The Younger Dryas, which occurred circa 12,900 to 11,700 years BP, was a return to glacial conditions which temporarily reversed the gradual climatic warming after the Last Glacial Maximum, which lasted from circa 27,000 to 20,000 years BP. The Younger Dryas was the last stage of the Pleistocene epoch that spanned from 2,580,000 to 11,700 years BP and it preceded the current, warmer Holocene epoch. The Younger Dryas was the most severe and longest lasting of several interruptions to the warming of the Earth's climate, and it was preceded by the Late Glacial Interstadial, an interval of relative warmth that lasted from 14,670 to 12,900 BP.
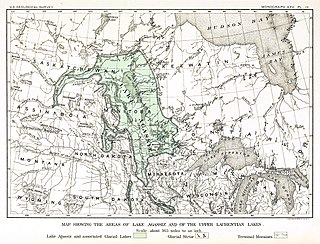
Lake Agassiz was a large proglacial lake that existed in central North America during the late Pleistocene, fed by meltwater from the retreating Laurentide Ice Sheet at the end of the last glacial period. At its peak, the lake's area was larger than all of the modern Great Lakes combined.
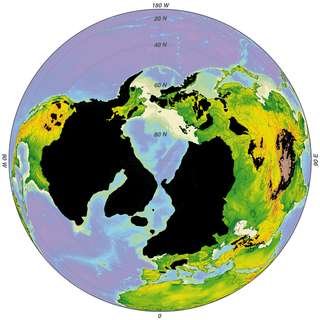
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago; the Greenland ice sheet; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from approximately 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene. The maximum ice extent occurred approximately 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum, also known as the Late Wisconsin in North America.

The Last Glacial Period (LGP), also known colloquially as the Last Ice Age or simply Ice Age, occurred from the end of the Last Interglacial to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago.

Glacial Lake Iroquois was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed at the end of the last ice age approximately 13,000 years ago. The lake was essentially an enlargement of the present Lake Ontario that formed because the St. Lawrence River downstream from the lake was blocked by the ice sheet near the present Thousand Islands. The level of the lake was approximately 30 m (~100 ft) above the present level of Lake Ontario.

A jökulhlaup is a type of glacial outburst flood. It is an Icelandic term that has been adopted in glaciological terminology in many languages. It originally referred to the well-known subglacial outburst floods from Vatnajökull, Iceland, which are triggered by geothermal heating and occasionally by a volcanic subglacial eruption, but it is now used to describe any large and abrupt release of water from a subglacial or proglacial lake/reservoir.

The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million years ago to the present.

An abrupt climate change occurs when the climate system is forced to transition at a rate that is determined by the climate system energy-balance. The transition rate is more rapid than the rate of change of the external forcing, though it may include sudden forcing events such as meteorite impacts. Abrupt climate change therefore is a variation beyond the variability of a climate. Past events include the end of the Carboniferous Rainforest Collapse, Younger Dryas, Dansgaard–Oeschger events, Heinrich events and possibly also the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum. The term is also used within the context of climate change to describe sudden climate change that is detectable over the time-scale of a human lifetime. Such a sudden climate change can be the result of feedback loops within the climate system or tipping points in the climate system.

Lake Algonquin was a prehistoric proglacial lake that existed in east-central North America at the time of the last ice age. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Huron, Georgian Bay, Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Nipigon, and Lake Nipissing.
The Older Dryas was a stadial (cold) period between the Bølling and Allerød interstadials, about 14,000 years Before Present, towards the end of the Pleistocene. Its date range is not well defined, with estimates varying by 400 years, but its duration is agreed to have been around two centuries.

The Oldest Dryas is a biostratigraphic subdivision layer corresponding to a relatively abrupt climatic cooling event, or stadial, which occurred during the last glacial retreat. The time period to which the layer corresponds is poorly defined and varies between regions, but it is generally dated as starting at 18.5–17 thousand years (ka) before present (BP) and ending 15–14 ka BP. As with the Younger and Older Dryas events, the stratigraphic layer is marked by abundance of the pollen and other remains of Dryas octopetala, an indicator species that colonizes arctic-alpine regions. The termination of the Oldest Dryas is marked by an abrupt oxygen isotope excursion, which has been observed at many sites in the Alps that correspond to this interval of time.
The Bølling–Allerød interstadial, also called the Late Glacial Interstadial, was an abrupt warm and moist interstadial period that occurred during the final stages of the Last Glacial Period. This warm period ran from 14,690 to 12,890 years before the present (BP). It began with the end of the cold period known as the Oldest Dryas, and ended abruptly with the onset of the Younger Dryas, a cold period that reduced temperatures back to near-glacial levels within a decade.

