
IV Corps was a corps-sized formation of the British Army, formed in both the First World War and the Second World War. During the First World War the corps served on the Western Front throughout its existence. During the Second World War it served in Norway and Britain until it was transferred to India, which was threatened with attack after Japan entered the war.

The First Battle of Ypres was a battle of the First World War, fought on the Western Front around Ypres, in West Flanders, Belgium. The battle was part of the First Battle of Flanders, in which German, French, Belgian armies and the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) fought from Arras in France to Nieuwpoort (Nieuport) on the Belgian coast, from 10 October to mid-November. The battles at Ypres began at the end of the Race to the Sea, reciprocal attempts by the German and Franco-British armies to advance past the northern flank of their opponents. North of Ypres, the fighting continued in the Battle of the Yser (16–31 October), between the German 4th Army, the Belgian army and French marines.

The Race to the Sea took place from about 17 September – 19 October 1914 during the First World War, after the Battle of the Frontiers and the German advance into France. The invasion had been stopped at the First Battle of the Marne (5–12 September) and was followed by the First Battle of the Aisne (13–28 September), a Franco-British counter-offensive. The term describes reciprocal attempts by the Franco-British and German armies to envelop the northern flank of the opposing army through the provinces of Picardy, Artois and Flanders, rather than an attempt to advance northwards to the sea. The "race" ended on the North Sea coast of Belgium around 19 October, when the last open area from Diksmuide to the North Sea was occupied by Belgian troops who had retreated after the Siege of Antwerp. The outflanking attempts had resulted in a number of encounter battles but neither side was able to gain a decisive victory.
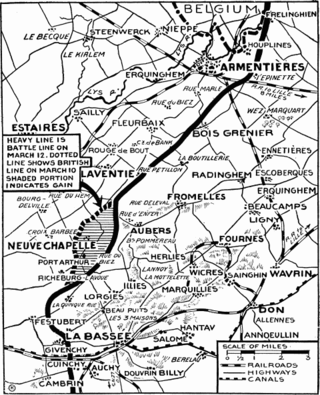
The Battle of Festubert was an attack by the British army in the Artois region of France on the western front during World War I. The offensive formed part of a series of attacks by the French Tenth Army and the British First Army in the Second Battle of Artois (3 May – 18 June 1915). After the failure of the breakthrough attempt by the First Army in the attack at Aubers Ridge tactics of a short hurricane bombardment and an infantry advance with unlimited objectives, were replaced by the French practice of slow and deliberate artillery-fire intended to prepare the way for an infantry attack.

The Battle of Neuve Chapelle took place in the First World War in the Artois region of France. The attack was intended to cause a rupture in the German lines, which would then be exploited with a rush to the Aubers Ridge and possibly Lille. A French assault at Vimy Ridge on the Artois plateau was also planned to threaten the road, rail and canal junctions at La Bassée from the south as the British attacked from the north. The British attackers broke through German defences in a salient at the village of Neuve-Chapelle but the success could not be exploited.

Winter operations 1914–1915 is the name given to military operations during the First World War, from 23 November 1914 – 6 February 1915, in the 1921 report of the British government Battles Nomenclature Committee. The operations took place on the part of the Western Front held by the British Expeditionary Force (BEF), in French and Belgian Flanders.

The Battle of Aubers was a British offensive on the Western Front on 9 May 1915 during the First World War. The battle was part of the British contribution to the Second Battle of Artois, a Franco-British offensive intended to exploit the German diversion of troops to the Eastern Front. The French Tenth Army was to attack the German 6th Army north of Arras and capture Vimy Ridge, preparatory to an advance on Cambrai and Douai. The British First Army, on the left (northern) flank of the Tenth Army, was to attack on the same day and widen the gap in the German defences expected to be made by the Tenth Army and to fix German troops north of La Bassée Canal.

The Battle of Arras, was an attempt by the French Army to outflank the German Army, which was attempting to do the same thing during the "Race to the Sea", their reciprocal attempts to exploit conditions created during the First Battle of the Aisne. At the First Battle of Picardy (22–26 September) each side had attacked expecting to advance round an open northern flank and found instead that troops had arrived from further south and extended the flank northwards.

The 13th Frontier Force Rifles was part of the British Indian Army, and after 1947, Pakistan Army. It was formed in 1922 by amalgamation of five existing regiments and consisted of five regular battalions. In 1947, it was allocated to the Pakistan Army.

V Corps was an army corps of the British Army that saw service in both the First and the Second World Wars. It was first organised in February 1915 and fought through the First World War on the Western front. It was recreated in June 1940, during the Second World War and was substantially reorganised in 1942 for participation in Operation Torch. It fought through the Tunisia Campaign and later the Italian Campaign.

The 7th (Meerut) Division was an infantry division of the Indian Army and before 1895, the Bengal Army, that saw active service during World War I.

The 3rd (Lahore) Division was an infantry division of the Indian Army and before 1895, the Bengal Army, first organised in 1852. It saw service during World War I as part of the Indian Corps in France before being moved to the Middle East where it fought against troops of the Ottoman Empire.
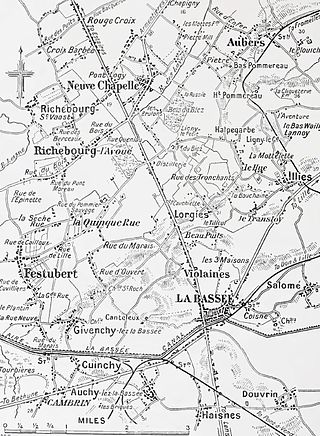
The Battle of La Bassée was fought by German and Franco-British forces in northern France in October 1914, during reciprocal attempts by the contending armies to envelop the northern flank of their opponent, which has been called the Race to the Sea. The 6th Army took Lille before a British force could secure the town and the 4th Army attacked the exposed British flank further north at Ypres. The British were driven back and the German army occupied La Bassée and Neuve Chapelle. Around 15 October, the British recaptured Givenchy-lès-la-Bassée but failed to recover La Bassée.
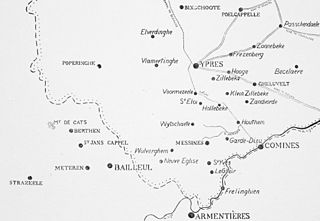
The Battle of Messines was fought in October 1914 between the armies of the German empire against the British empire and France, as part of what came to be called the Race to the Sea: reciprocal attempts by the German and Entente armies to attack beyond the northern flank of their opponent. The attempts to turn the northern flank led to several meeting engagements until the North Sea left neither side with a flank to aim at. The battle was fought between the river Douve and the Comines–Ypres canal.

The Battle of Armentières was fought by German and Franco-British forces in northern France in October 1914, during reciprocal attempts by the armies to envelop the northern flank of their opponent, which has been called the Race to the Sea. Troops of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) moved north from the Aisne front in early October and then joined in a general advance with French troops further south, pushing German cavalry and Jäger back towards Lille until 19 October. German infantry reinforcements of the 6th Army arrived in the area during October.
Indian Army during World War I order of battle
Lieutenant-General Sir Henry Fuller Maitland Wilson was a British Army officer who, throughout his long military career which spanned over four decades, served in the Second Anglo-Afghan War, the Second Boer War and the First World War, during which he served with distinction, commanding a division on the Western Front and an army corps in the lesser-known Salonikan campaign.

The Defence of Festubert was an engagement on the Western Front early in the First World War when Indian and British battalions of the 7th (Meerut) Division of the Indian Army defended the village of Festubert against a German attack from 23 to 24 November 1914. It was one of the first actions in the war in which an attack was made against a prepared defensive position. The British and Indian regiments that took part were awarded the battle honour Festubert 1914.
The First World War British Cavalry Corps was formed 9 October 1914.
The Garhwal Brigade was an infantry brigade of the British Indian Army formed in 1902 as a result of the Kitchener Reforms. It was mobilized as 20th (Garhwal) Brigade at the outbreak of the First World War as part of the 7th (Meerut) Division and departed for France. It served on the Western Front until November 1915. It then moved to Egypt where it joined the 10th Indian Division, by now designated as 20th Indian Brigade. It left the division in March 1916 and thereafter served as an independent brigade in the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. It was broken up in 1920.
















