The Federal Marriage Amendment (FMA), also referred to by proponents as the Marriage Protection Amendment, was a proposed amendment to the United States Constitution that would legally define marriage as a union of one man and one woman. The FMA would also prevent judicial extension of marriage rights to same-sex or other unmarried homosexual couples. An amendment to the U.S. Constitution requires the support of two thirds of each house of Congress and ratification by three fourths of the states. The last Congressional vote on the proposed amendment occurred in the House of Representatives on July 18, 2006, when the motion failed 236 to 187, falling short of the 290 votes required for passage in that body. The Senate has only voted on cloture motions with regard to the proposed amendment, the last of which was on June 7, 2006, when the motion failed 49 to 48, falling short of the 60 votes required to allow the Senate to proceed to consideration of the proposal and the 67 votes required to send the proposed amendment to the states for ratification.
This is a list of notable events in the history of LGBT rights that took place in the year 2004.

Many U.S. states enacted amendments to their state constitutions which prevented the recognition of some or all types of same-sex unions, but all such amendments were struck down by the Supreme Court of the United States on June 26, 2015, in the case of Obergefell v. Hodges. Some amendments prevented a state from legalizing same-sex marriage, civil unions and domestic partnerships, while others banned only same-sex marriage. By May 2012, voters in 30 states had approved such amendments. While the actual text of these amendments still remains written into the various state constitutions, the Obergefell decision has rendered them unenforceable insofar as they prevented same-sex couples from marrying.
This page contains a timeline of significant events regarding same-sex marriage and legal recognition of same-sex couples worldwide. It begins with the history of same-sex unions during ancient times, which consisted of unions ranging from informal and temporary relationships to highly ritualized unions, and continues to modern-day state-recognized same-sex marriage. Events concerning same-sex marriages becoming legal in a country or in a country's state are listed in bold.
The Tennessee Marriage Protection Amendment, also known as Tennessee Amendment 1 of 2006, is a state constitutional amendment banning same-sex unions. The referendum was approved by 81% of voters. It specified that only a marriage between a man and a woman could be legally recognized in the state of Tennessee. This prohibited same-sex marriages within the state, reinforcing previously existing statutes to the same effect until it was overturned by the Obergefell v. Hodges ruling in June 2015.
In response to court action in a number of states, the United States federal government and a number of state legislatures passed or attempted to pass legislation either prohibiting or allowing same-sex marriage or other types of same-sex unions.

Ballot Measure 2 of 1998 is a ballot measure, since ruled unconstitutional, that added an amendment to the Alaska Constitution that prohibited the recognition of same-sex marriage in Alaska. The Ballot measure was sparked by the lawsuit filed by Jay Brause and Gene Dugan, after the two men were denied a marriage license by the Alaska Bureau of Vital Statistics. In Brause v. Bureau of Vital Statistics, 1998 WL 88743, the Alaska Superior Court ruled that the state needed compelling reason to deny marriage licenses to same-sex couples and ordered a trial on the question. In response, the Alaska Legislature immediately proposed and passed Resolution 42, which became what is now known as Ballot Measure 2. Ballot Measure 2 passed via public referendum on November 3, 1998, with 68% of voters supporting and 32% opposing. The Bause case was dismissed following the passage of the ballot measure.
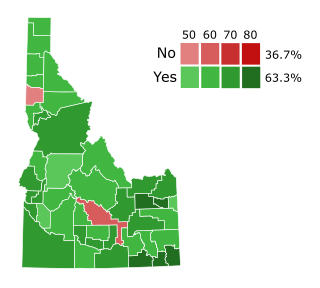
Idaho Amendment 2 of 2006 is an amendment to the Idaho Constitution that made it unconstitutional for the state to recognize or perform same-sex marriages or civil unions.
