Related Research Articles

Solar energy is the radiant energy from the Sun's light and heat, which can be harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar electricity, solar thermal energy and solar architecture. It is an essential source of renewable energy, and its technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems, concentrated solar power, and solar water heating to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include designing a building for better daylighting, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light-dispersing properties, and organize spaces that naturally circulate air.
A Trombe wall is a massive equator-facing wall that is painted a dark color in order to absorb thermal energy from incident sunlight and covered with a glass on the outside with an insulating air-gap between the wall and the glaze. A Trombe wall is a passive solar building design strategy that adopts the concept of indirect-gain, where sunlight first strikes a solar energy collection surface in contact with a thermal mass of air. The sunlight absorbed by the mass is converted to thermal energy (heat) and then transferred into the living space.

In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it does not involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices.

A greenhouse is a structure that is designed to regulate the temperature and humidity of the environment inside. There are different types of greenhouses, but they all have large areas covered with transparent materials that let sunlight pass and block it as heat. The most common materials used in modern greenhouses for walls and roofs are rigid plastic made of polycarbonate, plastic film made of polyethylene, or glass panes. When the inside of a greenhouse is exposed to sunlight, the temperature increases, providing a sheltered environment for plants to grow even in cold weather.

Solar thermal energy (STE) is a form of energy and a technology for harnessing solar energy to generate thermal energy for use in industry, and in the residential and commercial sectors. Solar thermal collectors are classified by the United States Energy Information Administration as low-, medium-, or high-temperature collectors. Low-temperature collectors are generally unglazed and used to heat swimming pools or to heat ventilation air. Medium-temperature collectors are also usually flat plates but are used for heating water or air for residential and commercial use.

Solar water heating (SWH) is heating water by sunlight, using a solar thermal collector. A variety of configurations are available at varying cost to provide solutions in different climates and latitudes. SWHs are widely used for residential and some industrial applications.
A solar chimney – often referred to as a thermal chimney – is a way of improving the natural ventilation of buildings by using convection of air heated by passive solar energy. A simple description of a solar chimney is that of a vertical shaft utilizing solar energy to enhance the natural stack ventilation through a building.

A solar thermal collector collects heat by absorbing sunlight. The term "solar collector" commonly refers to a device for solar hot water heating, but may refer to large power generating installations such as solar parabolic troughs and solar towers or non-water heating devices such as solar cookers or solar air heaters.

Passive house is a voluntary standard for energy efficiency in a building that reduces the building's carbon footprint. Conforming to these standards results in ultra-low energy buildings that require less energy for space heating or cooling. A similar standard, MINERGIE-P, is used in Switzerland. Standards are available for residential properties, and several office buildings, schools, kindergartens and a supermarket have also been constructed to the standard. Energy efficiency is not an attachment or supplement to architectural design, but a design process that integrates with architectural design. Although it is generally applied to new buildings, it has also been used for renovations.

A Zero-Energy Building (ZEB), also known as a Net Zero-Energy (NZE) building, is a building with net zero energy consumption, meaning the total amount of energy used by the building on an annual basis is equal to the amount of renewable energy created on the site or in other definitions by renewable energy sources offsite, using technology such as heat pumps, high efficiency windows and insulation, and solar panels.
A solar tracker is a device that orients a payload toward the Sun. Payloads are usually solar panels, parabolic troughs, Fresnel reflectors, lenses, or the mirrors of a heliostat.
Renewable heat is an application of renewable energy referring to the generation of heat from renewable sources; for example, feeding radiators with water warmed by focused solar radiation rather than by a fossil fuel boiler. Renewable heat technologies include renewable biofuels, solar heating, geothermal heating, heat pumps and heat exchangers. Insulation is almost always an important factor in how renewable heating is implemented.
Solar air conditioning, or "solar-powered air conditioning", refers to any air conditioning (cooling) system that uses solar power.
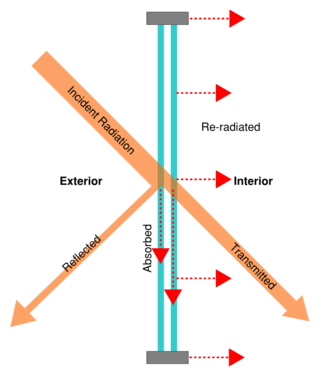
Solar gain is the increase in thermal energy of a space, object or structure as it absorbs incident solar radiation. The amount of solar gain a space experiences is a function of the total incident solar irradiance and of the ability of any intervening material to transmit or resist the radiation.

Solar energy is clean and renewable.

The Solar Umbrella House is a private residence in Venice, Los Angeles, California, remodeled using active and passive solar design strategies to enable the house to function independent of the electrical grid. The design was inspired by Paul Rudolph’s 1953 Umbrella House for Philip Hanson Hiss III's Lido Shores, Sarasota, development. Originally a small 650-square-foot (60 m2) bungalow, the owners added 1,150 sq ft (107 m2) in 2005, remodeling it in such a way that the house is almost 100% energy neutral.

Solar air heating is a solar thermal technology in which the energy from the sun, insolation, is captured by an absorbing medium and used to heat air. Solar air heating is a renewable energy heating technology used to heat or condition air for buildings or process heat applications. It is typically the most cost-effective out of all the solar technologies, especially in commercial and industrial applications, and it addresses the largest usage of building energy in heating climates, which is space heating and industrial process heating.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to solar energy:

The 2016 Proposition 63, titled Firearms and Ammunition Sales, is a California ballot proposition that passed on the November 8, 2016 ballot. It requires a background check and California Department of Justice authorization to purchase ammunition, prohibits possession of high-capacity ammunition magazines over ten rounds, levies fines for failing to report when guns are stolen or lost, establishes procedures for enforcing laws prohibiting firearm possession by specified persons, and requires California Department of Justice's participation in the federal National Instant Criminal Background Check System.

California produces more renewable energy than any other state in the United States except Texas. In 2018, California ranked first in the nation as a producer of electricity from solar, geothermal, and biomass resources and fourth in the nation in conventional hydroelectric power generation. As of 2017, over half of the electricity (52.7%) produced was from renewable sources.
References
- 1 2 "CHAPTER 12. Solar Shade Control [25980 - 25986]", California Legislative Information, State of California, 1978, Division 15. Energy Conservation and Development, retrieved May 16, 2020
- 1 2 Felicity Barringer (April 7, 2008). "Trees Block Solar Panels, and a Feud Ends in Court". The New York Times . Retrieved May 16, 2020.
- ↑ MARLA DICKERSON (November 15, 2008). "Hey, your shade trees are blocking my solar panels". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved May 16, 2020.
- ↑ JEFFREY S. KLEIN (October 2, 1986). "Sun Casts Its Shadow on the Solar Laws". Los Angeles Times . Retrieved May 16, 2020.


