| Kallakoopah | |
|---|---|
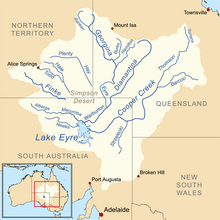 Map of the Lake Eyre Basin showing the Warburton River | |
| Location | |
| Country | Australia |
| State | South Australia |
| Region | Far North |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Mount Gason |
| • elevation | 17 m (56 ft) |
| Mouth | Warburton River |
• coordinates | 27°29′S138°15′E / 27.483°S 138.250°E |
• elevation | −5 m (−16 ft) |
| Length | 353 km (219 mi) |
| Basin features | |
| River system | Lake Eyre Basin |
| Waterholes | Dunchadunchadinna, Kuncherinna, Anarowdinna, Kalanchadinna, Murdawadinna and Muckratuckaalinna |
| [1] | |
The Kallakoopah Creek, part of the Lake Eyre basin, is a watercourse located in the southern part of the Simpson Desert in the Australian state of South Australia. It is an anabranch of Warburton Creek. [2]