Djibouti is a country in the Horn of Africa bordered by Somaliland to the east, Eritrea to west and the Red Sea to the north, Ethiopia to the west and south, and the Gulf of Aden to the east.
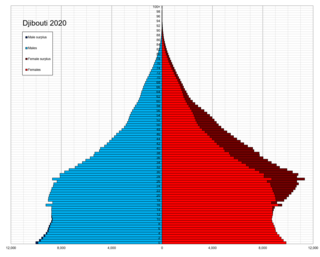
Demographic features of Djibouti include population density, ethnicity, education level, health, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects.

Obock is a small port town in Djibouti. It is located on the northern shore of the Gulf of Tadjoura, where it opens out into the Gulf of Aden. The town is home to an airstrip and has ferries to Djibouti City. The French form Obock derives from Arabic "Oboh", which is a deformation of Oboki, a name given to a local wadi.

Djibouti is the capital of Djibouti. It is located in the coastal Djibouti Region on the Gulf of Tadjoura.

Dikhil is a town in the western Dikhil Region of Djibouti. Lying east of Lake Abbe, It is situated about 122 km (76 mi) southwest of Djibouti City and 12 km (7.5 mi) north of the border with Ethiopia. It serves as the administrative centre of the Dikhil Region, and is home to the Afar and Somali ethnic groups. The town develops gardens and fruit trees.

The Dir is one of the largest and most prominent Somali clans in the Horn of Africa. They are also considered to be the oldest Somali stock to have inhabited the region. Its members inhabit Djibouti, Somalia, Ethiopia, and northeastern Kenya.

Ali Sabieh is the second largest city in Djibouti. It is situated about 98 kilometres Southwest of Djibouti City and 10 km (6 mi) north of the border with Ethiopia. It sprawls on a wide basin surrounded by granitic mountains on all sides. Ali Sabieh mild climate makes it a popular tourist destination for Djiboutians. The famous landmark of Ali Sabieh is located near the city.

Arta is a town in southeastern Djibouti. The center of the Arta Region, it is the country's sixth-largest city. As of 2010, the population was 11,043. Arta is situated on the Mountains of Arta and is famous for its mild climate. It is located some 41 kilometres west of the national capital, Djibouti City.

The Issa is a northern Somali clan, a sub-division of the Dir clan family.

The Djiboutians are the people inhabiting or originating from Djibouti. The country is mainly composed of two ethnic groups, the Somali and the Afar. It has many languages - though Somali and Afar are the most widely spoken ones, Arabic and French serve as the official languages. There is a small Djiboutian diaspora in North America, Europe, and Australia.

Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area of 23,200 km2 (8,958 sq mi).

The Front for the Liberation of the Somali Coast was a nationalist organization, and later a guerrilla group that fought for the independence of Djibouti from France. The Front de Libération de la Côte des Somalis (FLCS) was recognized as a national liberation movement by the Organization of African Unity (OAU), which participated in its financing. FLCS was able to obtain support from Arab countries such as Algeria.

Ali Aref Bourhan is a Djiboutian politician.
The following is a historical events of Addis Ababa, the capital of Ethiopia, including its formation prior to 20th century by chronology.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Cotonou, Benin.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Antananarivo, Madagascar.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso.
Bissau is a city in Guinea-Bissau, a country in West Africa, formerly part of the kingdom of Kaabu and part of the Mali Empire.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Kisangani, Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Djiboutian nationality law is regulated by the Constitution of Djibouti, as amended; the Djiboutian Nationality Code, and its revisions; and various international agreements to which the country is a signatory. These laws determine who is, or is eligible to be, a national of Djibouti. The legal means to acquire nationality, formal legal membership in a nation, differ from the domestic relationship of rights and obligations between a national and the nation, known as citizenship. Djiboutian nationality is typically obtained under the principle of jus soli, i.e. by birth in Djibouti, or jus sanguinis, born abroad to parents with Djiboutian nationality. It can be granted to persons with an affiliation to the country, or to a permanent resident who has lived in the country for a given period of time through naturalization.












