Related Research Articles

The voiced bilabial trill is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the sound is ⟨ʙ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is B\.

Tangut is an extinct language in the Sino-Tibetan language family.
Qiangic is a group of related languages within the Sino-Tibetan language family. They are spoken mainly in Southwest China, including Sichuan, Tibet and Yunnan. Most Qiangic languages are distributed in the prefectures of Ngawa, Garzê, Ya'an and Liangshan in Sichuan with some in Northern Yunnan as well.
The Ersuic languages are a Qiangic language cluster of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Ersu languages are spoken by about 20,000 people in China as reported by Sun (1982). Muya is reported to be related, but it is not known how it fits in.

The Gyalrongic languages constitute a branch of the Qiangic languages of Sino-Tibetan, although some propose that it may be part of a larger Rung languages group, and do not consider it to be particularly closely related to Qiangic, suggesting that similarities between Gyalrongic and Qiangic may be due to areal influence. However, other work suggests that Qiangic as a whole may in fact be paraphyletic, with the only commonalities of the supposed "branch" being shared archaisms and areal features that were encouraged by contact. Jacques & Michaud (2011) propose that Qiangic including Gyalrongic may belong to a larger Burmo-Qiangic group based on some lexical innovations.
Baima is a language spoken by 10,000 Baima people, of Tibetan ethnicity, in north-central Sichuan Province and Gansu Province, China. Baima is passed on from parents to children in Baima villages. It is spoken within the home domain and is not used in any media of mass communication.
Akha is the language spoken by the Akha people of southern China, eastern Burma, northern Laos, and northern Thailand.

Tatsuo Nishida was a professor at Kyoto University. His work encompasses research on a variety of Tibeto-Burman languages, he made great contributions in particular to the deciphering of the Tangut language.
The Nung or Nungish languages are a poorly described family of uncertain affiliation within the Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Yunnan, China and Burma. They include:

The Lolo-Burmese languages of Burma and Southern China form a coherent branch of the Sino-Tibetan family.

Mianning County is a county of Sichuan Province, China. It is under the administration of the Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture.
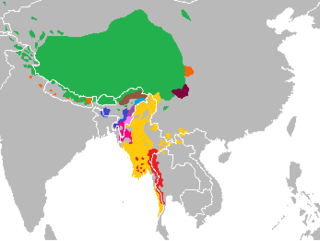
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail.
Yoshio Nishi was a Japanese scholar of Tibeto-Burman linguistics. He first studied linguistics while a student at the International Christian University (Tokyo) under the leadership of Roy Andrew Miller. After the master's coursework at the University of Tokyo and his time studying at Rangoon University, he taught at Kyushu University, Kagoshima University, Ehime University, and Kobe City University of Foreign Studies. In 1996 when the university newly founded the doctoral course at its graduate school, he was the only D-maru-gō professor of linguistics qualified to supervise doctoral students. He is now a professor emeritus at Kobe City University of Foreign Studies, and was nominated in 1993 as a distinguished professor at Central University of Nationalities in Beijing.
Proto-Tibeto-Burman is the reconstructed ancestor of the Tibeto-Burman languages, that is, the Sino-Tibetan languages, except for Chinese. An initial reconstruction was produced by Paul K. Benedict and since refined by James Matisoff. Several other researchers argue that the Tibeto-Burman languages sans Chinese do not constitute a monophyletic group within Sino-Tibetan, and therefore that Proto-Tibeto-Burman was the same language as Proto-Sino-Tibetan.
Guiqiong is a poorly attested Qiangic language of Sichuan and Tibet. There are differences in the phonology of the dialects, but communication is possible. Two or three varieties have low mutual intelligibility with the rest.
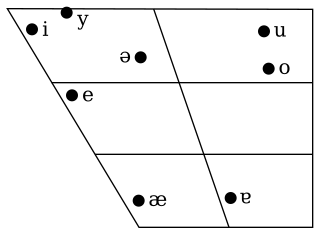
Lizu is a Qiangic language spoken in Western Sichuan, China. There are 4,000 speakers according to Sun (1982) and 7,000 speakers according to Chirkova (2008). Muli, where Lizu is spoken, is a multi-ethnic and multi-lingual county and Lizu has been historically influenced by Mandarin Chinese.
The Ersu language proper is a Sino-Tibetan spoken in western Sichuan, China. It is the most widely spoken of the three Ersu languages. There are 13,000 speakers according to Sun (1982).
The Naic or Naxish languages are a group of Sino-Tibetan languages that include Naxi, Na (Mosuo), Shixing (Xumi), and Namuyi (Namuzi). They have been variously classified as part of the Loloish or the Qiangic branch of Sino-Tibetan.
The Burmo-Qiangic or Eastern Tibeto-Burman languages are a proposed family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Southwest China and Myanmar. It consists of the Lolo-Burmese and Qiangic branches, including the extinct Tangut language.
The Huáyí yìyǔ refers to a series of vocabularies produced by Ming and Qing dynasty Chinese administration for the study of foreign languages. They are a precious source of phonological information, both for the study of Chinese pronunciation and for the study of the languages in question.
References
- 1 2 Yu (2012:1–2)
- ↑ Chirkova, Katia. 2015. A Phonological Sketch of Duoxu.
- ↑ Chirkova, Katia. 2014. The Duoxu Language and the Ersu-Lizu-Duoxu relationship. Linguistics of the Tibeto-Burman Area (37). doi : 10.1075/ltba.37.1.04chi
