The Federal Marriage Amendment (FMA) was a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution that would define marriage in the United States as a union of one man and one woman. The FMA would also prevent judicial extension of marriage rights to same-sex or other unmarried heterosexual couples. An amendment to the U.S. Constitution requires the support of two thirds of each house of Congress and ratification by three fourths of the states. The last Congressional vote on the proposed amendment occurred in the House of Representatives on July 18, 2006, when the motion failed 236 to 187, falling short of the 290 votes required for passage in that body. The Senate has only voted on cloture motions with regard to the proposed amendment, the last of which was on June 7, 2006, when the motion failed 49 to 48, falling short of the 60 votes required to allow the Senate to proceed to consideration of the proposal and the 67 votes required to send the proposed amendment to the states for ratification.

Utah Constitutional Amendment 3 was an amendment to the Utah state constitution that sought to define marriage as a union exclusively between a man and woman. It passed in the November 2, 2004, election, as did similar amendments in ten other states.
The Tennessee Marriage Protection Amendment, also known as Tennessee Amendment 1 of 2006, is a state constitutional amendment banning same-sex unions. The referendum was approved by 81% of voters. It specified that only a marriage between a man and a woman could be legally recognized in the state of Tennessee. This prohibited same-sex marriages within the state, reinforcing previously existing statutes to the same effect until it was overturned by the Obergefell v. Hodges ruling in June 2015.

Constitutional Amendment 2 of 2004 is an amendment to the Missouri Constitution that prohibited same-sex marriages from being recognized in Missouri. The Amendment passed via public referendum on August 3, 2004 with 71% of voters supporting and 29% opposing. Every county voted in favor of the amendment, with only the independent city of St. Louis voting against it.

Initiative 96 of 2004 is a ballot initiative that amended the Montana Constitution to prevent same-sex marriages from being conducted or recognized in Montana. The Initiative passed via public referendum on November 2, 2004 with 67% of voters supporting and 33% opposing.

Wisconsin Referendum 1 of 2006 was a referendum on an amendment to the Wisconsin Constitution that would invalidate same-sex marriages or any substantially similar legal status. The referendum was approved by 59% of voters during the general elections in November 2006. All counties in the state voted for the amendment except Dane County, which opposed it. The constitutional amendment created by Referendum 1 has been effectively nullified since June 26, 2015, when the United States Supreme Court ruled in Obergefell v. Hodges that state-level bans on same-sex marriage are unconstitutional.
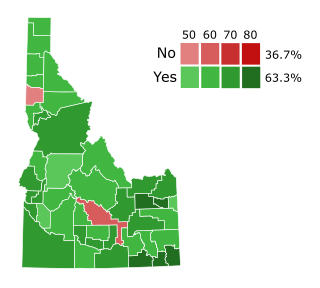
Idaho Amendment 2 of 2006 is an amendment to the Idaho Constitution that made it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions.

Constitutional Amendment 3 of 2004, is an amendment to the Arkansas Constitution that makes it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The referendum was approved by 75% of the voters.
Georgia Constitutional Amendment 1 of 2004, is an amendment to the Georgia Constitution that previously made it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The referendum was approved by 76% of the voters.

Kentucky Constitutional Amendment 1 of 2004, is an amendment to the Kentucky Constitution that made it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The referendum was approved by 75% of the voters.

Louisiana Constitutional Amendment 1 of 2004, is an amendment to the Louisiana Constitution that makes it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The referendum was approved by 78% of the voters.

Michigan Proposal 04-2 of 2004, is an amendment to the Michigan Constitution that made it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The referendum was approved by 59% of the voters.

North Dakota Constitutional Measure 1 of 2004, is an amendment to the North Dakota Constitution that makes it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The referendum was approved by 73% of the voters.

Section 15.11 is a provision in the Ohio Constitution that makes it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. Approved as a constitutional amendment in 2004 under the name of "Issue One", it received support from 61.7% of voters.

Oklahoma Question 711 of 2004, was an amendment to the Oklahoma Constitution that defined marriage as the union of a man and a woman, thus rendering recognition or performance of same-sex marriages or civil unions null within the state prior to its being ruled unconstitutional. The referendum was approved by 76 percent of the voters.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in the U.S. state of Wisconsin since October 6, 2014, upon the resolution of a lawsuit challenging the state's ban on same-sex marriage. On October 6, the U.S. Supreme Court refused to hear an appeal of an appellate court ruling in Wolf v. Walker that had found Wisconsin's ban on same-sex marriage unconstitutional. The appellate court issued its order prohibiting enforcement of the state's ban on same-sex marriage the next day and Wisconsin counties began issuing marriage licenses to same-sex couples immediately.
Same-sex marriage is fully legal and recognized in the U.S. state of Minnesota. Same-sex marriages have been recognized if performed in other jurisdictions since July 1, 2013, and the state began issuing marriage licenses to same-sex couples on August 1, 2013. After 51.9% of state voters rejected a constitutional amendment to ban same-sex marriage in November 2012, the Minnesota Legislature passed a same-sex marriage bill in May 2013, which Governor Mark Dayton signed on May 14, 2013. Minnesota was the second state in the Midwest, after Iowa, to legalize marriage between same-sex couples and the first in the region to do so by enacting legislation rather than by court order. Minnesota was the first state to reject a constitutional amendment banning same-sex marriage, though Arizona rejected one in 2006 that banned all legal recognition and later approved one banning only marriage.
















