
A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a single physical location. It is the most common type of computer network, used in homes and buildings including offices or schools, for sharing data and devices between each other, including Internet access. Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two most common technologies used for local area networks; historical network technologies include ARCNET, Token Ring and LocalTalk.

Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) is an Indian multinational technology company specializing in information technology services and consulting. Headquartered in Mumbai, it is a part of the Tata Group and operates in 150 locations across 46 countries. It is the second-largest Indian company by market capitalization.

A mixed-signal integrated circuit is any integrated circuit that has both analog circuits and digital circuits on a single semiconductor die. Their usage has grown dramatically with the increased use of cell phones, telecommunications, portable electronics, and automobiles with electronics and digital sensors.
The International Federation for Information Processing (IFIP) is a global organisation for researchers and professionals working in the field of computing to conduct research, develop standards and promote information sharing.

Carnegie Mellon Silicon Valley is a degree-granting branch campus of Carnegie Mellon University located in Mountain View, California. It was established in 2002 at the NASA Ames Research Center in Moffett Field.

Faqir Chand Kohli was a co-founder and the first CEO of TCS Tata Consultancy Services, India's largest software services company. He was also associated with other companies within Tata Group, including Tata Power Company and Tata Elxsi, and had been President of Indian Information Technology (IT) services advocacy body NASSCOM. He was a recipient of the Padma Bhushan, India's third-highest civilian honor, in 2002 for his contributions to the Indian software industry. He is referred to as the "Father of the Indian IT Industry", for his contributions to the establishment and growth of the Indian IT industry.

The Centre for Development of Advanced Computing, Thiruvananthapuram (C-DAC[T]) is a branch of the Indian Centre for Development of Advanced Computing based in Thiruvananthapuram.

The University of Technology of Troyes is a French university, in the academy of Reims. The UTT is part of the network of the three universities of technology, found by the University of Technology of Compiègne. Inspired by the American University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, these three universities are a French mixture between the universities of this country and its schools of engineers .UTT is ranked in the top 10 engineering schools 2017 in France by Usine Nouvelle.
TCS BaNCS is a core banking software suite developed by Tata Consultancy Services for use by retail banks.
Almost All Questions Answered or aAQUA is an Indian farmer knowledge exchange available at aaqua.org answering questions from farmers in four languages in any one of 420 districts in India and some places abroad.

Silicon Laboratories, Inc., commonly referred to as Silicon Labs, is a fabless global technology company that designs and manufactures semiconductors, other silicon devices and software, which it sells to electronics design engineers and manufacturers in Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure worldwide.
The Queen's Award for Enterprise: Innovation (Technology) (2001) was awarded on 20 April.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Networking is the Networking Products division of Hewlett Packard Enterprise ("HP"). HPE Networking and its predecessor entities have developed and sold networking products since 1979. Currently, it offers networking and switching products for small and medium sized businesses through its wholly owned subsidiary Aruba Networks. Prior to 2015, the entity within HP which offered networking products was called HP Networking.

Meru Networks was a supplier of wireless local area networks (WLANs) to healthcare, enterprise, hospitality, K-12 education, higher education, and other markets. Founded in 2002 and headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, United States, the company made its initial public offering in March 2010, and was acquired by Fortinet in May 2015.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to computing:

Redpine Signals was a fabless semiconductor company founded in 2001. The company made chipsets and system-level products for wireless networks. It served the Internet of Things and wireless embedded systems market, enabling all volume levels of chipsets and modules.
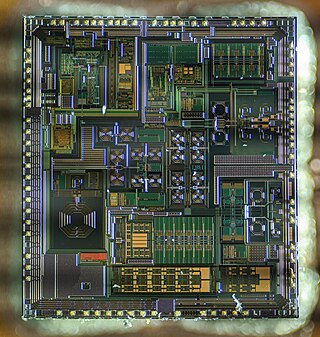
RF CMOS is a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) technology that integrates radio-frequency (RF), analog and digital electronics on a mixed-signal CMOS RF circuit chip. It is widely used in modern wireless telecommunications, such as cellular networks, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS receivers, broadcasting, vehicular communication systems, and the radio transceivers in all modern mobile phones and wireless networking devices. RF CMOS technology was pioneered by Pakistani engineer Asad Ali Abidi at UCLA during the late 1980s to early 1990s, and helped bring about the wireless revolution with the introduction of digital signal processing in wireless communications. The development and design of RF CMOS devices was enabled by van der Ziel's FET RF noise model, which was published in the early 1960s and remained largely forgotten until the 1990s.

K. J. Ray Liu is an American scientist, engineer, educator, and entrepreneur. He is the founder, former Chief Executive Officer, and now Chairman and Chief Technology Officer of Origin Wireless, Inc., which pioneers artificial intelligence analytics for wireless sensing and indoor tracking.












