
The Otranto Barrage was an Allied naval blockade of the Strait of Otranto between Brindisi in Italy and Corfu on the Greek side of the Adriatic Sea in the First World War. The blockade was intended to prevent the Austro-Hungarian Navy from escaping into the Mediterranean and threatening Allied operations there. The blockade was effective in preventing surface ships from escaping the Adriatic, but it had little or no effect on the submarines based at Cattaro.
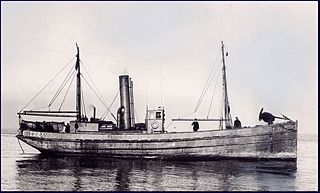
The CD-class naval drifters were armed naval drifters constructed in 1917 for the Royal Navy in Canada. 100 were ordered for use in British waters during World War I numbered from CD 1 to CD 100, of which 42 were transferred to the Royal Canadian Navy and 18 were transferred to the United States Navy. In British waters, they were used to patrol areas around Gibraltar and Bermuda. In Canadian waters, the Maritimes and in American waters, along the New England coast. Following the war, the drifters were either sold into mercantile service or scrapped. Some survived in British service to be used during World War II.
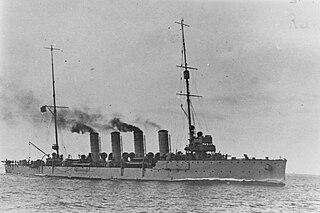
SMS Novara was a Novara-class scout cruiser of the Austro-Hungarian Navy which served during World War I. Built by the Danubius shipyard between December 1912 and January 1915, Novara was the third and final member of her class to enter service, some six months after the start of the war. She was armed with a battery of nine 10-centimeter (3.9 in) guns and had a top speed of 27 knots.

The Royal Naval Patrol Service (RNPS) was a branch of the Royal Navy active during both the First and Second World Wars. The RNPS operated many small auxiliary vessels such as naval trawlers for anti-submarine and minesweeping operations to protect coastal Britain and convoys.

The Castle-class minesweeper was a highly seaworthy naval trawler adapted for patrol, anti-submarine warfare and minesweeping duties and built to Admiralty specifications. Altogether 197 were built in the United Kingdom between 1916 and 1919, with others built in Canada, India and later New Zealand. Many saw service in the Second World War.

Naval trawlers are vessels built along the lines of a fishing trawler but fitted out for naval purposes; they were widely used during the First and Second World Wars. Some—known in the Royal Navy as "Admiralty trawlers"— were purpose-built to naval specifications, others adapted from civilian use. Fishing trawlers were particularly suited for many naval requirements because they were robust vessels designed to work heavy trawls in all types of weather, and had large clear working decks. A minesweeper could be created by replacing the trawl with a mine sweep. Adding depth charge racks on the deck, ASDIC sonar below, and a 3-inch (76 mm) or 4-inch (102 mm) gun in the bow equipped the trawler for anti-submarine duties.

SM U-4 or U-IV was a U-3-class submarine or U-boat built for and operated by the Austro-Hungarian Navy before and during the First World War. The submarine was built as part of a plan to evaluate foreign submarine designs, and was the second of two boats of the class built by Germaniawerft of Kiel, Germany.

The U-5 class was a class of three submarines or U-boats that were operated by the Austro-Hungarian Navy before and during World War I. The class was a part of the Austro-Hungarian Navy's efforts to competitively evaluate three foreign submarine designs.

SM U-6 or U-VI was a U-5-class submarine or U-boat built for and operated by the Austro-Hungarian Navy before and during the First World War. The submarine was built as part of a plan to evaluate foreign submarine designs, and was the second of three boats of the class built by Whitehead & Co. of Fiume after a design by Irishman John Philip Holland.
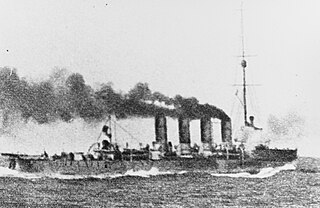
The Battle of the Strait of Otranto of 1917 was the result of an Austro-Hungarian raid on the Otranto Barrage, an Allied naval blockade of the Strait of Otranto. The battle took place on 15 May 1917, and was the largest surface action in the Adriatic Sea during World War I. The Otranto Barrage was a fixed barrier, composed of lightly armed drifters with anti-submarine nets coupled with minefields and supported by Allied naval patrols.

