
Iran has a long paved road system linking most of its towns and all of its cities. In 2011 the country had 173,000 kilometres (107,000 mi) of roads, of which 73% were paved. In 2008 there were nearly 100 passenger cars for every 1,000 inhabitants.

Hormozgan Province is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Its capital is the city of Bandar Abbas. The province is in the south of the country, in Iran's Region 2. facing Oman, the United Arab Emirates and the Hormuz Straits. Its area is 70,697 km2 (27,296 sq mi), The province has 14 islands in the Persian Gulf and 1,000 km (620 mi) of coastline.

Bandar Abbas is a city in the Central District of Bandar Abbas County, Hormozgan province, Iran, serving as capital of the province, the county, and the district. Bandar Abbas is a port on the southern coast of the country, on the Persian Gulf.

Greater Tunb and Lesser Tunb are two small islands in the eastern Persian Gulf, close to the Strait of Hormuz. They lie at 26°15′N55°16′E and 26°14′N55°08′E, respectively, some 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) from each other and 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of the Iranian island of Qeshm. The islands are administered by Iran as part of its Hormozgan Province.

Chābahār is a city in the Central District of Chabahar County, Sistan and Baluchestan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. It is a free port situated on the coast of the Gulf of Oman, and is Iran's southernmost city. The sister port city of Gwadar in Balochistan, Pakistan, is located about 170 kilometres (110 mi) to the east of Chabahar.
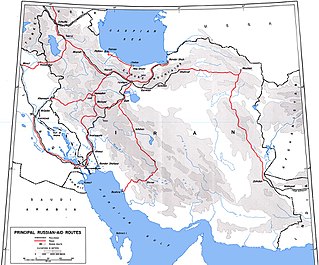
The Persian Corridor was a supply route through Iran into Soviet Azerbaijan by which British aid and American Lend-Lease supplies were transferred to the Soviet Union during World War II. Of the 17.5 million long tons of US Lend-Lease aid provided to the Soviet Union, 7.9 million long tons (45%) were sent through Iran.

The Islamic Republic of Iran Navy or Iranian Navy, officially abbreviated NEDAJA, is the naval warfare service branch of Iran's regular military, the Islamic Republic of Iran Army (Artesh). It is one of Iran's two maritime military branches, alongside the Navy of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).

Qeshm is an arrow-shaped Iranian island in the Strait of Hormuz, separated from the mainland by the Clarence Strait/Khuran in the Persian Gulf. and the largest in the Persian Gulf.

Iran Shipbuilding & Offshore Industries Complex Co (ISOICO) is an Iranian ship yard, located in the Persian Gulf, Strait of Hormuz, active as shipbuilder and ship-repairer of different types of vessels and offshore structures. ISOICO is a subsidiary of IDRO.

The Islamic Republic of Iran Railways is the national state-owned railway system of Iran. The Raja Passenger Train Company is an associate of the IR, and manages its passenger trains. The Railway Transportation Company is an associate of the IR, which manages its freight transport. The Ministry of Roads & Urban Development is the state agency that oversees the IRIR. Some 33 million tonnes of goods and 29 million passengers are transported annually by the rail transportation network, accounting for 9 percent and 11 percent of all transportation in Iran, respectively (2011).

The Islamic Republic of Iran Shipping Line Group, commonly known by its business name IRISL Group, is a shipping line based in and owned by Iran. Its fleet comprises 115 ocean-going vessels with a total capacity of 3.3 million tons deadweight (DWT), with 87 being ocean-going vessels owned by IRISL and the remaining 28 ships being owned under the flags of subsidiary companies, including Khazar Shipping, Valfajr and Iran-India Shipping. They are manned by 6,000 personnel who work under the Iranian flag in the Caspian Sea, Persian Gulf, international waters and various ports of the world.

Bandar Abbas County is in Hormozgan province, Iran. Its capital is the city of Bandar Abbas.

Qeshm County is in Hormozgan province, Iran. Its capital is the city of Qeshm.
A fixed link or fixed crossing is a permanent, unbroken road or rail connection across water that uses some combination of bridges, tunnels, and causeways and does not involve intermittent connections such as drawbridges or ferries. A bridge–tunnel combination is commonly used for major fixed links.
Bandar Khamir is a port city on the shores of the Persian Gulf in the Central District of Khamir County, Hormozgan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.

The International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC) is a 7,200-km long multi-mode network of ship, rail, and road route for moving freight between India, Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia, Central Asia and Europe. The route primarily involves moving freight from India, Iran, Azerbaijan and the Russian Federation via ship, rail and road. The objective of the corridor is to increase trade connectivity between major cities such as Mumbai, Moscow, Tehran, Baku, Bandar Abbas, Astrakhan, Bandar Anzali, etc. Dry runs of two routes were conducted in 2014, the first was Mumbai to Baku via Bandar Abbas and the second was Mumbai to Astrakhan via Bandar Abbas, Tehran and Bandar Anzali. The objective of the study was to identify and address key bottlenecks. The results showed transport costs were reduced by "$2,500 per 15 tons of cargo". Other routes under consideration include via Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan.

Qeshm is a coastal city in the Central District of Qeshm County, Hormozgan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
Hormuz District is in Bandar Abbas County, Hormozgan province, Iran. Its capital is the city of Hormuz.
Larak Rural District is in the Central District of Qeshm County, Hormozgan province, Iran. Its capital is the village of Larak Shahri.
In the second half of the 19th century, during the time of Nasser-al-Din Shah, a short horse-driven suburban railway was established south of Tehran that was later converted to steam. This line was closed in 1952.

















