 | |
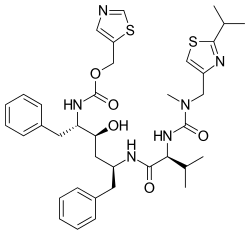 Chemical structures of simnotrelvir (top) and ritonavir (bottom) | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Simnotrelvir | SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitor |
| Ritonavir | Protease inhibitor |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | 先诺欣 (Xiannuoxin) |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | SIM0417, SSD8432 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Drug class | SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitor |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 72.5% [1] |
| Metabolism | hepatic (CYP3A) [1] |
| Elimination half-life | 3.1 h; 4.1 h with ritonavir [1] |
| Excretion | urine (55.4%), feces (36.7%) [1] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H30F3N5O4S2 |
| Molar mass | 549.63 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Simnotrelvir/ritonavir (trade name Xiannuoxin) is a pharmaceutical drug used for the treatment of COVID-19. [2] Simnotrelvir/ritonavir is a combination drug of simnotrelvir, an inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro, and ritonavir, [3] a CYP3A inhibitor.
Contents
It was developed by Simcere Pharmaceutical and conditionally approved in China by the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) in January 2023. [4] Results for the phase Ib trial are available. [5] In a phase II/III trial, it reduced the duration of symptoms by a median of 36 hours compared to placebo. [6]