Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin infections, typhoid fever, and urinary tract infections, among others. For some infections it is used in addition to other antibiotics. It can be taken by mouth, as eye drops, as ear drops, or intravenously.

Levofloxacin, sold under the brand name Levaquin among others, is an antibiotic medication. It is used to treat a number of bacterial infections including acute bacterial sinusitis, pneumonia, H. pylori, urinary tract infections, chronic prostatitis, and some types of gastroenteritis. Along with other antibiotics it may be used to treat tuberculosis, meningitis, or pelvic inflammatory disease. Use is generally recommended only when other options are not available. It is available by mouth, intravenously, and in eye drop form.

Ofloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. When taken by mouth or injection into a vein, these include pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infections, prostatitis, plague, and certain types of infectious diarrhea. Other uses, along with other medications, include treating multidrug resistant tuberculosis. An eye drop may be used for a superficial bacterial infection of the eye and an ear drop may be used for otitis media when a hole in the ear drum is present.

Xylazine is a structural analog of clonidine and an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist, sold under many trade names worldwide, most notably the Bayer brand name Rompun, as well as Anased, Sedazine and Chanazine.

Norfloxacin, sold under the brand name Noroxin among others, is an antibiotic that belongs to the class of fluoroquinolone antibiotics. It is used to treat urinary tract infections, gynecological infections, inflammation of the prostate gland, gonorrhea and bladder infection. Eye drops were approved for use in children older than one year of age.

Moxifloxacin is an antibiotic, used to treat bacterial infections, including pneumonia, conjunctivitis, endocarditis, tuberculosis, and sinusitis. It can be given by mouth, by injection into a vein, and as an eye drop.

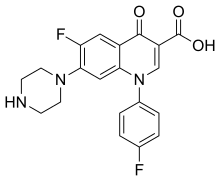
Pefloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. Pefloxacin has not been approved for use in the United States.

Cinoxacin is a quinolone antibiotic that has been discontinued in the U.K. as well the United States, both as a branded drug or a generic. The marketing authorization of cinoxacin has been suspended throughout the EU.

Temafloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic drug which was withdrawn from sale in the United States shortly after its approval in 1992 because of serious adverse effects resulting in three deaths. It is not marketed in Europe.

Flumequine is a synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections. It is a first-generation fluoroquinolone antibacterial that has been removed from clinical use and is no longer being marketed. The marketing authorization of flumequine has been suspended throughout the EU. It kills bacteria by interfering with the enzymes that cause DNA to unwind and duplicate. Flumequine was used in veterinarian medicine for the treatment of enteric infections, as well as to treat cattle, swine, chickens, and fish, but only in a limited number of countries. It was occasionally used in France to treat urinary tract infections under the trade name Apurone. However this was a limited indication because only minimal serum levels were achieved.

Prulifloxacin is an older synthetic antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone class undergoing clinical trials prior to a possible NDA submission to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is a prodrug which is metabolized in the body to the active compound ulifloxacin. It was developed over two decades ago by Nippon Shinyaku Co. and was patented in Japan in 1987 and in the United States in 1989.

Garenoxacin (INN) is a quinolone antibiotic for the treatment of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial infections.
Difloxacin (INN), marketed under the trade name Dicural, is a second-generation, synthetic fluoroquinolone antibiotic used in veterinary medicine. It has broad-spectrum, concentration dependent, bactericidal activity; however, its efficacy is not as good as enrofloxacin or pradofloxacin.

Clinafloxacin is an investigational fluoroquinolone antibiotic. Despite its promising antibiotic activity, the clinical development of clinafloxacin has been hampered by its risk for inducing serious side effects.
Decoquinate is a quinolone coccidiostat used in veterinary medicine.

Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well as in animal husbandry, specifically poultry production.

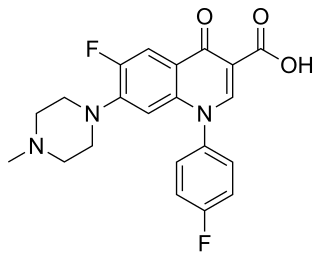
Nemonoxacin is a non-fluorinated quinolone antibiotic undergoing clinical trials. It has the same mechanism of action as fluouroquinolones; it inhibits DNA gyrase, preventing DNA synthesis, gene duplication, and cell division. At the end of 2016, it had reached market in Taiwan, Russia, the Commonwealth Independent States, Turkey, mainland China, and Latin America under the brand name Taigexyn. Nemonoxacin has completed phase 2 trials in the US and has moved on to phase 3 trials. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted nemonoxacin qualified infectious disease product (QIDP) and fast track designations for community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CAP) and acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections (ABSSSI).

Antibiotic use in livestock is the use of antibiotics for any purpose in the husbandry of livestock, which includes treatment when ill (therapeutic), treatment of a group of animals when at least one is diagnosed with clinical infection (metaphylaxis), and preventative treatment (prophylaxis). Antibiotics are an important tool to treat animal as well as human disease, safeguard animal health and welfare, and support food safety. However, used irresponsibly, this may lead to antibiotic resistance which may impact human, animal and environmental health.

Finafloxacin (Xtoro) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. In the United States, it is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat acute otitis externa caused by the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.

Grapiprant is a small molecule drug that belongs in the piprant class. This analgesic and anti-inflammatory drug is primarily used as a pain relief for mild to moderate inflammation related to osteoarthritis in dogs. Grapiprant has been approved by the FDA's Center for Veterinary Medicine and was categorized as a non-cyclooxygenase inhibiting non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) in March 2016.