
Prior to the Supreme Court's decision in Obergefell v. Hodges (2015), U.S. state constitutional amendments banning same-sex unions of several different types passed, banning legal recognition of same-sex unions in U.S. state constitutions, referred to by proponents as "defense of marriage amendments" or "marriage protection amendments." These state amendments are different from the proposed Federal Marriage Amendment, which would ban same-sex marriage in every U.S. state, and Section 2 of the Defense of Marriage Act, more commonly known as DOMA, which allowed the states not to recognize same-sex marriages from other states. The amendments define marriage as a union between one man and one woman and prevent civil unions or same-sex marriages from being legalized, though some of the amendments bar only the latter. The Obergefell decision in June 2015 invalidated these state constitutional amendments insofar as they prevented same-sex couples from marrying, even though the actual text of these amendments remain written into the state constitutions.

Arizona Proposition 107 was a proposed same-sex marriage ban, put before voters by ballot initiative in the 2006 general election. If passed, it would have prohibited the state of Arizona from recognizing same-sex marriages or civil unions. The state already had a statute defining marriage as the union of a man and a woman and prohibiting the recognition of same-sex marriages performed elsewhere.

Ballot Measure 2 of 1998 is a ballot measure, since ruled unconstitutional, that added an amendment to the Alaska Constitution that prohibited the recognition of same-sex marriage in Alaska. The Ballot measure was sparked by the lawsuit filed by Jay Brause and Gene Dugan, after the two men were denied a marriage license by the Alaska Bureau of Vital Statistics. In Brause v. Bureau of Vital Statistics, 1998 WL 88743, the Alaska Superior Court ruled that the state needed compelling reason to deny marriage licenses to same-sex couples and ordered a trial on the question. In response, the Alaska Legislature immediately proposed and passed Resolution 42, which became what is now known as Ballot Measure 2. Ballot Measure 2 passed via public referendum on November 3, 1998, with 68% of voters supporting and 32% opposing. The Bause case was dismissed following the passage of the ballot measure.

Wisconsin Referendum 1 of 2006 was a referendum on an amendment to the Wisconsin Constitution that would invalidate same-sex marriages or any substantially similar legal status. The referendum was approved by 59% of voters during the general elections in November 2006. All counties in the state voted for the amendment except Dane County, which opposed it. The constitutional amendment created by Referendum 1 has been effectively nullified since June 26, 2015, when the United States Supreme Court ruled in Obergefell v. Hodges that state-level bans on same-sex marriage are unconstitutional.

South Carolina Amendment 1 of 2006 amended the South Carolina Constitution to make it unconstitutional for the U.S. state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The referendum was approved by 78% of voters. Unlike the other sixteen such state amendments, South Carolina's explicitly disavows any effort to prevent private contracts between same-sex partners from being recognized—Virginia being the only state to do so.

Idaho Amendment 2 of 2006 is an amendment to the Idaho Constitution that made it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions.

Proposition 2 was a referendum for a state constitutional amendment placed on the ballot by the Texas legislature and approved by the voters at the November 8, 2005 general election. The measure added a new provision to the Texas Constitution, Article 1, Section 32, which provides that "Marriage in this state shall consist only of the union of one man and one woman", and "This state or a political subdivision of this state may not create or recognize any legal status identical or similar to marriage." Texas thus became the nineteenth US state to adopt constitutional amendment banning same-sex marriage. It was the most populous state to adopt a constitutional ban on same-sex marriage until California passed its ban in November 2008. The amendment was later invalidated after the Supreme Court legalized Same-Sex marriage nationwide following the decision in Obergefell v. Hodges in June 2015, though the amendment is still currently in the Texas Constitution.

Nebraska Initiative 416 was a 2000 ballot initiative that amended the Nebraska Constitution to make it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriage, same-sex civil unions or domestic partnerships. The referendum was approved on November 7, 2000, by 70% of the voters. The initiative has since been struck down in federal court and same-sex marriage is now legally recognized in the state of Nebraska.

The Amendment 774 of 2006, also known as Alabama Sanctity of Marriage Amendment, is an amendment to the Alabama Constitution that makes it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The legislature passed Alabama Act 2005-35, which placed this amendment on the election ballot. The referendum was approved by 81% of the voters.

Constitutional Amendment 3 of 2004, is an amendment to the Arkansas Constitution that makes it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The referendum was approved by 75% of the voters.
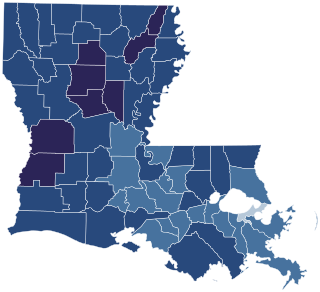
Louisiana Constitutional Amendment 1 of 2004, is an amendment to the Louisiana Constitution that makes it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions. The referendum was approved by 78% of the voters.

