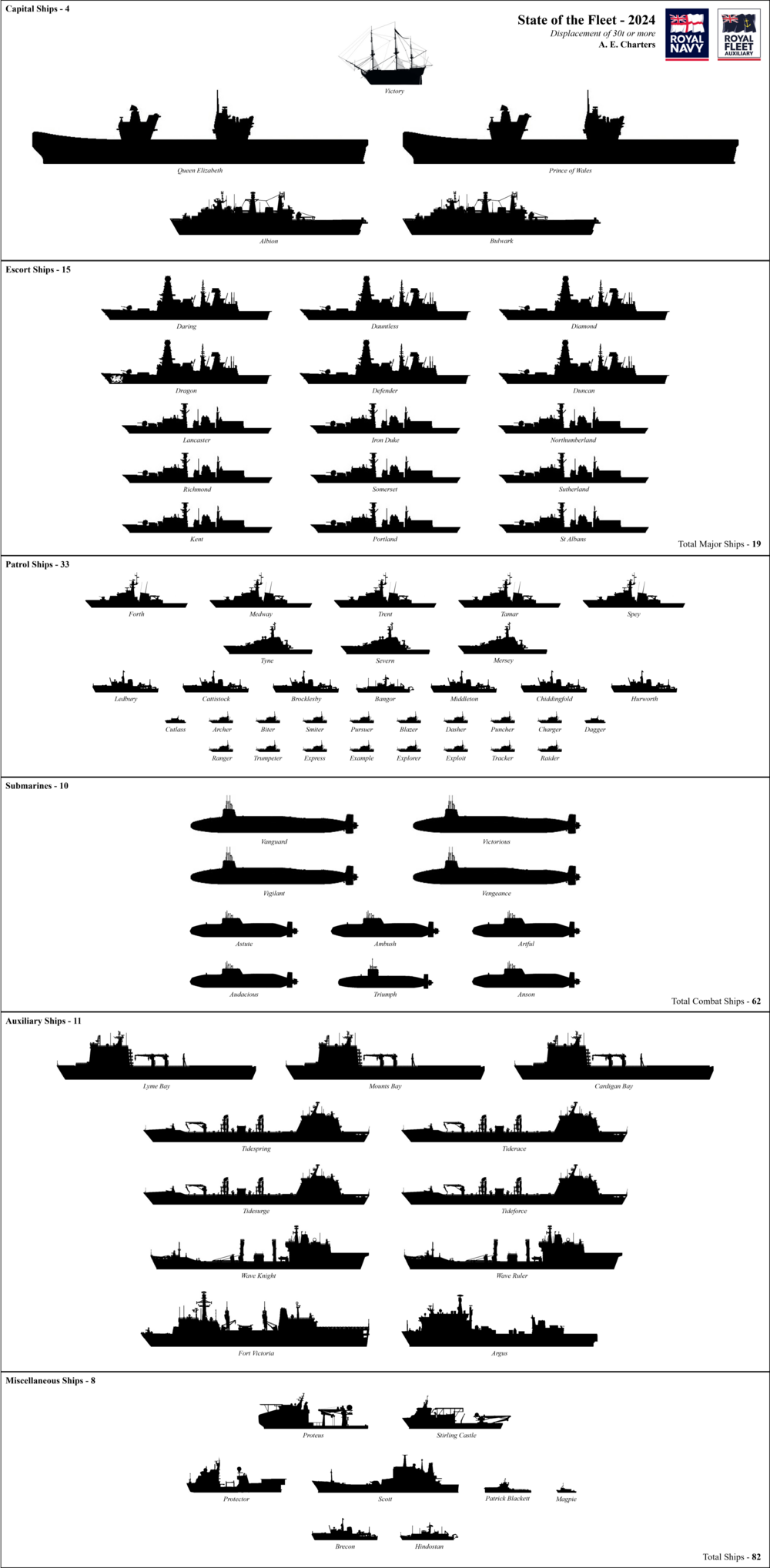
The Royal Navy is the principal naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Its assets include both commissioned warships and non-commissioned vessels. As of December 2025, there are 63 commissioned and active ships in the Royal Navy.
