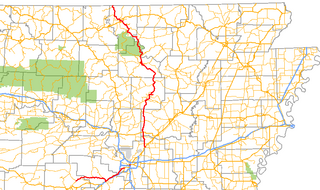
Highway 5 is a designation for three state highways in Arkansas. The southern segment of 44.99 miles (72.40 km) runs from Highway 7 in Hot Springs north to US Highway 70 (US 70) in Little Rock. A northern segment of 146.63 miles (235.98 km) begins at US Highway 67/US Highway 167 in Cabot and runs north to Missouri Route 5, including a lengthy overlap with Highway 25 between Heber Springs and Wolf Bayou. A portion of Highway 5 is designated as part of the Sylamore Scenic Byway.

State Road 2 is a former east–west state highway in the Arkansas Timberlands and Lower Arkansas Delta. The route was approximately 195 miles (314 km), and ran from US Route 67 (US 67) in Texarkana east to cross the Mississippi River near Lake Village, continuing as Mississippi Highway 10. On July 1, 1931, the route was entirely replaced by US Highway 82 (US 82) by the American Association of State Highway Officials (AASHTO). The route was maintained by the Arkansas Highway Department (AHD), now known as the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ArDOT).

Elkin's Ferry was the site of the 1864 Battle of Elkin's Ferry, an engagement of the Camden Expedition during the American Civil War. The battlefield is located about 10 miles (16 km) north of Prescott, Arkansas, spanning the Little Missouri River in Clark and Nevada counties in Arkansas. The 575-acre (233 ha) battlefield area was designated a part of the Camden Expedition Sites, a National Historic Landmark District made up of several of expedition's key sites, in 1994.

Jenkins' Ferry Battleground State Park is the site of the American Civil War battle of Jenkins' Ferry, also known as the Engagement at Jenkins' Ferry, fought on Saturday, April 30, 1864, in present-day Grant County, Arkansas. The park was listed in the U.S. National Register of Historic Places on January 21, 1970, and, with seven other sites, is part of the Camden Expedition Sites National Historic Landmark, designated a National Historic Landmark District on April 19, 1994.

U.S. Route 67 is a U.S. highway running from Presidio, Texas northeast to Sabula, Iowa. In the U.S. state of Arkansas, the route runs 279.15 miles (449.25 km) from the Texas border in Texarkana northeast to the Missouri border near Corning. The route passes through several cities and towns, including Hope, Benton, Little Rock, Jacksonville, Cabot, Beebe, Walnut Ridge, and Pocahontas.
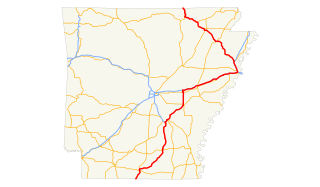
U.S. Route 63 is a north-south U.S. highway that begins in Ruston, LA. In the US state of Arkansas the highway enters the state from Louisiana concurrent with US 167 in Junction City. The highway zigzags through the state serving the major cities of Pine Bluff, West Memphis and Jonesboro. The highway exits the state at Mammoth Spring traveling into Missouri.

U.S. Route 62 is a U.S. highway running from El Paso, Texas northeast to Niagara Falls, New York. In the U.S. state of Arkansas, the route runs 329.9 miles from the Oklahoma border near Summers east to the Missouri border in St. Francis, serving the northern portion of the state. The route passes through several cities and towns, including Fayetteville, Springdale, Bentonville, Harrison, Mountain Home, Pocahontas, and also Piggott. US 62 runs concurrent with several highways in Arkansas including Interstate 49 and U.S. Route 71 between Fayetteville and Bentonville, U.S. Route 412 through much of the state, U.S. Route 65 in the Harrison area, and with U.S. Route 63 and U.S. Route 67 in northeast Arkansas.

Highway 190 is a designation for four state highways in Arkansas. Three are low-traffic rural highways in Grant County, with one designation along city streets in Pine Bluff. The rural segments were created in 1965 and 1966, with the Pine Bluff section created in 2000. All segments are maintained by the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ARDOT).

The Springfield to Fayetteville Road-Elkhorn Tavern Segment is a section of historic 19th-century roadway in Pea Ridge National Military Park in northwestern Arkansas. It is a dirt road, about 1 mile (1.6 km) long and 18 to 20 feet wide, that was built in 1835. The first major road through northwestern Arkansas, it connected Fayetteville, Arkansas with Springfield, Missouri. The road was part of the major northern route of the Trail of Tears, the forcible remove in the late 1830s of Native Americans from east of the Mississippi River to what is now Oklahoma. The road was also actively used by both Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War, and was the major route of advance by Confederate forces leading to the Battle of Pea Ridge, whose battlefield is preserved by the park.