Lake Maumee was a proglacial lake and an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 17,500 calendar years, or 14,000 Radiocarbon Years Before Present (RCYBP) as the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. As water levels continued to rise the lake evolved into Lake Arkona and then Lake Whittlesey.

The Weichselian glaciation was the last glacial period and its associated glaciation in northern parts of Europe. In the Alpine region it corresponds to the Würm glaciation. It was characterized by a large ice sheet that spread out from the Scandinavian Mountains and extended as far as the east coast of Schleswig-Holstein, northern Poland and Northwest Russia. This glaciation is also known as the Weichselian ice age, Vistulian glaciation, Weichsel or, less commonly, the Weichsel glaciation, Weichselian cold period (Weichsel-Kaltzeit), Weichselian glacial (Weichsel-Glazial), Weichselian Stage or, rarely, the Weichselian complex (Weichsel-Komplex).

Lake Vermont, also called Glacial Lake Vermont, was a temporary lake created by the retreating glaciers during the close of the last ice age. The lake once included land in the Canadian province of Quebec and the American states Vermont and New York. It was a geologic predecessor of Lake Champlain. Once the glacier retreated far enough north, it drained into Glacial Lake Candona, a geologic predecessor of the St. Lawrence River.
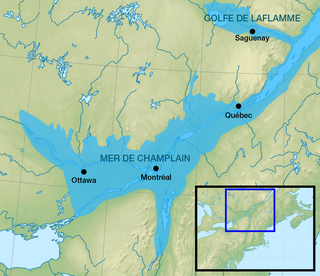
The Champlain Sea was a prehistoric inlet of the Atlantic Ocean into the North American continent, created by the retreating ice sheets during the closure of the last glacial period. The inlet once included lands in what are now the Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario, as well as parts of the American states of New York and Vermont. Today, the remains of the sea include the St. Lawrence Seaway, Lake Champlain, Lake of Two Mountains on the lower Ottawa River, the lower Saguenay River, as well as other lakes, islands and shores.
The phenomenon of paleoflooding is apparent in the geologic record over various spatial and temporal scales. It often occurred on a large scale, and was the result of either glacial ice melt causing large outbursts of freshwater, or high sea levels breaching bodies of freshwater. If a freshwater outflow event was large enough that the water reached the ocean system, it caused changes in salinity that potentially affected ocean circulation and global climate. Freshwater flows could also accumulate to form continental glacial lakes, and this is another indicator of large-scale flooding. In contrast, periods of high global sea level could cause marine water to breach natural dams and flow into bodies of freshwater. Changes in salinity of freshwater and marine bodies can be detected from the analysis of organisms that inhabited those bodies at a given time, as certain organisms are more suited to live in either fresh or saline conditions.

Meltwater pulse 1B (MWP1b) is the name used by Quaternary geologists, paleoclimatologists, and oceanographers for a period of either rapid or just accelerated post-glacial sea level rise that some hypothesize to have occurred between 11,500 and 11,200 calendar years ago at the beginning of the Holocene and after the end of the Younger Dryas. Meltwater pulse 1B is also known as catastrophic rise event 2 (CRE2) in the Caribbean Sea.

The Goldthwait Sea was a sea that emerged during the last deglaciation, starting around 13,000 years ago, covering what is now the Gulf of Saint Lawrence and surrounding areas. At that time, the land had been depressed under the weight of the Laurentide Ice Sheet, which was up to 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) thick. Areas on the Anticosti Island and low-lying regions of Quebec and the Maritimes bordering the Saint Lawrence were below sea level. As the land rebounded over the next 3,000 years, despite rising sea levels the sea retreated to roughly the present boundaries of the Gulf.
















