ClearType is Microsoft's implementation of subpixel rendering technology in rendering text in a font system. ClearType attempts to improve the appearance of text on certain types of computer display screens by sacrificing color fidelity for additional intensity variation. This trade-off is asserted to work well on LCD flat panel monitors.

Microsoft DirectX is a collection of application programming interfaces (APIs) for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms. Originally, the names of these APIs all began with "Direct", such as Direct3D, DirectDraw, DirectMusic, DirectPlay, DirectSound, and so forth. The name DirectX was coined as a shorthand term for all of these APIs and soon became the name of the collection. When Microsoft later set out to develop a gaming console, the X was used as the basis of the name Xbox to indicate that the console was based on DirectX technology. The X initial has been carried forward in the naming of APIs designed for the Xbox such as XInput and the Cross-platform Audio Creation Tool (XACT), while the DirectX pattern has been continued for Windows APIs such as Direct2D and DirectWrite.
Direct3D is a graphics application programming interface (API) for Microsoft Windows. Part of DirectX, Direct3D is used to render three-dimensional graphics in applications where performance is important, such as games. Direct3D uses hardware acceleration if available on the graphics card, allowing for hardware acceleration of the entire 3D rendering pipeline or even only partial acceleration. Direct3D exposes the advanced graphics capabilities of 3D graphics hardware, including Z-buffering, W-buffering, stencil buffering, spatial anti-aliasing, alpha blending, color blending, mipmapping, texture blending, clipping, culling, atmospheric effects, perspective-correct texture mapping, programmable HLSL shaders and effects. Integration with other DirectX technologies enables Direct3D to deliver such features as video mapping, hardware 3D rendering in 2D overlay planes, and even sprites, providing the use of 2D and 3D graphics in interactive media ties.

Virtual PC is a discontinued x86 emulator software for Microsoft Windows hosts and PowerPC-based Mac hosts. It was created by Connectix in 1997 and acquired by Microsoft in 2003, after which the program was renamed Microsoft Virtual PC. In July 2006, Microsoft released the Windows version free of charge. The Mac version was discontinued the same year following the Mac transition to Intel. In 2009, Microsoft released Windows Virtual PC, which is only compatible with Windows 7 hosts, and is the technical foundation for the latter's Windows XP Mode. Windows Virtual PC does not officially support MS-DOS or operating systems older than Windows XP Professional SP3 as guests. Virtual PC was discontinued in 2011 in favour of Hyper-V.

Dots per inch is a measure of spatial printing, video or image scanner dot density, in particular the number of individual dots that can be placed in a line within the span of 1 inch (2.54 cm). Similarly, dots per centimetre refers to the number of individual dots that can be placed within a line of 1 centimetre (0.394 in).

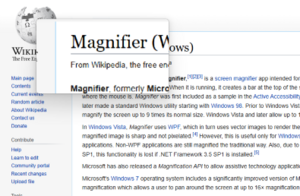
A screen magnifier is software that interfaces with a computer's graphical output to present enlarged screen content. By enlarging part of a screen, people with visual impairments can better see words and images. This type of assistive technology is useful for people with some functional vision; people with visual impairments and little or no functional vision usually use a screen reader.

Magnification is the process of enlarging the apparent size, not physical size, of something. This enlargement is quantified by a size ratio called optical magnification. When this number is less than one, it refers to a reduction in size, sometimes called de-magnification.

A magnifying glass is a convex lens that is used to produce a magnified image of an object. The lens is usually mounted in a frame with a handle. Beyond its primary function of magnification, this simple yet ingenious tool serves a variety of purposes. It can be employed to focus sunlight, harnessing the Sun's rays to create a concentrated hot spot at the lens's focus, which is often used for starting fires.

DirectShow, codename Quartz, is a multimedia framework and API produced by Microsoft for software developers to perform various operations with media files or streams. It is the replacement for Microsoft's earlier Video for Windows technology. Based on the Microsoft Windows Component Object Model (COM) framework, DirectShow provides a common interface for media across various programming languages, and is an extensible, filter-based framework that can render or record media files on demand at the request of the user or developer. The DirectShow development tools and documentation were originally distributed as part of the DirectX SDK. Currently, they are distributed as part of the Windows SDK.
ZoomText is a screen magnifier for Microsoft Windows developed by Ai Squared which was acquired by Freedom Scientific in 2016. The first version was released for DOS in 1988, and the first version for Windows was released in 1991. ZoomText is available in two editions: ZoomText Magnifier and ZoomText Magnifier/Reader, which includes a built-in screen reader.

Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, released five years earlier, which was then the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft Windows. It was released to manufacturing on November 8, 2006, and over the following two months, it was released in stages to business customers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and was made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; it is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.
Microsoft Windows SDK, and its predecessors Platform SDK, and .NET Framework SDK, are software development kits (SDKs) from Microsoft that contain documentation, header files, libraries, samples and tools required to develop applications for Microsoft Windows and .NET Framework. Platform SDK specializes in developing applications for Windows 2000, XP and Windows Server 2003. .NET Framework SDK is dedicated to developing applications for .NET Framework 1.1 and .NET Framework 2.0. Windows SDK is the successor of the two and supports developing applications for Windows XP and later, as well as .NET Framework 3.0 and later.
Desktop Window Manager is the compositing window manager in Microsoft Windows since Windows Vista that enables the use of hardware acceleration to render the graphical user interface of Windows.
Compared with previous versions of Microsoft Windows, features new to Windows Vista are numerous, covering most aspects of the operating system, including additional management features, new aspects of security and safety, new I/O technologies, new networking features, and new technical features. Windows Vista also removed some others.

Microsoft Expression Encoder is a discontinued transcoding and non-linear video editing software application for Microsoft Windows. It can create video streams for distribution via Microsoft Silverlight. This utility is created to record the screen for various purposes such asYouTube, Twitch etc.

Video magnifiers are electronic devices that use a camera and a display screen to perform digital magnification of printed materials. The display screen is usually LCD or a similar flat-screen technology, and the device usually includes a lamp to illuminate the source material. Video magnifiers are designed to be mostly used by people with low vision that cannot be helped using a conventional magnifying glass.

Visual Studio is an integrated development environment (IDE) developed by Microsoft. It is used to develop computer programs including websites, web apps, web services and mobile apps. Visual Studio uses Microsoft software development platforms including Windows API, Windows Forms, Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF), Microsoft Store and Microsoft Silverlight. It can produce both native code and managed code.
Some of the new features included in Windows 7 are advancements in touch, speech and handwriting recognition, support for virtual hard disks, support for additional file formats, improved performance on multi-core processors, improved boot performance, and kernel improvements.
Direct2D is a 2D vector graphics application programming interface (API) designed by Microsoft and implemented in Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, and also Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008.

Microsoft started development on the .NET Framework in the late 1990s originally under the name of Next Generation Windows Services (NGWS). By late 2001 the first beta versions of .NET Framework 1.0 were released. The first version of .NET Framework was released on 13 February 2002, bringing managed code to Windows NT 4.0, 98, 2000, ME and XP.