Proposition 2 was a referendum for a state constitutional amendment placed on the ballot by the Texas legislature and approved by the voters at the November 8, 2005 general election. The measure added a new provision to the Texas Constitution, Article 1, Section 32, which provides that "Marriage in this state shall consist only of the union of one man and one woman", and "This state or a political subdivision of this state may not create or recognize any legal status identical or similar to marriage." Texas thus became the nineteenth US state to adopt constitutional amendment banning same-sex marriage. It was the most populous state to adopt a constitutional ban on same-sex marriage until California passed its ban in November 2008.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in the U.S. state of Wisconsin since October 6, 2014, upon the resolution of a lawsuit challenging the state's ban on same-sex marriage. On October 6, the U.S. Supreme Court refused to hear an appeal of an appellate court ruling in Wolf v. Walker that had found Wisconsin's ban on same-sex marriage unconstitutional. The appellate court issued its order prohibiting enforcement of the state's ban on same-sex marriage the next day and Wisconsin counties began issuing marriage licenses to same-sex couples immediately.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in the U.S state of Iowa since a decision of the Iowa Supreme Court on April 3, 2009. Marriage licenses became available to same-sex couples on April 27.
Domestic partnerships in Wisconsin afford limited rights to same-sex couples. They have been recognized in Wisconsin since August 3, 2009. Domestic partnerships in Wisconsin provide select rights, such as the ability to inherit a partner's estate in the absence of a will, hospital and jail visitation, and the ability to access family medical leave to care for a sick partner. Wisconsin's domestic partnership registry does not provide for two-parent adoptions by persons of the same sex, and it confers far fewer rights, duties and protections than are associated with marriage. Wisconsin ended its domestic partnership registry on April 1, 2018.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in the U.S. state of Nevada since October 9, 2014, when a federal district court judge issued an injunction against Nevada's enforcement of its ban on same-sex marriage, acting on order from the Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals. A unanimous three-judge panel of the Ninth Circuit had ruled two days earlier that the state's ban on same-sex marriage was unconstitutional. Same-sex marriage was previously banned by an amendment to the Constitution of Nevada adopted in 2002.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in the U.S. state of Indiana since October 6, 2014. The state had previously restricted marriage to male-female couples by statute in 1986. By legislation passed in 1997, it denied recognition to same-sex relationships established in other jurisdictions. A lawsuit challenging the state's refusal to grant marriage licenses to same-sex couples, Baskin v. Bogan, won a favorable ruling from the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Indiana on June 25, 2014. Until the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Seventh Circuit granted an emergency stay of the district court's ruling on June 27, most Indiana counties issued marriage licenses to same-sex couples. The Court of Appeals affirmed the district court's ruling in Baskin on September 4. A ruling in Bowling v. Pence stated that the state must recognize same-sex marriages performed out-of-state and the decision was stayed until the Circuit ruled on the merits in similar cases. It also stated that the ruling would remain stayed if the circuit court stayed its decision in the related cases.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in the U.S state of Idaho since October 15, 2014.
Same-sex marriage has been legal in the U.S. state of Oklahoma since October 6, 2014, following the resolution of a lawsuit challenging the state's ban on same-sex marriage. On that day, following the U.S. Supreme Court's refusal to review the case that found the ban unconstitutional, the federal Tenth Circuit Court of Appeals ordered the state to recognize same-sex marriage.
Same-sex marriage in the U.S. state of Tennessee became legal with the U.S. Supreme Court ruling in Obergefell v. Hodges on June 26, 2015. That day, Governor Bill Haslam announced the state would follow the judicial order, and same-sex couples began to marry in Tennessee.
Same-sex marriage has been legally recognized in the U.S. state of Virginia since October 6, 2014, following a decision by the Supreme Court of the United States to refuse to hear an appeal of the Fourth Circuit Court of Appeals in the case Bostic v. Schaefer. Marriages of same-sex couples subsequently began at 1:00 p.m. on October 6 after the Circuit Court issued its mandate, and since then Virginia has performed legal marriages of same-sex couples and recognized out-of-state same-sex marriages.
Same-sex marriage in Arkansas is legal under the U.S. Supreme Court decision in Obergefell v. Hodges, a landmark case in which same-sex marriage bans were struck down on June 26, 2015. Prior to that, same-sex marriage in Arkansas was briefly legal for a period beginning on May 9, 2014, as the result of a ruling by Sixth Judicial Circuit Judge Chris Piazza, striking down the state's constitutional and legislative ban on same-sex marriage as violating the Constitution of the United States. Approximately 541 same-sex couples received marriage licenses in several Arkansas counties before the Arkansas Supreme Court stayed his ruling pending appeal on May 16, 2014.





