Related Research Articles

Carbamazepine, sold under the brand name Tegretol among others, is an anticonvulsant medication used in the treatment of epilepsy and neuropathic pain. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia along with other medications and as a second-line agent in bipolar disorder. Carbamazepine appears to work as well as phenytoin and valproate for focal and generalized seizures. It is not effective for absence or myoclonic seizures.

A mood stabilizer is a psychiatric medication used to treat mood disorders characterized by intense and sustained mood shifts, such as bipolar disorder and the bipolar type of schizoaffective disorder.

Valproate are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and prevent migraine headaches. They are useful for the prevention of seizures in those with absence seizures, partial seizures, and generalized seizures. They can be given intravenously or by mouth, and the tablet forms exist in both long- and short-acting formulations.
A psychiatric or psychotropic medication is a psychoactive drug taken to exert an effect on the chemical makeup of the brain and nervous system. Thus, these medications are used to treat mental illnesses. These medications are typically made of synthetic chemical compounds and are usually prescribed in psychiatric settings, potentially involuntarily during commitment. Since the mid-20th century, such medications have been leading treatments for a broad range of mental disorders and have decreased the need for long-term hospitalization, thereby lowering the cost of mental health care. The recidivism or rehospitalization of the mentally ill is at a high rate in many countries, and the reasons for the relapses are under research.
Anticonvulsants are a diverse group of pharmacological agents used in the treatment of epileptic seizures. Anticonvulsants are also increasingly being used in the treatment of bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder, since many seem to act as mood stabilizers, and for the treatment of neuropathic pain. Anticonvulsants suppress the excessive rapid firing of neurons during seizures. Anticonvulsants also prevent the spread of the seizure within the brain.

Ertapenem, sold under the brand name Invanz, is a carbapenem antibiotic medication used for the treatment of infections of the abdomen, the lungs, the upper part of the female reproductive system, and the diabetic foot.

Lamotrigine, sold under the brand name Lamictal among others, is a medication used to treat epilepsy and stabilize mood in bipolar disorder. For epilepsy, this includes focal seizures, tonic-clonic seizures, and seizures in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome. In bipolar disorder, lamotrigine has not been shown to reliably treat acute depression in any groups except for the severely depressed; but for patients with bipolar disorder who are not currently symptomatic, it appears to reduce the risk of future episodes of depression.
Absence seizures are one of several kinds of generalized seizures. In the past, absence epilepsy was referred to as "pyknolepsy," a term derived from the Greek word "pyknos," signifying "extremely frequent" or "grouped". These seizures are sometimes referred to as petit mal seizures ; however, usage of this terminology is no longer recommended. Absence seizures are characterized by a brief loss and return of consciousness, generally not followed by a period of lethargy. Absence seizures are most common in children. They affect both sides of the brain.

Myoclonus is a brief, involuntary, irregular twitching of a muscle, a joint, or a group of muscles, different from clonus, which is rhythmic or regular. Myoclonus describes a medical sign and, generally, is not a diagnosis of a disease. It belongs to the hyperkinetic movement disorders, among tremor and chorea for example. These myoclonic twitches, jerks, or seizures are usually caused by sudden muscle contractions or brief lapses of contraction. The most common circumstance under which they occur is while falling asleep. Myoclonic jerks occur in healthy people and are experienced occasionally by everyone. However, when they appear with more persistence and become more widespread they can be a sign of various neurological disorders. Hiccups are a kind of myoclonic jerk specifically affecting the diaphragm. When a spasm is caused by another person it is known as a provoked spasm. Shuddering attacks in babies fall in this category.

Valpromide is a carboxamide derivative of valproic acid used in the treatment of epilepsy and some affective disorders. It is rapidly metabolised (80%) to valproic acid but has anticonvulsant properties itself. It may produce more stable plasma levels than valproic acid or sodium valproate and may be more effective at preventing febrile seizures. However, it is over one hundred times more potent as an inhibitor of liver microsomal epoxide hydrolase. This makes it incompatible with carbamazepine and can affect the ability of the body to remove other toxins. Valpromide is no safer during pregnancy than valproic acid.

Ethosuximide, sold under the brand name Zarontin among others, is a medication used to treat absence seizures. It may be used by itself or with other antiseizure medications such as valproic acid. Ethosuximide is taken by mouth.
The emphasis of the treatment of bipolar disorder is on effective management of the long-term course of the illness, which can involve treatment of emergent symptoms. Treatment methods include pharmacological and psychological techniques.

Bipolar disorder in children, or pediatric bipolar disorder (PBD), is a rare mental disorder in children and adolescents. The diagnosis of bipolar disorder in children has been heavily debated for many reasons including the potential harmful effects of adult bipolar medication use for children. PBD is similar to bipolar disorder (BD) in adults, and has been proposed as an explanation for periods of extreme shifts in mood called mood episodes. These shifts alternate between periods of depressed or irritable moods and periods of abnormally elevated moods called manic or hypomanic episodes. Mixed mood episodes can occur when a child or adolescent with PBD experiences depressive and manic symptoms simultaneously. Mood episodes of children and adolescents with PBD are different from general shifts in mood experienced by children and adolescents because mood episodes last for long periods of time and cause severe disruptions to an individual's life. There are three known forms of PBD: Bipolar I, Bipolar II, and Bipolar Not Otherwise Specified (NOS). The average age of onset of PBD remains unclear, but reported age of onset ranges from 5 years of age to 19 years of age. PBD is typically more severe and has a poorer prognosis than bipolar disorder with onset in late-adolescence or adulthood.
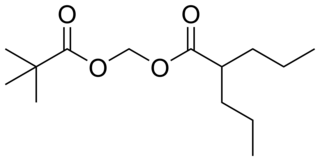
Valproate pivoxil is an anticonvulsant used in the treatment of epilepsy. It is the pivaloyloxymethyl ester derivative of valproic acid. It is likely a prodrug of valproic acid, as pivoxil esters are commonly employed to make prodrugs in medicinal chemistry.

A GABA analogue is a compound which is an analogue or derivative of the neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA).
Antimanic drugs are psychotropic drugs that are used to treat symptoms of mania. Though there are different causes of mania, the majority is caused by bipolar disorder, therefore antimanic drugs are mostly similar to drugs treating bipolar disorder. Since 1970s, antimanic drugs have been used specifically to control the abnormal elevation of mood or mood swings during manic episodes. One purpose of antimanic drugs is to alleviate or shorten the duration of an acute mania. Another objective is to prevent further cycles of mania and maintain the improvement achieved during the acute episode. The mechanism of antimanic drugs has not yet been fully known, it is proposed that they mostly affect chemical neurotransmitters in the brain. However, the usage of antimanic drugs should be consulted with a doctor or pharmacist due to their side effects and interactions with other drugs and food.

Fetal valproate spectrum disorder (FVSD), previously known as fetal valproate syndrome (FVS), is a rare disease caused by prenatal exposure to valproic acid (VPA), a medication commonly used to treat epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and migraines. This exposure can lead to a range of neurodevelopmental and physical symptoms, including cognitive impairments, developmental delays, autism spectrum disorder (ASD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and congenital malformations.