Contents
- Ceremonial/Historic ship
- Submarine service
- Surface fleet
- Auxiliary vessels
- Gallery
- Silhouettes
- See also
- Footnotes
- References
- External links
Of the commissioned vessels, fifteen are major surface combatants (two aircraft carriers, six guided missile destroyers and seven frigates) and ten are nuclear-powered submarines (four ballistic missile submarines and six fleet submarines). In addition the Navy possesses eight mine countermeasures vessels, twenty-six patrol vessels, two survey vessels, one icebreaker and one historic warship, Victory.
The total displacement of the Royal Navy's commissioned and active ships is approximately 401,600 tonnes.
The Royal Navy also includes a number of smaller non-commissioned assets. The naval training vessels Brecon and Hindostan can be found based at the Royal Navy stone frigates HMS Raleigh and the Britannia Royal Naval College, respectively. Non-commissioned Sea-class workboats, procured under Project Vahana, are operated by the Royal Navy in various support, survey and training roles, replacing previous P1000 Class Picket Boat vessels. [1] [2] [3] This class of vessel also incorporates an autonomous minehunting variant (known as the Arcims-class), [4] while another autonomous vessel, Madfox, is employed in varied roles including as a testbed for autonomous combat operations. [5] Madfox and other experimental vessels, including XV Patrick Blackett and APAC-24 (a crewless Pacific 24 rigid-hulled inflatable boat), are operated by the Fleet Experimentation Squadron within the Disruptive Capabilities and Technologies Office. [6] [7] [8] As of 2025, XV Excalibur, an Extra-Large Uncrewed Underwater Vehicle (XLUUV), was also operated by the Squadron [6] while other autonomous surface vessels, for minehunting, were in service and in the process of procurement from Thales Group. [9]
Besides the Royal Navy, the Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) and the Royal Marines operate their own flotillas of vessels which complement the assets of the Royal Navy. These vessels are not included in this list or the above figures. Nevertheless, combined, the Royal Navy and RFA have 73 vessels with a total displacement of about 673,600 tonnes, with the principal landing craft of the Royal Marines having an additional combined displacement of about 2,200 tonnes.
As a supporting contingent of His Majesty's Naval Service, the civilian Marine Services operate nearly 100 auxiliary ships (including coastal logistics, tugs and research vessels) in support of Royal Navy and Royal Fleet Auxiliary operations. [10] [11]
In the United Kingdom, the Royal Navy operates three main bases where commissioned ships are based: HMNB Portsmouth, HMNB Devonport and HMNB Clyde. A number of commissioned vessels, belonging to the University Royal Naval Units (URNU), are stationed at various other locations around the United Kingdom.
The Royal Navy's principal overseas base is HMS Jufair in Bahrain. [12] Until 2025/26, a general-purpose frigate and vessels belonging to the navy's 9th Mine Counter-Measures Squadron were forward-deployed there. However, HMS Lancaster was retired in Bahrain in December 2025, while the last remaining minehunter deployed there is planned for withdrawal in early 2026. This will leave the Royal Navy with no forward presence in the Persian Gulf, at least until (and if) alternative taskings can be arranged. [13] Two fast patrol boats, together with a forward-deployed River-class offshore patrol vessel, normally form part of the Gibraltar Squadron and are permanently based there. Four other River-class vessels are also forward-deployed: one in the Falkland Islands, one in the Caribbean and two in the Indo-Pacific region. Additionally, the United Kingdom maintains a Joint Logistics Support Base in Duqm, Oman. [14]
All ships and submarines currently in commission with the Royal Navy were built in the United Kingdom, with the exceptions of icebreaker Protector which was built in Norway and survey vessel Magpie which was substantially built in Ireland. All commissioned vessels of the Royal Navy bear the ship prefix "HMS", for His Majesty's Ship or His Majesty's Submarine.