SMS Árpád was a pre-dreadnought battleship built by the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the early 20th century. She was launched on 11 September 1901 as the second of three Habsburg-class battleships. Along with her sister ships, she participated at the bombardment of Ancona during World War I. Due to a shortage of coal, she was soon decommissioned after the bombardment of Ancona and used as harbor defense ship for the remainder of the war. After the war, all of the Habsburg-class battleships were ceded to Great Britain as war prizes. She was scrapped in Italy in 1921.

SMS Habsburg was a pre-dreadnought battleship built by the Austro-Hungarian Navy in 1899. The lead ship of the Habsburg class was launched on 9 September 1900. In 1903 and 1904, Habsburg and her sister ship Árpád conducted training exercises in the Mediterranean Sea. In 1906 and 1907, Habsburg was transferred to the III Battleship Division. One of her superstructure decks was removed to reduce weight and to modernize the vessel in 1910.

The SC-1 class was a large class of submarine chasers built during World War I for the United States Navy. They were ordered in very large numbers in order to combat attacks by German U-boats, with 442 boats built from 1917 to 1919.

SMS Körös was the name ship of the Körös-class river monitors built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy. Completed in 1892, the ship was part of the Danube Flotilla, and fought various Allied forces from Belgrade down the Danube to the Black Sea during World War I. After brief service with the Hungarian People's Republic at the end of the war, she was transferred to the newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, and renamed Morava. She remained in service throughout the interwar period, although budget restrictions meant she was not always in full commission.

Nino Bixio was a protected cruiser built by the Italian Regia Marina in the early 1910s. She was the lead ship of the Nino Bixio class, which were built as scouts for the main Italian fleet. She was equipped with a main battery of six 120-millimeter (4.7 in) guns and had a top speed in excess of 26 knots, but her engines proved to be troublesome in service. Nino Bixio saw service during World War I and briefly engaged the Austro-Hungarian cruiser SMS Helgoland in 1915. Her career was cut short in the post-war period due to severe cuts to the Italian naval budget, coupled with her unreliable engines. Nino Bixio was stricken from the naval register in March 1929 and sold for scrap.

Marsala was a protected cruiser built by the Italian Regia Marina in the 1910s. She was the second and final member of the Nino Bixio class, which were built as scouts for the main Italian fleet. She was equipped with a main battery of six 120-millimeter (4.7 in) guns and had a top speed in excess of 26 knots, but her engines proved to be troublesome in service. Marsala spent World War I based at Brindisi; she was involved in the Battle of the Otranto Straits in May 1917, where she briefly engaged Austro-Hungarian cruisers. Marsala's career was cut short in November 1927 when she was stricken from the naval register and sold for scrap, the result of her unreliable engines and drastic cuts to the naval budget.

SMS Saida was a Novara-class scout cruiser built for the Austro-Hungarian Navy in the early 1910s. The ship was armed with a main battery of nine 10 cm (3.9 in) guns, and six twin 53.3 cm (21.0 in) torpedo tubes were added in 1917. She was built by the Cantiere Navale Triestino shipyard from 1911 to 1914, entering service days after the outbreak of World War I. She spent the war as a flotilla leader, conducting raids and patrols in the narrow waters of the Adriatic Sea.

T2 was a seagoing torpedo boat operated by the Royal Yugoslav Navy between 1923 and 1939. Originally 77 T, a 250t-class torpedo boat of the Austro-Hungarian Navy built in 1914, she was armed with two 66 mm (2.6 in) guns and four 450 mm (17.7 in) torpedo tubes, and could carry 10–12 naval mines. She saw active service during World War I, performing convoy, patrol, escort, minesweeping and minelaying tasks, anti-submarine operations, and shore bombardment missions. In 1917, the suffixes of all Austro-Hungarian torpedo boats were removed, and thereafter she was referred to as 77. Present in the Bocche di Cattaro during the short-lived mutiny by Austro-Hungarian sailors in early February 1918, members of her crew raised the red flag but undertook no other mutinous actions. 77 was part of the escort force for the Austro-Hungarian dreadnought Szent István during the action that resulted in the sinking of that ship by Italian torpedo boats in June 1918.

USS Richard Bulkeley was a minesweeping trawler leased from the British Royal Navy. Built as HMT Richard Bulkeley, the ship was a Mersey class trawler, purpose-built for service with the Auxiliary Patrol. On 12 July 1919, it was sunk by a mine while removing minefields in the North Sea.




















