Brown Hill Creek, also known as Willawilla in the Kaurna language, is a watercourse flowing from the Adelaide Hills through in the inner south suburbs of the Adelaide metropolitan area, in the Australian state of South Australia. It is part of the Patawalonga River catchment.

The River Torrens, is the most significant river of the Adelaide Plains. It was one of the main reasons for the siting of the city of Adelaide, capital of South Australia. It flows 85 kilometres (53 mi) from its source in the Adelaide Hills near Mount Pleasant, across the Adelaide Plains, past the city centre and empties into Gulf St Vincent between Henley Beach South and West Beach. The upper stretches of the river and the reservoirs in its watershed supply a significant part of the city's water supply.
Torrens Park is a mainly residential large inner-southern suburb of Adelaide, incorporating some of the foothills and adjacent to the original "Mitcham Village". It was named after Sir Robert Richard Torrens, the instigator of the Torrens title system of land registration and transfer, who built a large home in the area which he named Torrens Park.

The Moonee Ponds Creek is a creek and major tributary of the Yarra River running through urban Melbourne, Victoria, Australia from northern to inner suburbs. In 2004 a reporter for The Age described it as "arguably the most abused tributary of the Yarra River, and part of the true underside of Melbourne".
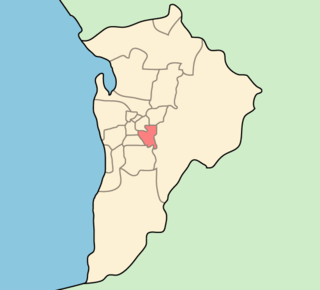
The City of Burnside is a local government area in the South Australian city of Adelaide stretching from the Adelaide Parklands into the Adelaide foothills with an area of 2,753 hectares. It was founded in August 1856 as the District Council of Burnside, the name of a property of an early settler, and was classed as a city in 1943. The LGA is bounded by Adelaide, Adelaide Hills Council, Campbelltown, Mitcham, Norwood Payneham and St Peters and Unley.

Mullum Mullum Creek is a creek in the outer eastern suburbs of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. It is the main watercourse of the Mullum Mullum Valley, a tributary of the Yarra River and Yarra Valley. For tens of thousands of years it was used as a food and tool source sustainably by the Wurundjeri people, Indigenous Australians of the Kulin nation, who spoke variations of the Woiwurrung language group.

Morphettville Racecourse is the main horse racing course for the Australian state of South Australia, incorporating two separate tracks. It is situated in the Adelaide suburb of Morphettville, and is about 10 km from the Adelaide city centre, and is home to the South Australian Jockey Club.
Mount Osmond is a small suburb of 2,497 people in the South Australian capital city of Adelaide. It is part of the City of Burnside local government area and located in the foothills of the Adelaide Hills, five kilometres south east of the city centre. The suburb is high on the hill of the same name, which is the last hill on the right when approaching Adelaide down the South Eastern Freeway before the road levels out onto the Adelaide Plains. It is bounded to the north by the suburb of Beaumont, to the north-east by Burnside, to the east by Waterfall Gully, to the south by Leawood Gardens/Eagle On The Hill, to the south-west by Urrbrae, to the west by Glen Osmond and to the north-west by St Georges.
Greenhill Road is a major road in Adelaide, South Australia, that provides a connection to the eastern and hills suburbs. Its western section, running along the south side of Adelaide Parklands, forms part of Adelaide's City Ring Route.

Wayville is an inner-southern suburb of Adelaide in the City of Unley. It is most notable for hosting of the Royal Adelaide Show at the Adelaide Showgrounds.

Darebin Creek is a creek that runs through the northern suburbs of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. It is the main watercourse of the Darebin Valley and a major tributary of the Yarra River. For tens of thousands of years it was used as a food and tool source sustainably by the Wurundjeri people, Indigenous Australians of the Kulin nation alliance, who spoke variations of the Woiwurrung language group.
Fullarton Road is a main road in the South Australian capital city of Adelaide.

Cross Road is a major arterial road that travels east–west through the inner southern suburbs of the Australian city of Adelaide. It is designated route A3.

Gardiners Creek, originally known as Kooyongkoot Creek, is an urban stream in the eastern suburbs of Melbourne, and part of the Yarra River catchment.

Brown Hill Creek is a south-eastern suburb of Adelaide in the City of Mitcham in South Australia, named in 1991 after Brown Hill Creek which flows from east to west through the locality. The creek itself was named after Brown Hill which rises immediately south-east of Mitcham village.

Iron Cove Creek, a southern tributary of the Parramatta River, is an urban stream west of Sydney Harbour, located in the inner-western Sydney suburbs of Croydon, Ashfield, Haberfield and Five Dock in New South Wales, Australia.

The Patawalonga River is a river located in the western suburbs of the Adelaide metropolitan area, in the Australian state of South Australia. It drains an area of flat, swampy lands formerly known as the Cowandilla Plains or The Reedbeds, which in the mid-20th century were drained by engineering works, enabling the establishment of Adelaide Airport and the development of residential housing.

Cup and Saucer Creek, an urban watercourse of the Cooks River catchment, is located in the Canterbury-Bankstown region of Sydney, in New South Wales, Australia.

The Yarrowee River is a perennial river of the Corangamite catchment, located in the Central Highlands region of the Australian state of Victoria.

The Urrbrae Wetland is a constructed urban wetland in the Australian state of South Australia located in the suburb of Urrbrae in the Adelaide metropolitan area. It was constructed to manage flood water from the nearby Adelaide Hills and has been developed to provide ecological and educational benefits. The wetland covers approximately 6 hectares of land which is onsite of Urrbrae Agricultural High School. The area of water is approximately 4 hectares and when full, contains approximately 13.5 million litres of water.