
Canemah was an early settlement in the U.S. state of Oregon located near the Willamette River. Canemah was annexed to Oregon City in 1928.

The Willamette River flows northwards down the Willamette Valley until it meets the Columbia River at a point 101 miles from the Pacific Ocean, in the U.S. state of Oregon.

The steamship Altona operated from 1890 to 1907 on the Willamette River in the U.S. state of Oregon. In 1907, she was transferred to Alaska.

North Star was a sternwheel steamer that operated in western Montana and southeastern British Columbia on the Kootenay and Columbia rivers from 1897 to 1903. The vessel should not be confused with other steamers of the same name, some of which were similarly designed and operated in British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington.

Gwendoline was a sternwheel steamer that operated on the Kootenay River in British Columbia and northwestern Montana from 1893 to 1899. The vessel was also operated briefly on the Columbia River in the Columbia Valley.

From 1886 to 1920, steamboats ran on the upper reaches of the Columbia and Kootenay in the Rocky Mountain Trench, in western North America. The circumstances of the rivers in the area, and the construction of transcontinental railways across the trench from east to west made steamboat navigation possible.

The Multnomah was one of the first steamboats to operate on the Willamette and Yamhill rivers. This vessel should not be confused with the Multnomah, a steamboat built in Portland, Oregon in 1885, which was larger and of a much different design.

The steamboat Shoalwater was the sixth steamer to operate on the upper Willamette River, which refers to the part of the river above Willamette Falls at Oregon City. In a short career of six years, Shoalwater was renamedFenix, Franklin, and Minnie Holmes. Shoalwater was the first steamboat in Oregon to suffer a boiler explosion, although no fatalities resulted.

Washington was an early steamboat operated in the states of California and Oregon. Washington was built in California and was initially operated on the Sacramento River. In 1851, the steamer was purchased and brought on a ship to the Oregon Territory, where it was operated on the Willamette River until the summer of 1853. Washington was sold again, and then transferred to the Oregon coast, where it operated on the Umpqua River, on the Coquille River and on Coos Bay. Washington was able to operate for shorter distances over the open ocean along the Oregon coast. The steamer was wrecked by a boiler explosion in December 1857, near Scottsburg, O.T., on the Umpqua river.

Rival was a sternwheel steamboat that ran on the Willamette River between Oregon City and Portland, Oregon from 1860 to 1868. Rival was intended to be a boat which would promise low fares in an effort to beat a steamboat monopoly which was then in formation.
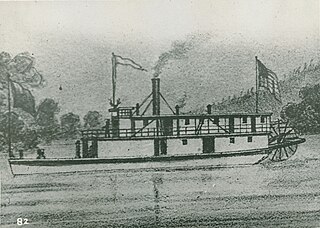
Elk was a stern-wheel driven steamboat built on the Willamette River in 1857 at Canemah, Oregon. This steamboat is chiefly remembered for its destruction by a boiler explosion in which by good fortune no one was seriously hurt. A folklore tale later arose about this disaster.

Portland was a side wheel steamer built at Portland, Oregon in the summer of 1853. This vessel was chiefly remembered for its dramatic destruction in 1857 by being washed over Willamette Falls, an incident which killed its captain and a deckhand. The death of the captain, Arthur Jamieson, was one of at least four brothers, all steamboat officers, who were killed in three separate steamboating accidents occurring between 1857 and 1861 in Oregon and in British Columbia.

Unio was a small sternwheel-driven steamboat which operated on the Willamette and Yamhill rivers from 1861 to 1869. This vessel is primarily remembered for its having been named Unio when built in 1861, in the first year of the American Civil War, and then having the name completed, to Union, by a new, staunchly pro-Union owner, James D. Miller. Union appears to have sunk in 1869, been salvaged, and then dismantled, with the machinery going to a new steamer then being built for service on the Umpqua River.

The People's Transportation Company operated steamboats on the Willamette River and its tributaries, the Yamhill and Tualatin rivers, in the State of Oregon from 1862 to 1871. For a brief time this company operated steamers on the Columbia River, and for about two months in 1864, the company operated a small steamer on the Clackamas River.

Alert was a sternwheeler steamboat which operated on the Willamette River, in Oregon, United States, from 1865 to 1875. Originally built for and owned by the Willamette Steam Navigation Co., it was soon acquired by the People's Transportation Company, a steamboat line which held a near-monopoly on Willamette River transportation. This vessel was rebuilt in 1871, and ran until 1875, when it was dismantled.

James Clinton was a steamboat which operated on the upper Willamette River from 1856 to 1861. Although the Clinton was said to have been "not a very good boat.", it was the first steamer ever to reach Eugene, Oregon. James Clinton was destroyed in April 1861, when a large fire broke out at Linn City, Oregon in a shoreside structure near to where the vessel was moored.

Wenat was a stern-wheel steamboat that, under the name Swan, was built and operated, briefly, on the Tualatin River, in the state of Oregon. In 1858, Swan was sold, moved to the lower Willamette River, renamed Cowlitz, and placed on a route between Portland, Oregon the Cowlitz River.

Dayton was a steamboat which operated on the Willamette and Columbia rivers from 1868 to 1881. Dayton operated on the Willamette from 1868 to 1876, mostly upriver from Willamette Falls, including a route on the Yamhill River to Dayton, Oregon, after which the steamer was named. From 1876 to 1881, Dayton was employed on a run from Portland to Monticello, W.T., which was located on the site of what is now Longview, Washington.

Relief was a stern-wheel driven steamboat that operated on the Willamette River from 1858 to 1865. Relief ran for a short time on the route from Portland to Oregon City, Oregon. After being bought out by the competition, Relief was lined around Willamette Falls to the upper Willamette, where it became the first steamboat to reach Springfield. This vessel should not be confused with a later vessel, also named Relief, which operated on the Columbia and Lewis rivers from 1906 to 1931.

George Anson Pease (1830-1919) was a well-known steamboat captain in the Pacific Northwest region on the United States, who was active from the earliest days of steamboat navigation on the Willamette River in the 1850s. He worked in various roles until the early 1900s, commanding numerous vessels during that time. During a flood in 1861, while in command of the sternwheeler Onward, Pease rescued 40 people from a flood in the area of Salem, Oregon.


























