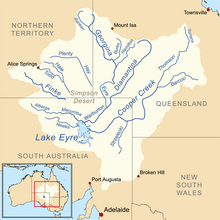
Lake Eyre, officially known as Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre, is an endorheic lake in the east-central part of the Far North region of South Australia, some 700 km (435 mi) north of Adelaide. The shallow lake is the depocentre of the vast endorheic Lake Eyre basin, and contains the lowest natural point in Australia, at approximately 15 m (49 ft) below sea level. On the rare occasions that it fills completely, it is the largest lake in Australia, covering an area of up to 9,500 km2 (3,668 sq mi). When the lake is full, it has the same salinity as seawater, but becomes hypersaline as the lake dries up and the water evaporates.

The Diamantina River is a major river in Central West Queensland and the far north of South Australia.

The Lake Eyre basin is a drainage basin that covers just under one-sixth of all Australia. It is the largest endorheic basin in Australia and amongst the largest in the world, covering about 1,200,000 square kilometres (463,323 sq mi), including much of inland Queensland, large portions of South Australia and the Northern Territory, and a part of western New South Wales. The basin is also one of the largest, least-developed arid zone basins with a high degree of variability anywhere. It supports only about 60,000 people and has no major irrigation, diversions or flood-plain developments. Low density grazing that sustains a large amount of wildlife is the major land use, occupying 82% of the total land within the basin. The Lake Eyre basin of precipitation to a great extent geographically overlaps the Great Artesian Basin underneath.

The Cooper Creek is a river in the Australian states of Queensland and South Australia. It was the site of the death of the explorers Burke and Wills in 1861. It is sometimes known as the Barcoo River from one of its tributaries and is one of three major Queensland river systems that flow into the Lake Eyre basin. The flow of the creek depends on monsoonal rains falling months earlier and many hundreds of kilometres away in eastern Queensland. It is 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) in length.

The Finke River, or Larapinta in the Indigenous Arrernte language, is a river in central Australia, whose bed courses through the Northern Territory and the state of South Australia. It is one of four main rivers of the Lake Eyre Basin and thought to be the oldest riverbed in the world. It flows for only a few days a year. When this happens, its water usually disappears into the sands of the Simpson Desert, rarely if ever reaching Lake Eyre.

The Georgina River is the north-westernmost of the three major rivers of the Channel Country in Central West Queensland, that also flows through a portion of the Northern Territory, in central Australia. Part of the Lake Eyre basin, the Georgina flows in extremely wet years into Lake Eyre.

The Mawson Plateau, located at 30°6′38″S139°25′19″E is part of the northern Flinders Ranges, located on the Mount Freeling pastoral lease in South Australia, 140 kilometres (87 mi) east of Lyndhurst and adjacent to the northeastern boundary of Arkaroola.

An anabranch is a section of a river or stream that diverts from the main channel or stem of the watercourse and rejoins the main stem downstream. Local anabranches can be the result of small islands in the watercourse. In larger anabranches, the flow can diverge for a distance of several or even hundreds of kilometers before rejoining the main channel.

The Officer Creek, part of the Lake Eyre basin, is an ephemeral watercourse located in the Far North region in the Australian state of South Australia.
The Cooper Creek catfish, also known as the Cooper Creek tandan, is a species of catfish of the family Plotosidae, and is the only species of the genus Neosiluroides. The species’ scientific name Neosiluroides came from the genus Neosilurus to which the Cooper Creek Catfish bears some resemblance. The second part of its name, cooperensis, is a reference to the sole location of the species in the Cooper Creek Catchment. It is an eel-tailed freshwater fish that resides in the Cooper Creek system of the Lake Eyre drainage in southern Queensland, Australia. This species grows up to about 46.0 centimetres (18.1 in) SL.

The Kallakoopah Creek, part of the Lake Eyre basin, is a watercourse located in the southern part of the Simpson Desert in the Australian state of South Australia. It is an anabranch of Warburton Creek.

The Tirari Desert is a 15,250 square kilometres (5,888 sq mi) desert in the eastern part of the Far North region of South Australia. It stretches 212 km from north to south and 153 km from east to west.

The Goyder Lagoon is a large ephemeral swamp in the Australian state of South Australia in the state's Far North region. The lake is part of the Diamantina River floodplain, lying beside the Birdsville Track close to the state border with Queensland.
Playford River is a river in the Northern Territory of Australia and has a length of 406 km. The river originates near the base of Mount Morgan then flows in a southerly direction before veering west and eventually discharging into Lake De Burgh. The Playford has three tributaries: Buchanan Creek, Desert Creek and Eastern Creek—as well as a number of permanent waterholes. These include Tobacco waterhole, Ibis waterhole, Upper and Lower Amazon Lagoon and Xmas megahole.

Macumba River, once known as Treuer River, is an ephemeral freshwater stream in the far north of South Australia, that is part of the Lake Eyre Basin.

Yapunyah Waterhole lies in the Mulga Lands bioregion of western Queensland. The waterhole is about two kilometres long and covers approximately 22 hectares when full. It is defined as a permanent waterhole in a region where permanent waterholes are extremely rare and therefore provide important refuges for aquatic plants and animals. These rare waterholes were also vital for Aboriginal people and provided both spiritual and physical nourishment.

The Alberga River, also known as the Alberga Creek, is an ephemeral river that is part of the Lake Eyre basin located in the Far North region of the Australian state of South Australia.

The Strzelecki Creek, part of the Lake Eyre basin, is an ephemeral watercourse located in the Australian state of South Australia.

Eyre Creek is a tributary of the Warburton River. It flows from the western southwest corner of Queensland into the northeastern corner of South Australia.