Maps
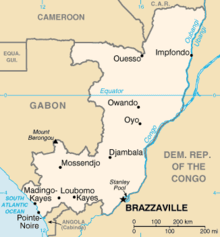
- UN Map
- UNHCR Atlas Map
- ReliefWeb
- UNJLC Rail map of Southern Africa
- misses line to Franceville
Railway stations in the Republic of the Congo (Congo) include:

| Station name | Route(s) |
|---|---|
| Bilinga | Brazzaville – Pointe-Noire railway station Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Bodissa | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Bouanza | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Brazzaville | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Byiamba | M'binda – Mont Belo |
| Dolisie (Loubomo) | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Hinda | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Kibossi | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Kibouende | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Kikembo | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Kimbaouka | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Kimbedi | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Kingoyi | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Kipambou-Kayes | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Les Saras | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Loualou | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Loudima | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Loulombo | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Loutété | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Madingou | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Madzia | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Maïsa | M'binda – Mont Belo |
| Makabama | M'binda – Mont Belo |
| Makassou Makola | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Makoko | M'binda – Mont Belo |
| Malemba | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Massembo-Loubaki | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Matoumbou | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Mayogongo | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| M'binda | M'binda – Mont Belo |
| Mboukou | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Mfilou | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Mfoubou | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Mindouli | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Missafou | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Mont Belo | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire M'binda – Mont Belo |
| Mossendjo | M'binda – Mont Belo |
| Moubotsi | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Moukondo | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Moukoungoulou | M'binda – Mont Belo |
| Moutela | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Mpounga | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Mvoungouti | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Mvouti | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Nemba | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Ngabouloumou | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Ngoma-Tse-Tse | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire |
| Ngondji | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Nkayi | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Nkougni | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Ntombo | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Nzombo | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Pointe Noire | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Tao-Tao | Brazzaville – Pointe Noire Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Tchitondi | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Tié-Tié | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Tsessi | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Tsoumbou | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
| Yanga | Loutété – Pointe Noire |
(610mm gauge, isolated)
Modes of transport in Gabon include rail, road, water, and air. The one rail link, the Trans-Gabon Railway, connects the port of Owendo with the inland town of Franceville. While most of the country is connected by roads, not all areas are accessible. Much of the road network remains unpaved, and it primarily revolves around seven "national routes" labeled N1 through N7. The largest seaports are Port-Gentil and the newer Owendo, and 1,600 km of inland waterways are navigable. There are three international airports, eight other paved airports, and over 40 with unpaved runways. Nearly 300 km of pipelines carry petroleum products, mainly crude oil.
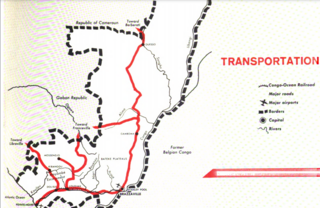
Transport in the Republic of Congo includes land, air and water modes. Over 3,000 km (1,900 mi) of paved roads are in use. The two international airports are Maya-Maya Airport and Pointe Noire Airport.
The Chemin de fer Arnaud, now Chemin de fer Arnaud Quebec is a private Canadian short line railway owned by Société ferroviaire et portuaire de Pointe-Noire (SFPPN) operating in the province of Quebec.

The Wabush Lake Railway is a short line railway operating in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada.

The Trans-Gabon Railway is the only railway in Gabon. It runs 670 km (420 mi) east from Owendo port station in Libreville to Franceville via numerous stations, the main ones being Ndjolé, Lopé, Booué, Lastoursville and Moanda.

Dolisie, known as Loubomo between 1975 and 1991, is a city and a commune. It is the capital of Niari in the south western of the Republic of the Congo, the country's third largest city and an important commercial centre. The city lies on the eastern edge of the coastal rainforest and has a population of 117,920.

Mbinda is a village in the Republic of Congo, lying on the border with Gabon. It is the administrative seat of the Mbinda District.

The Congo–Ocean Railway links the Atlantic port of Pointe-Noire with Brazzaville, a distance of 502 kilometres (312 mi). It bypasses the rapids on the lower Congo River; from Brazzaville, river boats are able to ascend the Congo River and its major tributaries, including the Oubangui River to Bangui.
Mossendjo is a town and a commune located in the Niari Department of the Republic of the Congo.

The Departments of the Republic of the Congo are divided into 86 districts and 6 communes; which are further subdivided into urban communities and rural communities ; which are further subdivided into quarters or neighborhoods (quartiers) and villages. Note the departments of Brazzaville and Pointe-Noire are made of 1 commune each, then divided in urban districts (arrondissements).
The COMILOG Cableway was one of the longest cableways in the world, until its closure in 1986. The ropeway conveyor ran for 76 km from Moanda in the Haut-Ogooué Province of south eastern Gabon to Mbinda in the Republic of Congo.
Railway stations in Sierra Leone include:

The list of railway stations in Cameroon includes:

Railway stations in Angola include:
Mayoko is a town in the Mayoko District, Niari Department, east of the Republic of the Congo.
The Quebec North Shore and Labrador Railway is a private Canadian regional railway that stretches 414 kilometres (257 mi) through the wilderness of northeastern Quebec and western Labrador. It connects Labrador City, Labrador, with the port of Sept-Îles, Quebec, on the north shore of the St. Lawrence River. QNS&L is owned by Iron Ore Company of Canada (IOC), and is a common carrier.

The Republic of the Congo faces a number of ongoing health challenges.

Oil and gas dominate the extraction industries of the Republic of the Congo, also referred to as Congo-Brazzaville. The petroleum industry accounted for 89% of the country’s exports in 2010. Among African crude oil producers in 2010, The Congo ranked seventh. Nearly all of the country's hydrocarbons were produced off-shore. The minerals sector is administered by the Department of Mines and Geology. Presently no major mining activities are underway, although there are some small-scale domestic operations. However, the country does have numerous large-scale undeveloped resources. The country has recently attracted a strong influx of international companies seeking to tap into the vast mineral wealth.

Western Labrador Rail Services, Inc. is a rail operation of Genesee & Wyoming Canada, Inc. created in 2010 by the combination of three short line railways: Arnaud Railway, Bloom Lake Railway, and Wabush Lake Railway. The operation provides rail transportation services to mining companies operating in the provinces of Newfoundland and Labrador and Québec, Canada.

The Compagnie minière de l'Ogooué, or COMILOG, is a manganese mining and processing company based in Moanda, Gabon. It is a subsidiary of the French metallurgical group Eramet. The company is the world's second largest producer of manganese ore. At first the ore was carried by a cableway to the border with the Republic of the Congo, then by rail to the sea at Pointe-Noire. In the 1980s a railway was built to carry the ore through Gabon to the sea near Libreville.