 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| MedlinePlus | a605016 |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | N/A |
| Protein binding | 76% (trovafloxacin) |
| Metabolism | Quickly hydrolyzed to trovafloxacin |
| Elimination half-life | 9 to 12 hours (trovafloxacin) |
| Excretion | Fecal and renal (trovafloxacin) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
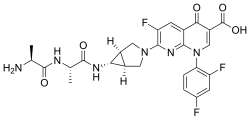
| Formula | C26H25F3N6O5 |
| Molar mass | 558.518 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Alatrofloxacin (Trovan IV) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic developed by Pfizer, delivered as a mesylate salt. [1]
Trovafloxacin and alatrofloxacin were both withdrawn from the U.S. market in June 2006 due to hepatotoxicity leading to liver transplant or death. [2] [3]