Constitutional Amendment 2 of 1998 amended the Constitution of Hawaii, granting the state legislature the power to prevent same-sex marriage from being conducted or recognized in Hawaii. Amendment 2 was the first constitutional amendment adopted in the United States that specifically targeted same-sex partnerships.

2006 Virginia Question 1, the Marshall-Newman Amendment is an amendment to the Constitution of Virginia that defines marriage as solely between one man and one woman and bans recognition of any legal status "approximat[ing] the design, qualities, significance, or effects of marriage". The amendment was ratified by 57% of the voters on November 7, 2006. It became part of the state Constitution as Section 15-A of Article 1. In 2014, the amendment was ruled unconstitutional in Bostic v. Schaefer.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in Wisconsin since October 6, 2014, upon the resolution of a lawsuit challenging the state's ban on same-sex marriage. On October 6, the U.S. Supreme Court refused to hear an appeal of an appellate court ruling in Wolf v. Walker that had found Wisconsin's ban on same-sex marriage unconstitutional. The appellate court issued its order prohibiting enforcement of the state's ban on same-sex marriage the next day and Wisconsin counties began issuing marriage licenses to same-sex couples immediately. Wisconsin had previously recognized domestic partnerships, which afforded limited legal rights to same-sex couples, from August 2009 until they were discontinued in April 2018.

Arizona Proposition 102 was an amendment to the constitution of the state of Arizona adopted by a ballot measure held in 2008. It added Article 30 of the Arizona Constitution, which says: "Only a union of one man and one woman shall be valid or recognized as a marriage in this state." The amendment added a constitutional ban on same-sex marriage to existing statutory bans in place since 1996. In October 2014, Article 30 of the Arizona Constitution was struck down as unconstitutional in the United States District Court for the District of Arizona, and is no longer enforced by the state of Arizona, which now allows and recognizes same-sex marriages.

The 2009 Washington Referendum 71 (R-71) legalized domestic partnership in Washington state, the first statewide referendum in the United States that extended to LGBT people the rights and responsibility of domestic partnership. The bill had passed State Legislature, and it was signed into law by the Governor in May 2009, but opponents gathered enough signatures to put the measure before the voters, who returned ballots by mail over three weeks ending on November 3, 2009, approving the measure 53% to 47%. The new law went into effect 30 days later, on December 3, 2009.

North Carolina Amendment 1 was a legislatively referred constitutional amendment in North Carolina that amended the Constitution of North Carolina to prohibit the state from recognizing or performing same-sex marriages or civil unions. The amendment did not prohibit domestic partnership agreements, but defined male–female marriage as "the only domestic legal union" considered valid or recognized in the state. On May 8, 2012, North Carolina voters approved the amendment, 61% to 39%, with a voter turnout of 35%. On May 23, 2012, the amendment took effect.
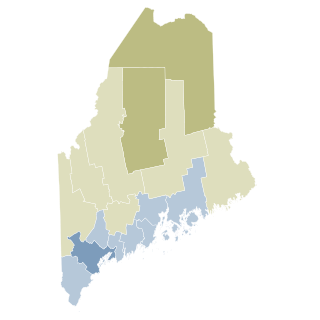
Maine Question 1 was a voter referendum on an initiated state statute that occurred on November 6, 2012. The referendum was held to determine whether or not to legalize same-sex marriage. The referendum passed with a 53-47% vote legalizing same-sex marriage in Maine.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in Virginia since October 6, 2014, following the decision of the U.S. Supreme Court not to hear an appeal of the Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals' ruling in Bostic v. Schaefer. Same-sex marriages subsequently began at 1:00 p.m. on October 6 after the Fourth Circuit issued its mandate, and since then Virginia has performed legal marriages of same-sex couples and recognized out-of-state same-sex marriages. Previously, the state had passed a statute prohibiting same-sex marriage in 1975, and further restrictions were added in 1997 and 2004, which made "void and unenforceable" any arrangements between same-sex couples bestowing the "privileges or obligations of marriage". Voters approved an amendment to the Constitution of Virginia reinforcing the existing laws in 2006. On January 14, 2014, a U.S. district court judge ruled in Bostic that Virginia's statutory and constitutional ban on the state recognition of same-sex marriages were unconstitutional, a decision upheld by the Fourth Circuit on July 28, 2014.

The 2006 Virginia State Elections took place on Election Day, November 7, 2006, the same day as the U.S. House and the U.S. Senate elections in the state. The only statewide elections on the ballot were three constitutional referendums to amend the Virginia State Constitution. Because Virginia state elections are held on off-years, no statewide officers or state legislative elections were held. All referendums were referred to the voters by the Virginia General Assembly.


















