The 1814–15 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 26, 1814, and August 10, 1815. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 14th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1815. They occurred during President James Madison's second term. Elections were held for all 182 seats, representing 18 states.

The 1812–13 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 3, 1812, and April 30, 1813. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 13th United States Congress convened on May 24, 1813. They coincided with James Madison being re-elected president.

The 1810–11 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1810, and August 2, 1811. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 12th United States Congress convened on November 4, 1811. They occurred during President James Madison's first term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1806–07 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1806 and August 4, 1807. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 10th United States Congress convened on October 26, 1807. They occurred during Thomas Jefferson's second term. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.
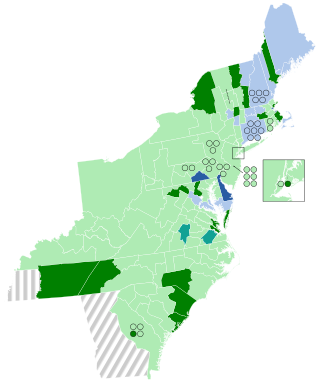
The 1804–05 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 24, 1804, and August 5, 1805. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 9th United States Congress convened on December 2, 1805. The elections occurred at the same time as President Thomas Jefferson's re-election. Elections were held for all 142 seats, representing 17 states.

The 1800–01 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between April 29, 1800, and August 1, 1801. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 7th United States Congress convened on December 7, 1801. They were held at the same time as the 1800 presidential election, in which Vice President Thomas Jefferson, a Democratic Republican, defeated incumbent President John Adams, a Federalist. Elections were held for all 106 seats, representing 15 states.
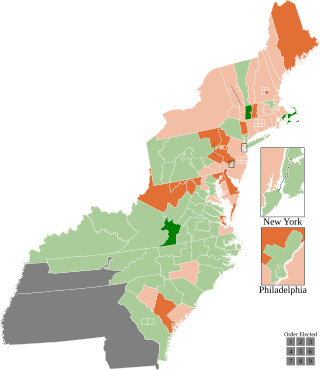
The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

Meredith Poindexter Gentry was an American politician who represented Tennessee's eighth and seventh districts in the United States House of Representatives.

The 1812 United States presidential election in Pennsylvania took place as part of the 1812 United States presidential election. Voters chose 25 representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for President and Vice President.

The 1810 census revealed dramatic population growth in Ohio since 1800, resulting in its representation increasing from a single Representative to six, resulting in the State being broken up into 6 districts, abolishing the at-large district. Jeremiah Morrow (Democratic-Republican), who had served since Ohio achieved statehood in 1803, retired to run for U.S. Senator, so that all six seats were open. Its elections were held October 13, 1812.

A special election was held in Georgia's at-large congressional district on December 13, 1813 to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of William W. Bibb (DR) on November 6, 1813, after being elected to the Senate.

Louisiana held its first United States House of Representatives elections following its April 1812 admission to the Union on September 28–30, 1812. A special election for a seat in the 12th Congress and a general election for a seat in the 13th Congress were held at the same time, and had nearly-identical results.

Kentucky gained four seats after the 1810 census.

North Carolina gained one representative as a result of the census of 1810. Its elections were held April 30, 1813, after the term began but before Congress's first meeting.

South Carolina gained one representative as a result of the 1810 census, increasing from 8 seats to 9. Its elections were held October 12–13, 1812.

Virginia gained one seat after the 1810 census, bringing its representation in the House of Representatives to 23 seats, the largest number Virginia would ever have. Virginia went from having the most representatives to having the second-most tied with Pennsylvania. New York, with its 27 seats, surpassed Virginia and remained the most populous state until the late 1960s.

Elections in Tennessee are held to fill various local, state, and federal seats. Special elections may be held to fill vacancies at other points in time. Statewide legislative referrals and referendums may also be on the ballot in some elections. Tennessee is one of thirteen states that holds its presidential primaries on Super Tuesday.

Tennessee elected its members August 2–3, 1827, after the term began but before the new Congress convened.
The 1813 Connecticut gubernatorial election took place on April 12, 1813.