
Proboscidea is a taxonomic order of afrotherian mammals containing one living family (Elephantidae) and several extinct families. First described by J. Illiger in 1811, it encompasses the elephants and their close relatives. Three species of elephant are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant.

Paenungulata is a clade of "sub-ungulates", which groups three extant mammal orders: Proboscidea, Sirenia, and Hyracoidea (hyraxes). At least two more possible orders are known only as fossils, namely Embrithopoda and Desmostylia.

Mammutidae is an extinct family of proboscideans belonging to Elephantimorpha. It is best known for the mastodons, which inhabited North America from the Late Miocene until their extinction at beginning of the Holocene, around 11,000 years ago. The earliest fossils of the group are known from the Late Oligocene of Africa, around 24 million years ago, and fossils of the group have also been found across Eurasia. The name "mastodon" derives from Greek, μαστός "nipple" and ὀδούς "tooth", referring to their characteristic teeth.

Moeritherium is an extinct genus of basal proboscideans from the Eocene of North and West Africa. It was related to elephants and, more distantly, to sea cows and hyraxes.

Arsinoitherium is an extinct genus of paenungulate mammals belonging to the extinct order Embrithopoda. It is related to elephants, sirenians, and hyraxes. Arsinoitheres were superficially rhinoceros-like herbivores that lived during the Late Eocene and the Early Oligocene of North Africa from 36 to 30 million years ago, in areas of tropical rainforest and at the margin of mangrove swamps. A species described in 2004, A. giganteum, lived in Ethiopia about 27 million years ago.

Chilgatherium is the earliest and most primitive representative of the family Deinotheriidae. It is known from late Oligocene fossil teeth found in the Ethiopian district of Chilga.

Embrithopoda ("heavy-footed") is an order of extinct mammals known from Asia, Africa and Eastern Europe. Most of the embrithopod genera are known exclusively from jaws and teeth dated from the late Paleocene to the late Eocene; however, the order is best known from its terminal member, the elephantine Arsinoitherium.

Daouitherium is an extinct genus of early proboscideans that lived during the early Eocene some 55 million years ago in North Africa.

Numidotherium is an extinct genus of early proboscideans, discovered in 1984, that lived during the middle Eocene of North Africa some 46 million years ago. It was about 90–100 cm (35–39 in) tall at the shoulder and weighed about 250–300 kg (550–660 lb).

Phosphatherium escuillei is a basal proboscidean that lived from the Late Paleocene to the early stages of the Ypresian age. Research has suggested that Phosphatherium existed during the Eocene period.

Barytherium is a genus of an extinct family (Barytheriidae) of primitive proboscideans that lived during the late Eocene and early Oligocene in North Africa. The type species is Barytherium grave, found at the beginning of the 20th century in Fayum, Egypt. Since then, more complete specimens have been found at Dor el Talha, Libya. More fossils were also discovered in 2011 in the Aidum area in Dhofar by Oman's Ministry of Heritage and Culture, which was named Barytherium omansi.

Stegotetrabelodon is an extinct genus of primitive elephantid from the Late Miocene to Early Pliocene of Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, and Italy.

Eritherium is an extinct genus of early Proboscidea found in the Ouled Abdoun basin, Morocco. It lived about 60 million years ago. It was first named by Emmanuel Gheerbrant in 2009 and the type species is Eritherium azzouzorum. Eritherium is the oldest, smallest and most primitive known elephant relative.
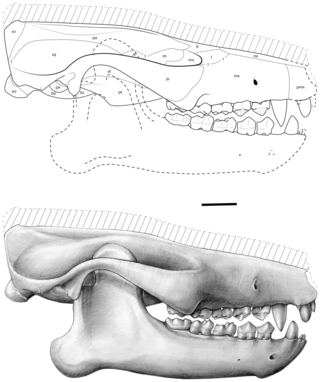
Ocepeia is an extinct genus of afrotherian mammal that lived in present-day Morocco during the middle Paleocene epoch, approximately 60 million years ago. First named and described in 2001, the type species is O. daouiensis from the Selandian stage of Morocco's Ouled Abdoun Basin. A second, larger species, O. grandis, is known from the Thanetian, a slightly younger stage in the same area. In life, the two species are estimated to have weighed about 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) and 10 kg (22 lb), respectively, and are believed to have been specialized leaf-eaters. The fossil skulls of Ocepeia are the oldest known afrotherian skulls, and the best-known of any Paleocene mammal in Africa.

The Oulad Abdoun Basin is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years.
The Lignites de Soissonais is a geologic formation in the Var, Marne departments of France. It preserves fossils dating back to the Ypresian stage of the Eocene period.
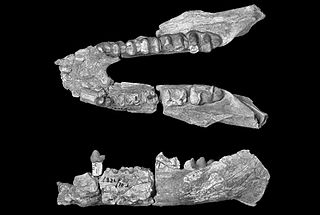
Arcanotherium is an extinct genus of early proboscidean belonging to the family Numidotheriidae that lived in North Africa during the late Eocene/early Oligocene interval.
Saloumia is an extinct genus of the order Proboscidea. It is one of the oldest members of the order and lived in the middle Eocene of Senegal. It is known only from a single molar, whose pronounced bumpy chewing surface indicates it is probably closely related to Moeritherium.
Dagbatitherium is an extinct genus of proboscideans. So far a single molar from the phosphate basins of Togo in West Africa has been found. The fossil dates to the Middle Eocene, around 47 million years ago. A striking feature of the tooth are the three pairs of cusps oriented transversely to the longitudinal axis of the tooth. This feature is found in more derived proboscideans, which are grouped in the Elephantiformes. For its age, Dagbatitherium is the earliest member of Elephantiformes to date. Furthermore, it is characterized by a low tooth crown and a humped occlusal pattern. The genus was described in 2021.
Grand Daoui is a quarry in the Ouled Abdoun Basin of Morocco known for its fossils. It is the discovery place of Phosphatherium escuilliei, the earliest known proboscidean. It was the location for several field parties between 1997 and 2001, which allowed survey of the geological and paleontological context of Phosphatherium localities. It is also rich in marine vertebrae fossils. All Phosphatherium remains to date have been found in the quarry. The discovery of fossils there has aided in the study of early African placental fauna. The marine snake Palaeophis maghrebianus is also known from the locality, as well as the primitive gavialoid Argochampsa krebsi.

















