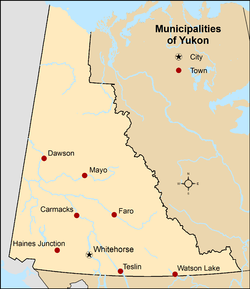
This is a list of communities in Yukon, Canada.

This is a list of communities in Yukon, Canada.
| Name | Status [1] | Official name | Incorporation date [2] | 2021 Census of Population [3] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population (2021) | Population (2016) | Change | Land area (km2) | Population density (/km2) | ||||
| Carmacks | Town | Village of Carmacks | November 1, 1984 | 588 | 493 | +19.3% | 36.87 | 15.9 |
| Dawson | Town | City of Dawson [a] | January 9, 1902 | 1,577 | 1,375 | +14.7% | 30.91 | 51.0 |
| Faro | Town | Town of Faro | June 13, 1969 | 440 | 348 | +26.4% | 199.89 | 2.2 |
| Haines Junction | Town | Village of Haines Junction | October 1, 1984 | 688 | 613 | +12.2% | 34.30 | 20.1 |
| Mayo | Town | Village of Mayo | June 1, 1984 | 188 | 200 | −6.0% | 0.98 | 191.8 |
| Teslin | Town | Village of Teslin | August 1, 1984 | 239 | 255 | −6.3% | 3.77 | 63.4 |
| Watson Lake | Town | Town of Watson Lake | April 1, 1984 | 1,133 | 1,083 | +4.6% | 109.77 | 10.3 |
| Whitehorse | City | City of Whitehorse | June 1, 1950 | 28,201 | 25,085 | +12.4% | 413.94 | 68.1 |
| Total municipalities | 33,054 | 29,452 | +12.2% | 830.43 | 39.8 | |||
| Yukon | 40,232 | 35,874 | +12.1% | 472,345.44 | 0.1 | |||
These areas lie within the Unorganized Yukon, which covers 99.8% of the territory's land mass.
Statistics Canada recognizes two census subdivisions in Yukon that are classified as hamlets. [5]
The Gazetteer of Yukon recognized 96 localities as of February 2012. [6] Two of these localities, Tagish and Upper Liard, are designated as census subdivisions by Statistics Canada, though are classified as settlements. [5]
Dalton Post or Shäwshe is a former trading post and First Nations community on the Tatshenshini River. It was on the Dalton Trail near the Haines Highway. Today, it is a prime Pacific salmon fishing spot and serves as a base for whitewater rafting expeditions on the Tatshenshini and Alsek Rivers in the Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Park.
Jakes Corner is a spot on the road, at historical mile 866 of the Alaska Highway, at the junction with connections to the Tagish Road and the Atlin Road. There are a small number of area residents, the junction being best known for a gas station and café. The gas station has numerous examples of old machinery.
Klukshu's more recent history is as a seasonal aboriginal fishing community, benefitting from a large Chinook salmon run. Located near the Haines Highway, it has no permanent population. Interpretive information is provided by the Champagne and Aishihik First Nations.
Little Salmon is located on the Robert Campbell Highway between Faro and Carmacks, and stretches along the lake of the same name and the Yukon River. The only non-residential establishment is the Yukon government highway maintenance camp at Drury Creek. It was formerly an important settlement of the Little Salmon/Carmacks First Nation.
Silver City, a historic mining town, is today only the residence of a small number of people, one household being a bed and breakfast establishment. It is located at historical mile 1053 of the Alaska Highway. It contains an airport, Silver City Airport.
Sulphur or Sulphur Creek was a mining camp south-east of Dawson on a creek of the same name that flows into the Indian River. A post office was opened there on 28 October 1903 by G. W. Coffin. It was closed in July 1922. The place is mentioned in Jack London's story, "To Build a Fire".
The Gazetteer of Yukon recognized 29 settlements as of February 2012. [6] Eleven of these settlements are designated as census subdivisions by Statistics Canada. [5]
Herschel was a settlement on Herschel Island, serving as a whaling station, North-West Mounted Police post and Hudson's Bay Company store. It has been long abandoned, and shoreline erosion is threatening to wipe out the remaining buildings.
Stewart River is a former settlement at the juncture of the Yukon and Stewart rivers. A few buildings and cabins remain, as well as private museum, which are threatened by erosion. It was founded as a trading post in the 1880s before the Klondike Gold Rush to serve placer miners working along the Stewart River. The Burian family was still living there in the late 1980s.
Statistics Canada recognizes five census subdivisions in Yukon that are classified as Indian settlements, [5] and four census subdivisions as self-governments. [5]
Miner's Prayer was settled near the Blackstone River Mining Concern, providing a retreat where the miners could indulge in billiards, alcohol and other entertainment otherwise forbidden on the mining settlement. Today it is home to fewer than thirty permanent residents. It can be accessed by gravel road veering west from mile 57 on the Dempster Highway.