The Butterfield Overland Mail Route Lee Creek Road Segment is a historic stretch of road in Crawford County, Arkansas. It is a 3.1-mile (5.0 km) segment of Lee Creek Road, which diverges from Arkansas Highway 220 north of Cedarville. This road section appears to closely follow the original alignment of the main road in the region in 1839, which connected Fayetteville and Van Buren. This road was used by the Butterfield Overland Mail service between 1858 and 1861. It is a gravel roadway about 12 feet (3.7 m) wide, with several deeply-cut sections.

The Butterfield Overland Mail Route Lucian Wood Road Segment is a historic stretch of road in Crawford County, Arkansas. It is a 3-mile (4.8 km) segment of Lucian Wood Road, extending northward from a junction with Armer Lane in Cedarville. This road section appears to closely follow the original alignment of the main road in the region in 1839, which connected Fayetteville and Van Buren. This road was used by the Butterfield Overland Mail service between 1858 and 1861, along what was described as one that route's roughest sections. It is now an improved and graded gravel roadway about 12 feet (3.7 m) wide, with several deeply-cut sections.
The Memphis to Little Rock Road-Henard Cemetery Road Segment is a section of historic roadway in Monroe County, Arkansas. It consists of 650 metres (2,130 ft) of the middle of Henard Cemetery Road, located northeast of the hamlet of Zent in the far northeastern part of the county. The roadway section is one of three known places where the original 19th-century appearance of the first road to connect Memphis, Tennessee to Little Rock, Arkansas is preserved. The far ends of the road have been impacted by development and agriculture, and do not convey the sense of the road's early appearance. The road is also historically important as it was used as part of the Trail of Tears, the forced removal of Native Americans east of the Mississippi River to what is now Oklahoma.
The Memphis to Little Rock Road-Bayou Two Prairie Segment is a historic military road section in Lonoke County, Arkansas. Located north of Lonoke near the hamlet of Brownsville, the road section was part of the 1828 Memphis to Little Rock Military Road. It was used in the 1830s during the Trail of Tears removal of eastern Native American tribes, and was used by military forces on both sides of the American Civil War leading up to the Battle of Brownsville.
The Memphis to Little Rock Road-Brownsville Segment is a historic military road section in Lonoke County, Arkansas. Located north of Lonoke near the hamlet of Brownsville, the road section was part of the 1828 Memphis to Little Rock Military Road. It was used in the 1830s during the Trail of Tears removal of eastern Native American tribes, and was used by military forces on both sides of the American Civil War leading up to the Battle of Brownsville.
The Military Road-Cadron Segment is a portion of 19th-century roadway in Faulkner County, Arkansas, near the city of Conway. It consists of an original section of a military road built in the mid-1830s between Little Rock and the military outpost at Fort Smith, through what was then frontier territory. It is one of the only known surviving sections of the early military roads that crossed the Arkansas Territory, which is located west of Little Rock. The road is further notable as one of the routes by which Native Americans were relocated to Indian Territory from points east of the Mississippi River.

The Little Rock to Cantonment Gibson Rd-Fourth Street Segment is a history stretch of 19th-century roadbed in rural Pope County, Arkansas. It consists of about one mile of gravel roadway, now designated Fourth Street, east of Atkins, extending from Union Grove Loop in the west to Oakland Drive in the east. It is about 18 feet (5.5 m) wide, and is built on an embankment for much of its length. Completed by early 1828 as a military road connecting Little Rock to what is now Fort Gibson in Oklahoma, the road is historically significant for its use as part of the Trail of Tears removal of eastern Native Americans to the Indian Territory that is now Oklahoma.

The Little Rock to Cantonment Gibson Road-Short Mountain Segment is a historic 19th-century road section in Logan County, Arkansas. It is located northwest of Paris, consisting of 3.7 miles (6.0 km) of Short Mountain Road, extending westward from its crossing with Short Mountain Creek. The roadbed is about 12 feet (3.7 m) wide, and is heavily banked for much of its length. Built in 1828, it was originally part of the military road connecting Little Rock, Arkansas to what is now Gibson, Oklahoma. The road has been documented to be part of the Trail of Tears migration route.
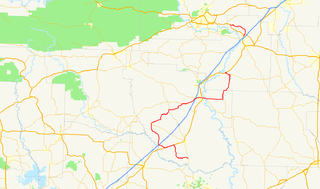
Highway 51 is a designation for two north–south state highways in Southwest Arkansas. One route of 53.37 miles (85.89 km) begins Highway 53 near Whelen Springs and runs north to US Highway 67 in Donaldson. A second route of 7.92 miles (12.75 km) runs parallel to US 270 northwest of Malvern. Both routes are maintained by the Arkansas Department of Transportation (ArDOT).




















