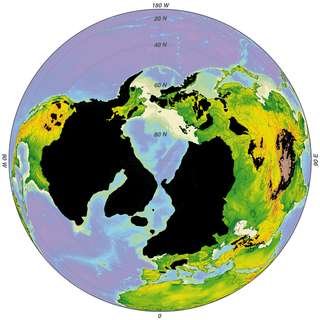
The Wisconsin glaciation, also called the Wisconsin glacial episode, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex, peaking more than 20,000 years ago. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago; the Greenland ice sheet; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from approximately 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene. The maximum ice extent occurred approximately 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum, also known as the Late Wisconsin in North America.

The Last Glacial Period (LGP), also known colloquially as the Last Ice Age or simply Ice Age, occurred from the end of the Last Interglacial to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago.

The Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square miles, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.58 million years ago to the present.

The Cordilleran ice sheet was a major ice sheet that periodically covered large parts of North America during glacial periods over the last ~2.6 million years.
The Bull Lake glaciation is the name of a glacial period in North America that is part of the Quaternary Ice Age. The Bull Lake glaciation began about 200,000 years ago and ended about 130,000 years ago, and was concurrent with the Illinoian Stage of the Quaternary Ice Age. There is disagreement over these time frames, however, and further research is necessary.

The Great Falls of the Missouri River are a series of waterfalls on the upper Missouri River in north-central Montana in the United States. From upstream to downstream, the five falls along a 10-mile (16 km) segment of the river are:

The glacial history of Minnesota is most defined since the onset of the last glacial period, which ended some 10,000 years ago. Within the last million years, most of the Midwestern United States and much of Canada were covered at one time or another with an ice sheet. This continental glacier had a profound effect on the surface features of the area over which it moved. Vast quantities of rock and soil were scraped from the glacial centers to its margins by slowly moving ice and redeposited as drift or till. Much of this drift was dumped into old preglacial river valleys, while some of it was heaped into belts of hills at the margin of the glacier. The chief result of glaciation has been the modification of the preglacial topography by the deposition of drift over the countryside. However, continental glaciers possess great power of erosion and may actually modify the preglacial land surface by scouring and abrading rather than by the deposition of the drift.

The proglacial lakes of Minnesota were lakes created in what is now the U.S. state of Minnesota in central North America in the waning years of the last glacial period. As the Laurentide Ice Sheet decayed at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation, lakes were created in depressions or behind moraines left by the glaciers. Evidence for these lakes is provided by low relief topography and glaciolacustrine sedimentary deposits. Not all contemporaneous, these glacial lakes drained after the retreat of the lobes of the ice sheets that blocked their outlets, or whose meltwaters fed them. There were a number of large lakes, one of which, Glacial Lake Agassiz, was the largest body of freshwater known to have existed on the North American continent; there were also dozens of smaller and more transitory lakes filled from glacial meltwater, which shrank or dried as the ice sheet retreated north.
Lake Bassano was a proglacial lake that formed in the Late Pleistocene during the deglaciation of south-central Alberta by the impoundment of a re-established drainage system and addition of glacial meltwater. It is associated with the development of through-flowing drainage within the Red Deer River basin in particular, and the South Saskatchewan drainage network in general. Approximately 7,500 square kilometres (2,900 sq mi) of the Bassano basin is covered with lacustrine sediments. These sediments are bordered by the topographically higher Buffalo Lake Moraine to the west, the Suffield Moraine to the east and the Lethbridge Moraine to the south.
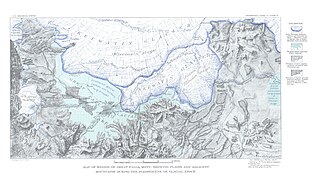
Lake Great Falls was a prehistoric proglacial lake which existed in what is now central Montana in the United States between 15,000 BCE and 11,000 BCE. Centered on the modern city of Great Falls, Montana, Glacial Lake Great Falls extended as far north as Cut Bank, Montana, and as far south as Holter Lake. At present-day Great Falls, the Glacial Lake Great Falls reached a depth of 600 feet.

