Related Research Articles

In human genetics, the Y-chromosomal Adam, is the patrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) from whom all currently living humans are descended. He is the most recent male from whom all living humans are descended through an unbroken line of their male ancestors. The term Y-MRCA reflects the fact that the Y chromosomes of all currently living human males are directly derived from the Y chromosome of this remote ancestor.

Haplogroup G (M201) is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup. It is one of two branches of the parent haplogroup GHIJK, the other being HIJK.

E-M215 or E1b1b, formerly known as E3b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. E-M215 has two basal branches, E-M35 and E-M281. E-M35 is primarily distributed in North Africa and the Horn of Africa, and occurs at moderate frequencies in the Middle East, Europe, and Southern Africa. E-M281 occurs at a low frequency in Ethiopia.
Haplogroup D1 or D-M174 is a subclade of haplogroup D-CTS3946. This male haplogroup is found primarily in East Asia, Magar-ethnic Nepal and the Andaman Islands. It is also found regularly with lower frequency in Central Asia, Siberia and Mainland Southeast Asia, and, more rarely, in Europe and the Middle East.

Haplogroup F, also known as F-M89 and previously as Haplogroup FT, is a very common Y-chromosome haplogroup. The clade and its subclades constitute over 90% of paternal lineages outside of Africa.
Haplogroup Q-M3 (Y-DNA) is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. Haplogroup Q-M3 is a subclade of Haplogroup Q-L54. Haplogroup Q-M3 was previously known as Haplogroup Q3; currently Q-M3 is Q1b1a1a below Q1b-M346.
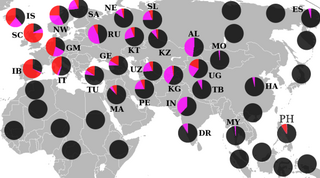
Haplogroup R1, or R-M173, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. A primary subclade of Haplogroup R (R-M207), it is defined by the SNP M173. The other primary subclade of Haplogroup R is Haplogroup R2 (R-M479).

In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by specific mutations in the non-recombining portions of DNA on the male-specific Y chromosome (Y-DNA). Individuals within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats (STRs) and single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The Y-chromosome accumulates approximately two mutations per generation, and Y-DNA haplogroups represent significant branches of the Y-chromosome phylogenetic tree, each characterized by hundreds or even thousands of unique mutations.

Haplogroup R, or R-M207, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is both numerous and widespread among modern populations.
In genetic genealogy, a unique-event polymorphism (UEP) is a genetic marker that corresponds to a mutation that is likely to occur so infrequently that it is believed overwhelmingly probable that all the individuals who share the marker, worldwide, will have inherited it from the same common ancestor, and the same single mutation event.
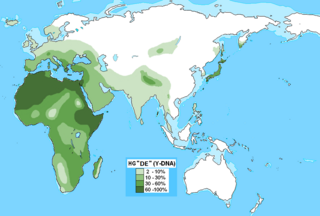
Haplogroup DE is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is defined by the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutations, or UEPs, M1(YAP), M145(P205), M203, P144, P153, P165, P167, P183. DE is unique because it is distributed in several geographically distinct clusters. An immediate subclade, haplogroup D, is mainly found in East Asia, parts of Central Asia, and the Andaman Islands, but also sporadically in West Africa and West Asia. The other immediate subclade, haplogroup E, is common in Africa, and to a lesser extent the Middle East and southern Europe.

Haplogroup CT is a human Y chromosome haplogroup. CT has two basal branches, CF and DE. DE is divided into a predominantly Asia-distributed haplogroup D-CTS3946 and a predominantly Africa-distributed haplogroup E-M96, while CF is divided into an East Asian, Native American, and Oceanian haplogroup C-M130 and haplogroup F-M89, which dominates most non-African populations.

Haplogroup BT M91, also known as Haplogroup A1b2, is a Y-chromosome haplogroup. BT is a subclade of haplogroup A1b (P108) and a sibling of the haplogroup A1b1 (L419/PF712).

Haplogroup CF, also known as CF-P143 and CT(xDE), is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. CF is defined by the SNP P143, and its existence and distribution are inferred from the fact that haplogroups descended from CF include most human male lineages in Eurasia, Oceania, and The Americas. CF descends from CT (CT-M168), and is the sibling of DE. CF has two basal branches, Haplogroup C and Haplogroup F.
E-M35, also known as E1b1b1-M35, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. E-M35 has two basal branches, E-V68 and E-Z827. E-V68 and E-Z827 are primarily distributed in North Africa and the Horn of Africa, and occur at lower frequencies in the Middle East, Europe, and Southern Africa.

Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
Haplogroup E-V68, also known as E1b1b1a, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup found in North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Western Asia and Europe. It is a subclade of the larger and older haplogroup, known as E1b1b or E-M215. The E1b1b1a lineage is identified by the presence of a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) mutation on the Y chromosome, which is known as V68. It is a subject of discussion and study in genetics as well as genetic genealogy, archaeology, and historical linguistics.
E-Z827, also known as E1b1b1b, is a major human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is the parent lineage to the E-Z830 and E-V257 subclades, and defines their common phylogeny. The former is predominantly found in the Middle East; the latter is most frequently observed in North Africa, with its E-M81 subclade observed among the ancient Guanche natives of the Canary Islands. E-Z827 is also found at lower frequencies in Europe, and in isolated parts of Southeast Africa.
Haplogroup A-L1085, also known as haplogroup A0-T is a human Y-DNA haplogroup. It is part of the paternal lineage of almost all humans alive today. The SNP L1085 has played two roles in population genetics: firstly, most Y-DNA haplogroups have diverged from it and; secondly, it defines the undiverged basal clade A-L1085*.

Haplogroup E-M2, also known as E1b1a1-M2, is a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. E-M2 is primarily distributed within Africa followed by West Asia. More specifically, E-M2 is the predominant subclade in West Africa, Central Africa, Southern Africa, and the region of the African Great Lakes; it also occurs at moderate frequencies in North Africa, and the Middle East. E-M2 has several subclades, but many of these subhaplogroups are included in either E-L485 or E-U175. E-M2 is especially common among indigenous Africans who speak Niger-Congo languages, and was spread to Southern Africa and East Africa through the Bantu expansion.
References
- 1 2 The Y Chromosome Consortium, T. Y. C. (2002). "A Nomenclature System for the Tree of Human Y-Chromosomal Binary Haplogroups" (PDF). Genome Research. 12 (2). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: 339–48. doi:10.1101/gr.217602. PMC 155271 . PMID 11827954.
- ↑ Weale, Michael E.; et al. (2003). "Rare Deep-Rooting Y Chromosome Lineages in Humans: Lessons for Phylogeography". Genetics. 165 (1): 229–34. doi:10.1093/genetics/165.1.229. PMC 1462739 . PMID 14504230.
- ↑ Henn, BM; et al. (2008). "Y-chromosomal evidence of a pastoralist migration through Tanzania to southern Africa". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105 (31). PNAS: 10693–8. Bibcode:2008PNAS..10510693H. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801184105 . PMC 2504844 . PMID 18678889.
Phylogenetic tree of human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroups | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mitochondrial Eve (L) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| L0 | L1–6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| L1 | L2 | L3 | L4 | L5 | L6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| M | N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CZ | D | E | G | Q | O | A | S | R | I | W | X | Y | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C | Z | B | F | R0 | pre-JT | P | U | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HV | JT | K | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H | V | J | T | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||