
Solar energy is radiant light and heat from the Sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies such as solar power to generate electricity, solar thermal energy, and solar architecture. It is an essential source of renewable energy, and its technologies are broadly characterized as either passive solar or active solar depending on how they capture and distribute solar energy or convert it into solar power. Active solar techniques include the use of photovoltaic systems, concentrated solar power, and solar water heating to harness the energy. Passive solar techniques include orienting a building to the Sun, selecting materials with favorable thermal mass or light-dispersing properties, and designing spaces that naturally circulate air.

In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it does not involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices.

Daylighting is the practice of placing windows, skylights, other openings, and reflective surfaces so that direct or indirect sunlight can provide effective internal lighting. Particular attention is given to daylighting while designing a building when the aim is to maximize visual comfort or to reduce energy use. Energy savings can be achieved from the reduced use of artificial (electric) lighting or from passive solar heating. Artificial lighting energy use can be reduced by simply installing fewer electric lights where daylight is present or by automatically dimming or switching off electric lights in response to the presence of daylight – a process known as daylight harvesting.

Lighting or illumination is the deliberate use of light to achieve practical or aesthetic effects. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources like lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight. Daylighting is sometimes used as the main source of light during daytime in buildings. This can save energy in place of using artificial lighting, which represents a major component of energy consumption in buildings. Proper lighting can enhance task performance, improve the appearance of an area, or have positive psychological effects on occupants.

A heliostat is a device that includes a mirror, usually a plane mirror, which turns so as to keep reflecting sunlight toward a predetermined target, compensating for the Sun's apparent motions in the sky.

Landscape lighting or garden lighting refers to the use of outdoor illumination of private gardens and public landscapes; for the enhancement and purposes of safety, nighttime aesthetics, accessibility, security, recreation and sports, and social and event uses.

A solar tracker is a device that orients a payload toward the Sun. Payloads are usually solar panels, parabolic troughs, Fresnel reflectors, lenses, or the mirrors of a heliostat.

Light tubes are structures that transmit or distribute natural or artificial light for the purpose of illumination and are examples of optical waveguides.

A fiber-optic cable, also known as an optical-fiber cable, is an assembly similar to an electrical cable but containing one or more optical fibers that are used to carry light. The optical fiber elements are typically individually coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable is used. Different types of cable are used for fiber-optic communication in different applications, for example long-distance telecommunication or providing a high-speed data connection between different parts of a building.
A photovoltaic system, also called a PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and convert sunlight into electricity, a solar inverter to convert the output from direct to alternating current, as well as mounting, cabling, and other electrical accessories to set up a working system. Many utility-scale PV systems use tracking systems that follow the sun's daily path across the sky to generate more electricity than fixed-mounted systems.
Sopogy short for Solar Power Technology was a solar thermal technology supplier founded in 2002 at the Honolulu, Hawaii-based clean technology incubator known as Energy Laboratories. The company began its research on concentrating solar thermal energy to produce solar steam and thermal heat for absorption chillers or industrial process heat. The company has also developed applications that incorporate its solar collectors to generate electricity and desalination. Sopogy's name origin comes from industry key words "So" from solar "po" from power and "gy" from energy and technology. The company has its OEM and IPP sales teams along with research and development located in Honolulu, and in 2006 expanded its manufacturing, C&I and oil and gas sales teams in its Silicon Valley facility. Pacific Business News and Greentech Media reported that the VC-funded micro-concentrator solar power firm was shutting down operations based on statements from its President David Fernandez, however Hitachi Power Systems acquired Sopogy in a private transaction in 2014.

A solar lamp, also known as a solar light or solar lantern, is a lighting system composed of an LED lamp, solar panels, battery, charge controller and there may also be an inverter. The lamp operates on electricity from batteries, charged through the use of a solar photovoltaic panel.

A green museum is a museum that incorporates concepts of sustainability into its operations, programming, and facility. Many green museums use their collections to produce exhibitions, events, classes, and other programming to educate the public about the natural environment. Many, but not all, green museums reside in a building featuring sustainable architecture and technology. Green museums interpret their own sustainable practices and green design to present a model of behavior.
Skyline Solar was a Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) company based in Mountain View, California. The company developed medium-concentration photovoltaic systems to produce electricity for commercial, industrial and utility scale solar markets. The company was founded in 2007 by Bob MacDonald, Bill Keating and Eric Johnson. The operation of the company appears to have ceased in late 2012 and the website is deactivated.

A skylight is a light-permitting structure or window, usually made of transparent or translucent glass, that forms all or part of the roof space of a building for daylighting and ventilation purposes.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to solar energy:
Remote Skylights are optical systems capable of providing natural light to unlit locations. An arrangement of parabolic reflectors and optical fiber cables, transport natural sunlight to areas that would otherwise be dark or be lit artificially.
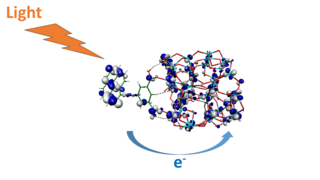
Solar energy conversion describes technologies devoted to the transformation of solar energy to other (useful) forms of energy, including electricity, fuel, and heat. It covers light-harvesting technologies including traditional semiconductor photovoltaic devices (PVs), emerging photovoltaics, solar fuel generation via electrolysis, artificial photosynthesis, and related forms of photocatalysis directed at the generation of energy rich molecules.
There are many practical applications for solar panels or photovoltaics. From the fields of the agricultural industry as a power source for irrigation to its usage in remote health care facilities to refrigerate medical supplies. Other applications include power generation at various scales and attempts to integrate them into homes and public infrastructure. PV modules are used in photovoltaic systems and include a large variety of electrical devices.
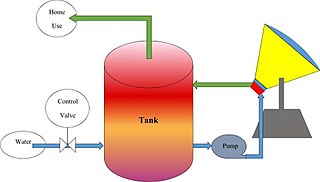
The combination of photovoltaic (PV) technology, solar thermal technology, and reflective or refractive solar concentrators has been a highly appealing option for developers and researchers since the late 1970s and early 1980s. The result is what is known as a concentrated photovoltaic thermal (CPVT) system which is a hybrid combination of concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) and photovoltaic thermal (PVT) systems.
















