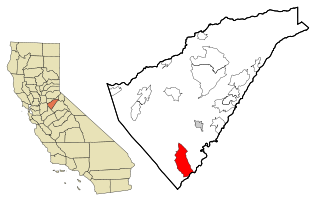
Copperopolis is an unincorporated town and census-designated place (CDP) in Calaveras County, California, United States. The population was 3,671 at the 2010 census, up from 2,363 at the 2000 census. The town is located along State Route 4 and is registered as California Historical Landmark #296.

Columbia State Historic Park, also known as Columbia Historic District, is a state park unit and National Historic Landmark District preserving historic downtown Columbia, California, United States. It includes almost 30 buildings built during the California Gold Rush, most of which remain today. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1961.

The Quincy Mine is an extensive set of copper mines located near Hancock, Michigan. The mine was owned by the Quincy Mining Company and operated between 1846 and 1945, although some activities continued through the 1970s. The Quincy Mine was known as "Old Reliable," as the Quincy Mine Company paid a dividend to investors every year from 1868 through 1920. The Quincy Mining Company Historic District is a United States National Historic Landmark District; other Quincy Mine properties nearby, including the Quincy Mining Company Stamp Mills, the Quincy Dredge Number Two, and the Quincy Smelter are also historically significant.

Keweenaw National Historical Park is a unit of the U.S. National Park Service. Established in 1992, the park celebrates the life and history of the Keweenaw Peninsula in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As of 2009, it is a partly privatized park made up of two primary units, the Calumet Unit and the Quincy Unit, and 21 cooperating "Heritage Sites" located on federal, state, and privately owned land in and around the Keweenaw Peninsula. The National Park Service owns approximately 1,700 acres (690 ha) in the Calumet and Quincy Units. Units are located in Baraga, Houghton, Keweenaw, and Ontonagon counties.
The following is a list of Registered Historic Places in Iron County, Michigan. The list includes 79 structures and historic districts that are significant for their architectural, historical, or industrial/economic importance.
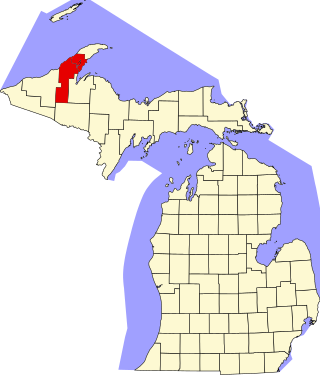
This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Houghton County, Michigan.

The following is a list of Registered Historic Places in Keweenaw County, Michigan.
This National Park Service list is complete through NPS recent listings posted July 28, 2023.

Fort Wilkins Historic State Park is a historical park operated by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources at Copper Harbor, Michigan. The park preserves the restored 1844 army military outpost, Fort Wilkins, which was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1970. The state park's 700 acres (280 ha) include camping and day-use facilities as well as the Copper Harbor Lighthouse, built in 1866. The park is a "Cooperating Site" of the Keweenaw National Historical Park.

The Calumet Historic District is a National Historic Landmark District that encompasses most of the village of Calumet, Michigan. The district was designated in 1989 for the community's importance in the history of the region's copper mining industry.

The J. Vivian Jr. and Company Building is a commercial building located at 342 Hecla Street in Laurium, Michigan. Constructed in the Italian Renaissance Revival and Italianate architectural styles, it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2003.

The Quincy Smelter, also known as the Quincy Smelting Works, is a former copper smelter located on the north side of the Keweenaw Waterway in Ripley, Michigan. It is a contributing property of the Quincy Mining Company Historic District, a National Historic Landmark District. The smelter was built in 1898 by the Quincy Mining Company, operating from 1898 to 1931 and again from 1948 to 1971. The smelter was part of a Superfund site from 1986 to 2013.

The Hines Mansion is a historic house in Provo, Utah, United States. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It was built in 1895 for R. Spencer Hines and his wife Kitty. At the time the mansion was built, it was recognized as one of the finest homes in Provo. The Hines Mansion was designated to the Provo City Historic Landmarks Registry on March 7, 1996.

The Provo Downtown Historic District is a 25-acre (10 ha) historic area located in Provo, Utah, United States. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The Copperopolis Armory is a Civil War armory located at 695 Main St. in Copperopolis, California. The brick Greek Revival building was constructed in 1864 to house the Union Guard of Copperopolis, the town's regiment of the Union Army. Copperopolis largely owed its existence to the war; the town grew due to a boom in local copper mining in 1860, which stemmed from the Union Army's need for copper ammunition. The armory served a variety of purposes for the Union Guard; at the building, new soldiers were enlisted, training was conducted, and arms and supplies were stored. Military balls, victory celebrations, and the local funeral ceremonies for Abraham Lincoln also took place in the armory. The armory also held an 1837 bronze cannon, which was used for ceremonial purposes and arms training; the cannon remains in the building and is one of the few American bronze cannons from the era in California. After the war, the Independent Order of Odd Fellows bought the building, which they converted to a social hall. In 1940, the armory became a community center.

Reed's Store is a historic building located at 679 Main St. in Copperopolis, California. William K. Reed, a miner and one of the first discoverers of copper in Copperopolis, built the store in 1861 to serve the growing mining town. The two-story brick store was designed in the Neoclassical style, a common design for commercial establishments at the time. Reed's Store was the most successful store in Copperopolis until 1867, when a fire and the declining copper industry greatly diminished the town's population. Various lessees rented the store until mine owner Charles Ames bought it in 1890; Ames sold the store to merchant Charles Fontana by 1900. In 1906, the store became the property of the Union Copper Mining Company, which made the building its headquarters. The company, later renamed the Calaveras Copper Mining Company, occupied the building throughout the town's 1909–1929 copper boom. The store is now one of four buildings remaining from the 1860s in Calaveras; it is adjacent to two others, the Copperopolis Armory and the Honigsberger Store.

The McCarthy General Store is a historic former general store and boarding house at Kennecott and Skolai Streets in the small community of McCarthy, Alaska, located in the heart of Wrangell-St. Elias National Park and Preserve. At two stories in height and measuring 47 by 56 feet, it is McCarthy's largest building, and one of its oldest. It was built in 1914, during the mining boom at nearby Kennecott. The store occupied the ground floor of the building, and the upper level had eleven rooms for boarders. The building was abandoned after the mining boom ended in the 1930s,.
The McCarthy Power Plant, also known as the Mother Lode Coalition Mining Company Power House and the Mother Lode Plant, is a historic power plant building in the small community of McCarthy, Alaska, in the heart of Wrangell-St. Elias National Park and Preserve. It is a three-story wood-frame structure with a clerestory roof, located on the banks of McCarthy Creek. It was built in 1917, after the arrival of the Copper River and Northwestern Railway in the area kicked of a building boom. The coal-fired power plant was built to provide electricity for the operation of a tramway and other facilities of the Kennecott mines. Most of the transmission lines and the tramway were destroyed by avalanches in 1919, and other changes made soon afterward made the power plant unnecessary, and its turbine was moved up to Kennecott.

