The Shonkin Sag is a prehistoric fluvioglacial landform located along the northern edge of the Highwood Mountains in the state of Montana in the United States. The Sag is a river channel formed by the Missouri River and glacial meltwater pouring from Glacial Lake Great Falls. It is one of the most famous prehistoric meltwater channels in the world.
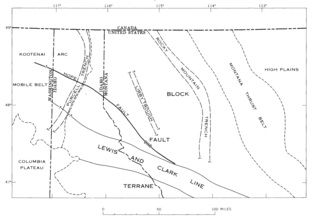
The Purcell Trench, also known as the Kootenay River Valley is a large valley on the western side of the northern part of North America's Rocky Mountains. The trench extends approximately 179 miles (288 km) from Lake Pend Oreille, Idaho, down the Kootenay River (north) to Kootenay Lake, up the north arm to Duncan Lake. It joins the Rocky Mountain Trench another 50 miles (80 km) northward at the south tip of Kinbasket Lake, in British Columbia. The trench bottom is 1 to 7 miles wide and is 1,750 to 2,100 feet above sea level. The trench is nearly a straight north or south line. Some of its topography has been carved into U-shaped glacial valleys, it is primarily a product of geologic faulting. The trench splits the Columbia Mountains between the Purcell Mountains on the east and the Selkirk Mountains on the west.
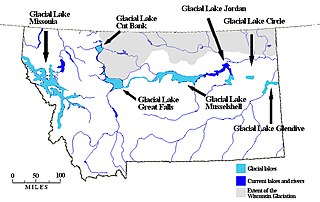
Lake Jordan was a glacial lake formed during the late Pleistocene along the Jordan River. After the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated, water melting off the glacier accumulated between the Rocky Mountains and the ice sheet. The lake drained along the front of the ice sheet, eastward towards the Yellowstone River and Glacial Lake Glendive.
Before the Pleistocene Ice Age, circa two million years before present (YBP), the rivers in North, South Dakota and eastern Montana drained northeast into Canada and then into Hudson Bay. The Keewatin Lobe of the continental ice sheet, block the flow of water northward and impounded it along the ice front. Lakes formed, until the waters could find a new way to drain. Initially, the north flowing rivers followed the front of the glacier eastward and into a valley that passed between Garrison and Riverdale, to the Turtle Lake area, and on into Sheridan County. This is known as the preglacial McClean River. This valley became blocked by the glacier and the glacial lake identified as Lake McKenzie formed. Eventually, water level rose to crest the south ridge a point near Riverdale — at the site of the modern Garrison Dam and a diversion trench was cut. The modern Missouri River follows this pathway.

Lake Circle was a glacial lake that formed during the late Pleistocene epoch along the Redwater River in eastern Montana. After the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated, glacial ice melt accumulated in the basin surrounded by the ridges of the preglacial valley and the retreating glacier. Southwest of Nickwall are the remnants of a broad abandoned valley with long side slopes. The valley runs north from Redwater Creek to the Missouri River. The bottom is poorly drained and about 1 mile (1.6 km) in width. It lies 2,015 to 2,020 feet above the sea level and 40 to 50 feet above the Missouri River bottomland. The upland slopes are extensive, clear and flat. The valleys surrounding it are dissected with V-shaped coulees. The difference between the Redwater valley and those around it reflect stream erosion vs. lake sedimentation. The drift in the valleys, appears to be as left by the glacier in the previously created valleys. Using the dating of lake deposits near Great Falls, Montana, the Havre lobe of the Laurentide Ice Sheet dammed the ancestral Missouri River during the late Wisconsin Glacial Period.

The basin that held Pleistocene Lake Musselshell is in the lower (north-flowing) reach of the river. It is underlain mostly by highly erodible Cretaceous Colorado shale, Montana group sandstone, siltstone and shale, and Hell Creek sandstone and shale. The bedrock is gently folded and affected by local faults and joints. There is a sequence of nine terraces and more than 100 glacial boulders. The terraces are older than the erratics as the erratics rest on the terraces.

Lake Cut Bank was a glacial lake formed during the late Pleistocene along the Missouri and Sun Rivers. After the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated, water melting off the glacier accumulated between the Rocky Mountinas and the ice sheet. The lake drained along the front of the ice sheet, eastward towards the Judith River and the Missouri River.

Lake Chouteau was a glacial lake formed during the late Pleistocene along the Teton River. After the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated, water melting off the glacier accumulated between the Rocky Mountains and the ice sheet. The lake drained along the front of the ice sheet, eastward towards the Judith River and the Missouri River.
The Keewatin ice sheet was a major ice sheet that periodically covered large parts of North America during glacial periods over the last ~2.6 million years. This included the following areas:














