Twenty-four known prisoner-of-war camps existed across Canada during the First World War. The ethnic groups arrested and detained in internment camps were Austro-Hungarians (mostly Ukrainians) and Germans. Austro-Hungarian Prisoners were mainly residents of Canada from Ukraine, part of Serbia, the Czech Republic, Slovakia. Since Ukraine, part of Serbia, the Czech Republic and Slovakia were then provinces of the empire of Austria-Hungary, many still had Austro-Hungarian citizenship and were considered to be resident enemy aliens. William Dostock, for example, who immigrated to Canada in 1910 from Austria-Hungary and was not yet naturalized was interned from 1915–1920 as an enemy alien. [1]
German prisoners were mainly residents of Canada from Germany. Germans formed a large proportion of the detainees since Canada served as a place of detention for German prisoners of war on behalf of the British. [1]
The prisoners were given various tasks; many worked in the forests as logging crews. In addition to the main camps, there were branch camps and labour camps. [1]
| Camp | Location | Province | Type of Buildings | Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amherst Internment Camp | Amherst | Nova Scotia | Malleable Iron Foundry | April 1915 to September 1919 |
| Beauport | Quebec | The Armoury | December 1914 to June 1916 | |
| Castle Mountain Internment Camp | Banff & Castle Mountain | Alberta | Dominion Park | July 1915 to July 1917 |
| Brandon | Manitoba | Exhibition Building | September 1914 to July 1916 | |
| Edgewood | British Columbia | Bunk Houses | August 1915 to September 1916 | |
| Fernie & Morrissey | British Columbia | Rented premises | June 1915 to October 1918 | |
| Halifax | Nova Scotia | Halifax Citadel | September 1914 to October 1918 | |
| Jasper | Alberta | Dominion Park | February 1916 to August 1916 | |
| Kapuskasing, Ontario | Ontario | Bunk Houses | December 1914 to February 1920 | |
| Kingston, Ontario | Ontario | Fort Henry | August 1914 to November 1917 | |
| Lethbridge | Alberta | Exhibition Building | September 1914 to November 1916 | |
| Monashee & Mara Lake | British Columbia | Tents and Bunkhouses | June 1915 to July 1917 | |
| Montreal | Quebec | Immigration Hall | August 1914 to November 1918 | |
| Eaton Internment Camp | Munson Eaton | Alberta Saskatchewan | Railway Cars | October 1918 to March 1919 |
| Nanaimo | British Columbia | Provincial government building | September 1914 to September 1915 | |
| Niagara Falls | Ontario | The Armoury | December 1914 to August 1918 | |
| Petawawa | Ontario | Militia Camp | December 1914 to May 1916 | |
| Revelstoke & Field & Otter | British Columbia | Bunk Houses | September 1915 to October 1916 | |
| Sault Ste. Marie | Ontario | The Armoury | January 1915 to January 1918 | |
| Spirit Lake | Spirit Lake | Quebec | Bunk Houses | January 1915 to January 1917 |
| Toronto | Ontario | Stanley Barracks | December 1914 to October 1916 | |
| Winnipeg | Manitoba | Fort Osborne | September 1914 to July 1916 | |
| Valcartier | Quebec | Militia Camp | April 1915 to October 1915 | |
| Vernon | British Columbia | Provincial government building | September 1914 to February 1920 |

Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire or the Dual Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military and diplomatic alliance, it consisted of two sovereign states with a single monarch who was titled both Emperor of Austria and King of Hungary. Austria-Hungary constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy: it was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after Hungary terminated the union with Austria on 31 October 1918.

Czechoslovakia was a landlocked state in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland became part of Nazi Germany, while the country lost further territories to Hungary and Poland. Between 1939 and 1945, the state ceased to exist, as Slovakia proclaimed its independence and Carpathian Ruthenia became part of Hungary, while the German Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia was proclaimed in the remainder of the Czech Lands. In 1939, after the outbreak of World War II, former Czechoslovak President Edvard Beneš formed a government-in-exile and sought recognition from the Allies.

Pan-Slavism, a movement that took shape in the mid-19th century, is the political ideology concerned with promoting integrity and unity for the Slavic people. Its main impact occurred in the Balkans, where non-Slavic empires had ruled the South Slavs for centuries. These were mainly the Byzantine Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Venice.

The Eastern Front or Eastern Theater of World War I, for Russia Second Patriotic War, was a theater of operations that encompassed at its greatest extent the entire frontier between Russia and Romania on one side and Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, the Ottoman Empire, and Germany on the other. It ranged from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south, involved most of Eastern Europe, and stretched deep into Central Europe. The term contrasts with the Western Front, which was being fought in Belgium and France.

The krone was the official currency of Austria-Hungary from 1892 until the dissolution of the empire in 1918. The subunit was one hundredth of the main unit, and was called a Heller in the Austrian and a fillér in the Hungarian part of the Empire.

The United States of Greater Austria was an unrealised proposal made in 1906 to federalize Austria-Hungary to help resolve widespread ethnic and nationalist tensions. It was conceived by a group of scholars surrounding Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, notably by the ethnic Romanian lawyer and politician Aurel Popovici.

The Ukrainian Canadian internment was part of the confinement of "enemy aliens" in Canada during and for two years after the end of the First World War. It lasted from 1914 to 1920, under the terms of the War Measures Act.
In customary international law, an enemy alien is any native, citizen, denizen or subject of any foreign nation or government with which a domestic nation or government is in conflict and who is liable to be apprehended, restrained, secured and removed. Usually, the countries are in a state of declared war.

Gakovo is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Sombor municipality, in the West Bačka District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population is 2,201.

Internment of German resident aliens and German-American citizens occurred in the United States during the periods of World War I and World War II. During World War II, the legal basis for this detention was under Presidential Proclamation 2526, made by President Franklin Delano Roosevelt under the authority of the Alien Enemies Act.
Upon the outbreak of World War I, Ukraine was not an independent political entity or state. The majority of the territory that makes up the modern country of Ukraine was part of the Russian Empire with a notable far western region administered by the Austro-Hungarian Empire, and the border between them dating to the Congress of Vienna in 1815.

The Castle Mountain Internment Camp, located in Banff National Park, Alberta, was the largest internment facility in the Canadian Rockies, housing several hundred prisoners at any one time. Established on July 13, 1915, a total of 660 enemy aliens were interned at the facility during its entire operation.

Fort Oglethorpe, Georgia was a German-American internment camp in Catoosa County, Georgia, during and after World War I. Facilities at the fort were used to detain some 4,000 enemy military personnel, prisoners of war, and civilian internees arrested under the Alien and Sedition Acts, between 1917 and 1920. After it was deactivated in 1947, the Camp's facilities formed the basis for the present day town of Fort Oglethorpe, Georgia.

The Austro-Hungarian Armed Forces occupied Serbia from late 1915 until the end of World War I. Austria-Hungary's declaration of war against Serbia on 28 July 1914 marked the beginning of the war. After three unsuccessful Austro-Hungarian offensives between August and December 1914, a combined Austro-Hungarian and German offensive breached the Serbian front from the north and west in October 1915, while Bulgaria attacked from the east. By January 1916, all of Serbia had been occupied by the Central Powers.

The Czechoslovak Italian Legion was a legion of Czechoslovak volunteers formed late in World War I. The first formal Czechoslovak Volunteers Group was formed in Italian prisoner-of-war camps in Santa Maria Capua Vetere, near Naples and matured at Padula near Salerno. In January 1918, the headquarters of the 6th Italian Army finally agreed to form reconnaissance squadrons from Czechoslovak and Southern Slav volunteers. In September 1918, the 39th Regiment of the Czechoslovak Italian Legion was formed from those volunteer reconnaissance squadrons. The following regiments of Czechoslovak Italian Legion were formed in April and May 1918:

Veľký Meder is a town in the Dunajská Streda District, Trnava Region in southwestern Slovakia.
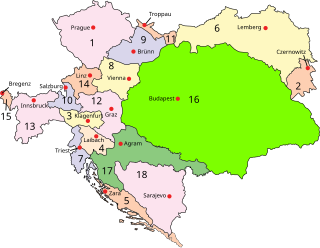
The dissolution of Austria-Hungary was a major geopolitical event that occurred as a result of the growth of internal social contradictions and the separation of different parts of Austria-Hungary. The more immediate reasons for the collapse of the state were World War I, the 1918 crop failure, general starvation and the economic crisis. The Austro-Hungarian Empire had additionally been weakened over time by a widening gap between Hungarian and Austrian interests. Furthermore, a history of chronic overcommitment rooted in the 1815 Congress of Vienna in which Metternich pledged Austria to fulfill a role that necessitated unwavering Austrian strength and resulted in overextension. Upon this weakened foundation, additional stressors during World War I catalyzed the collapse of the empire. The 1917 October Revolution and the Wilsonian peace pronouncements from January 1918 onward encouraged socialism on the one hand, and nationalism on the other, or alternatively a combination of both tendencies, among all peoples of the Habsburg monarchy.
An Internment Camp in Vernon, BC was established to hold enemy aliens and POWs during the First World War. Once Canada entered World War I, fears of enemy aliens on the home front began to arise. To combat this, the Canadian Government implemented the War Measures Act which gave them the authority to intern and disenfranchise enemy aliens living in Canada. Approximately 8,500 enemy aliens were interned across Canada, with majority of the 24 camps located around the Rocky Mountains and large population centres in Ontario. Vernon housed the permanent camp in British Columbia, operating from September 18, 1914, to February 20, 1920.

Between 7–9 million soldiers surrendered and were held in prisoner-of-war camps during World War I. All nations pledged to follow the Hague Conventions on fair treatment of prisoners of war, and the survival rate for POWs was generally, though not always, much higher than that of combatants at the front.
| Part of a series on the |
| Military history of Canada |
|---|
 |