
The International Seabed Authority (ISA) is a Kingston, Jamaica-based intergovernmental body of 167 member states and the European Union established under the 1982 UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and its 1994 Agreement on Implementation. The ISA's dual mission is to authorize and control development of mineral related operations in the international seabed considered the "common heritage of all mankind" and also protect the ecosystem of the seabed, ocean floor and subsoil in "The Area" beyond national jurisdiction. The ISA is to safeguard the international deep sea, the waters below 200 meters or 656 feet, where photosynthesis is hampered by inadequate light. Governing approximately half of the total area of the world's oceans, the ISA is to exercise oversight of activities that might threaten biological diversity and harm the marine environment. The Authority operates as an autonomous international organization with its own Assembly, Council and Secretariat.

The United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea Treaty, is an international treaty that establishes a legal framework for all marine and maritime activities. As of July 2024, 169 States and the European Union are parties.

The Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties (VCLT) is an international agreement that regulates treaties among sovereign states.

The terms international waters or transboundary waters apply where any of the following types of bodies of water transcend international boundaries: oceans, large marine ecosystems, enclosed or semi-enclosed regional seas and estuaries, rivers, lakes, groundwater systems (aquifers), and wetlands.

Territorial waters are informally an area of water where a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potentially the extended continental shelf. In a narrower sense, the term is often used as a synonym for the territorial sea.

Law of the sea is a body of international law governing the rights and duties of states in maritime environments. It concerns matters such as navigational rights, sea mineral claims, and coastal waters jurisdiction.

An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine resources, including energy production from water and wind.
Freedom of navigation (FON) is a principle of law of the sea that ships flying the flag of any sovereign state shall not suffer interference from other states, apart from the exceptions provided for in international law. In the realm of international law, it has been defined as “freedom of movement for vessels, freedom to enter ports and to make use of plant and docks, to load and unload goods and to transport goods and passengers". This right is now also codified as Article 87(1)a of the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea.
The Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage is a treaty that was adopted on 2 November 2001 by the General Conference of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). The convention is intended to protect "all traces of human existence having a cultural, historical or archaeological character" which have been under water for over 100 years. This extends to the protection of shipwrecks, sunken cities, prehistoric art work, treasures that may be looted, sacrificial and burial sites, and old ports that cover the oceans' floors. The preservation of underwater cultural heritage is significant as it allows for the retelling of numerous historical events. As part of its duty to conduct scientific research and provide continuous education on the importance of underwater cultural heritage, UNESCO strives to maintain these sites for the enjoyment of current and future generations. The convention may provide a customary framework to help raise awareness and seek to combat the illegal looting and pirating occurring in waters worldwide. As an international body, member states of the convention agree to work towards the preservation of sunken cultural property within their jurisdiction and the high seas.
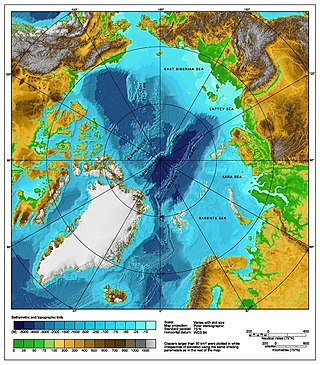
The Arctic consists of land, internal waters, territorial seas, exclusive economic zones (EEZs) and international waters above the Arctic Circle. All land, internal waters, territorial seas and EEZs in the Arctic are under the jurisdiction of one of the eight Arctic coastal states: Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States. International law regulates this area as with other portions of Earth.
Maritime Security Regimes are codes and conventions of behavior agreed upon by coastal states to provide a degree of security within territorial waters and on the high seas.

The Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works, usually known as the Berne Convention, was an international assembly held in 1886 in the Swiss city of Berne by ten European countries with the goal of agreeing on a set of legal principles for the protection of original work. They drafted and adopted a multi-party contract containing agreements for a uniform, border-crossing system that became known under the same name. Its rules have been updated many times since then. The treaty provides authors, musicians, poets, painters, and other creators with the means to control how their works are used, by whom, and on what terms. In some jurisdictions these type of rights are referred to as copyright; on the European continent they are generally referred to as authors' rights or makerright.

The Convention on the Continental Shelf was an international treaty created to codify the rules of international law relating to continental shelves. The treaty, after entering into force 10 June 1964, established the rights of a sovereign state over the continental shelf surrounding it, if there be any. The treaty was one of three agreed upon at the first United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. It has since been superseded by a new agreement reached in 1982 at UNCLOS III.

The United States was among the nations that participated in the third United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea, which took place from 1974 through 1982 and resulted in the international treaty known as the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). The United States also participated in the subsequent negotiations of modifications to the treaty from 1990 to 1994. The UNCLOS came into force in 1994. Although the United States now recognizes the UNCLOS as a codification of customary international law, it has not ratified it.
Transit passage is a concept of the law of the sea, which allows a vessel or aircraft the freedom of navigation or overflight solely for the purpose of continuous and expeditious transit of a strait between one part of the high seas or exclusive economic zone and another. The requirement of continuous and expeditious transit does not preclude passage through the strait for the purpose of entering, leaving or returning from a state bordering the strait, subject to the conditions of entry to that state. The transit passage may be exercised regardless of the nationality (flag) of the ship, its form of ownership, the merchant or government status of a ship or warship, the private or government status of an aircraft.

Arctic cooperation and politics are partially coordinated via the Arctic Council, composed of the eight Arctic states: the United States, Canada, Iceland, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Russia, and Denmark with Greenland and the Faroe Islands. The dominant governmental power in Arctic policy resides within the executive offices, legislative bodies, and implementing agencies of the eight Arctic countries, and to a lesser extent other countries, such as United Kingdom, Germany, European Union and China. NGOs and academia play a large part in Arctic policy. Also important are intergovernmental bodies such as the United Nations and NATO.

The Pacific Islands Forum Fisheries Agency (FFA) is an intergovernmental agency established in 1979 to facilitate regional co-operation and co-ordination on fisheries policies between its member states in order to achieve conservation and optimum utilisation of living marine resources, in particular highly migratory fish stocks, for the benefit of the peoples of the region, in particular the developing countries. The office campus is located in Honiara, Solomon Islands

The United Nations agreement on biodiversity beyond national jurisdiction or BBNJ Agreement, also referred to by some stakeholders as the High Seas Treaty or Global Ocean Treaty, is a legally binding instrument for the conservation and sustainable use of marine biological diversity of areas beyond national jurisdiction. There is some controversy over the popularized name of the agreement. It is an agreement under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS). The text was finalised during an intergovernmental conference at the UN on 4 March 2023 and adopted on 19 June 2023. Both states and regional economic integration organizations can become parties to the treaty.













