
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated –COO− form under biological conditions), and an imidazole side chain (which is partially protonated), classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH. Initially thought essential only for infants, it has now been shown in longer-term studies to be essential for adults also. It is encoded by the codons CAU and CAC.

Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates.

Succinyl coenzyme A synthetase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reversible reaction of succinyl-CoA to succinate. The enzyme facilitates the coupling of this reaction to the formation of a nucleoside triphosphate molecule from an inorganic phosphate molecule and a nucleoside diphosphate molecule. It plays a key role as one of the catalysts involved in the citric acid cycle, a central pathway in cellular metabolism, and it is located within the mitochondrial matrix of a cell.
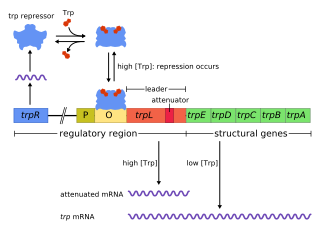
The trp operon is a group of genes that are transcribed together, encoding the enzymes that produce the amino acid tryptophan in bacteria. The trp operon was first characterized in Escherichia coli, and it has since been discovered in many other bacteria. The operon is regulated so that, when tryptophan is present in the environment, the genes for tryptophan synthesis are repressed.

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).
The hisB gene, found in the enterobacteria, in Campylobacter jejuni and in Xylella/Xanthomonas encodes a protein involved in catalysis of two step in histidine biosynthesis, namely the bifunctional Imidazoleglycerol-phosphate dehydratase/histidinol-phosphatase.

3-Amino-1,2,4-triazole (3-AT) is a heterocyclic organic compound that consists of a 1,2,4-triazole substituted with an amino group.

6-Phosphogluconolactonase (EC 3.1.1.31, 6PGL, PGLS, systematic name 6-phospho-D-glucono-1,5-lactone lactonohydrolase) is a cytosolic enzyme found in all organisms that catalyzes the hydrolysis of 6-phosphogluconolactone to 6-phosphogluconic acid in the oxidative phase of the pentose phosphate pathway:

Phosphofructokinase (PFK) is a kinase enzyme that phosphorylates fructose 6-phosphate in glycolysis.
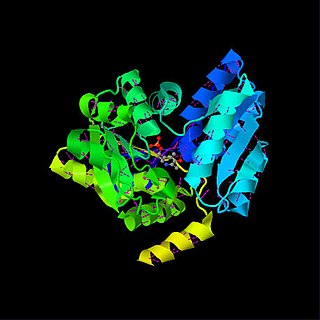
Serine dehydratase or L-serine ammonia lyase (SDH) is in the β-family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent (PLP) enzymes. SDH is found widely in nature, but its structural and properties vary among species. SDH is found in yeast, bacteria, and the cytoplasm of mammalian hepatocytes. SDH catalyzes is the deamination of L-serine to yield pyruvate, with the release of ammonia.

In enzymology, a phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase (PRAI) is an enzyme that catalyzes the third step of the synthesis of the amino acid tryptophan.
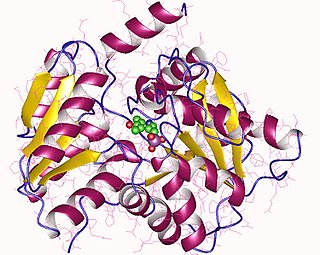
The enzyme L-serine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.17) catalyzes the chemical reaction

Threonine ammonia-lyase (EC 4.3.1.19, systematic name L-threonine ammonia-lyase (2-oxobutanoate-forming), also commonly referred to as threonine deaminase or threonine dehydratase, is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the conversion of L-threonine into α-ketobutyrate and ammonia:
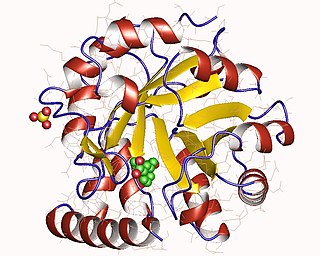
The enzyme indole-3-glycerol-phosphate synthase (IGPS) (EC 4.1.1.48) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.10) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.46) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme GDP-mannose 4,6-dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.47) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme methylglyoxal synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a guanylate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
3-hydroxydecanoyl-(acyl-carrier-protein) dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.60, D-3-hydroxydecanoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] dehydratase, 3-hydroxydecanoyl-acyl carrier protein dehydrase, 3-hydroxydecanoyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase, β-hydroxydecanoyl thioester dehydrase, β-hydroxydecanoate dehydrase, beta-hydroxydecanoyl thiol ester dehydrase, FabA, β-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase, HDDase, β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydrase, (3R)-3-hydroxydecanoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] hydro-lyase) is an enzyme with systematic name (3R)-3-hydroxydecanoyl-(acyl-carrier protein) hydro-lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction


















