
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 2, 1920. Republican senator Warren G. Harding of Ohio defeated Democratic governor James M. Cox of Ohio. It was the first election held after the end of the First World War, and the first election after the ratification of the Nineteenth Amendment which gave equal votes to men and women. It was the third presidential election in which both major party candidates were registered in the same home state, and the last time that the state was not New York. It was the first presidential election to have its results broadcast by radio. Coincidentally, the election was held on Harding's 55th birthday.

The lieutenant governor and speaker of the Senate of Tennessee is the presiding officer of the Tennessee Senate and first in line in the succession to the office of governor of Tennessee in the event of the death, resignation, or removal from office through impeachment and conviction of the governor of Tennessee.

John Isaac Cox was an American politician who served as the 29th governor of Tennessee from 1905 to 1907. He was elevated to the position when Governor James B. Frazier resigned, and, as Speaker of the Tennessee Senate, he was the first in the line of succession. He failed to win his party's nomination for a second term, and returned to the state senate, where he remained until 1913. Cox also served as a county judge, city attorney, and local postmaster, and spent two terms in the Tennessee House of Representatives.

James Beriah Frazier was an American politician who served as the 28th governor of Tennessee from 1903 to 1905, and subsequently as a United States senator from Tennessee from 1905 to 1911. As governor, he reduced the state's debt and enacted mine safety regulations. He also attempted to control whitecapping.

Malcolm Rice Patterson was an American politician and jurist. He served in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1901 to 1906, and as the 30th governor of Tennessee from 1907 to 1911. He later served as a circuit court judge in Memphis (1923–1934), and wrote a weekly column for the Memphis Commercial Appeal (1921–1933).

Thomas Clarke Rye was an American politician who served as the 32nd governor of Tennessee from 1915 to 1919. An ardent supporter of prohibition of alcoholic beverages, he helped reunify the state's Democratic Party, which had been divided over the issue for nearly a decade. Rye is perhaps best remembered for enacting the "Ouster Law," which was aimed at curbing the power of political boss E. H. Crump.
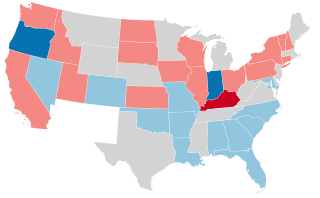
The 1908–09 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were primarily chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1906 and 1907, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. However, some states had already begun direct elections during this time. Oregon pioneered direct election and experimented with different measures over several years until it succeeded in 1907. Soon after, Nebraska followed suit and laid the foundation for other states to adopt measures reflecting the people's will. By 1912, as many as 29 states elected senators either as nominees of their party's primary or in conjunction with a general election.

Walter Preston Brownlow was an American politician who represented Tennessee's 1st district in the U.S. House of Representatives from 1897 until his death in 1910. He is remembered for obtaining large federal appropriations for his district, as well as for his intraparty political battles with Chattanoogans Henry Clay Evans and Newell Sanders over control of the state Republican Party. Along with his congressional tenure, Brownlow served as Doorkeeper of the United States House of Representatives from 1881 to 1883, and published the Jonesboro Herald and Tribune from 1876 to 1910.

Richard Wilson Austin was an American politician, attorney and diplomat. A Republican, he served in the United States House of Representatives from 1909 to 1919, representing Tennessee's 2nd district. Prior to his congressional tenure, he worked as a United States Marshal from 1897 to 1906, and served as the U.S. consul to Glasgow, Scotland, from 1906 to 1907.

The Tennessee Democratic Party (TNDP) is the affiliate of the Democratic Party in Tennessee. The party was founded in 1826 initially as the Jacksonian Party. The Tennessee Democratic Party was born out of President Andrew Jackson's populist philosophy of Jacksonian democracy in the mid to late-1820s. After Jackson left office, the Democratic Party struggled in the state as the Whig Party would go on to be the dominant party in Tennessee until its collapse after the 1852 Election. Prior to the Civil War, as a result of the collapse of the former Whig Party, the Democratic Party became the dominant party in the state. After the war ended, the Republican Party would be the dominant political party during Reconstruction, but once Reconstruction ended, the Democratic Party would dominate Tennessee Politics up until 2011 when the Republican Party would gain firm control of Tennessee State Government.

The 1926 United States Senate special election in Massachusetts was held on November 2, 1926.

The 1896–97 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1896 and 1897, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 3.

The 1868–69 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were prior to the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1868 and 1869, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 1.

The 1822–23 United States Senate elections were held on various dates in various states. As these U.S. Senate elections were before the ratification of the Seventeenth Amendment in 1913, senators were chosen by state legislatures. Senators were elected over a wide range of time throughout 1822 and 1823, and a seat may have been filled months late or remained vacant due to legislative deadlock. In these elections, terms were up for the senators in Class 2.

The 1946 United States Senate special election in North Dakota took place on June 25, 1946. Democratic Senator John Moses, first elected in 1944, died on March 3, 1945, just two months into his term. Republican Governor Fred G. Aandahl appointed State Senator Milton Young to fill the vacancy and a special election was scheduled.

The 1916 United States Senate election in Tennessee was held on November 7, 1916. Incumbent Democratic Senator Luke Lea ran for re-election to a second term, but was defeated for the Democratic nomination by U.S. Representative Kenneth McKellar. McKellar won the general election against Republican Governor of Tennessee Ben W. Hooper.
The 1946 Massachusetts general election was held on November 5, 1946, throughout Massachusetts. Primary elections took place on June 18.

The 1932 Tennessee gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1932. Democratic nominee Hill McAlister defeated Republican nominee John McCall and Independent nominee Lewis S. Pope with 42.8% of the vote.

The 1910 Tennessee gubernatorial election was held on November 8, 1910. Incumbent Democratic governor Malcolm R. Patterson initially sought a third term but withdrew from the race after securing his party's nomination. Senator and former Democratic governor Robert Love Taylor was nominated after Patterson's withdrawal. On the Republican side, Ben W. Hooper defeated Alfred A. Taylor, Robert's brother, for the Republican nomination. In the general election, Ben W. Hooper defeated Robert Love Taylor with 51.89% of the vote.

The 1908 Tennessee gubernatorial election was held on November 3, 1908. Incumbent Democratic governor Malcolm R. Patterson defeated Republican nominee G. N. Tillman with 53.73% of the vote.



















