
The Cherokee are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern North Carolina, southeastern Tennessee, southwestern Virginia, edges of western South Carolina, northern Georgia and northeastern Alabama.

Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the United States government for the relocation of Native Americans who held original Indian title to their land as a sovereign independent state. The concept of an Indian territory was an outcome of the U.S. federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the U.S. government was one of assimilation.

William Blount was an American politician, landowner and Founding Father who was one of the signers of the Constitution of the United States. He was a member of the North Carolina delegation at the Constitutional Convention of 1787 and led the efforts for North Carolina to ratify the Constitution in 1789 at the Fayetteville Convention. He then served as the only governor of the Southwest Territory and played a leading role in helping the territory gain admission to the union as the state of Tennessee. He was selected as one of Tennessee's initial United States Senators in 1796, serving until he was expelled for treason in 1797.

John Ross was the Principal Chief of the Cherokee Nation from 1828 to 1866; he served longer in that position than any other person. Described as the Moses of his people, Ross influenced the nation through such tumultuous events as the relocation to Indian Territory and the American Civil War.
The Nickajack Expedition in 1794 was a long-running battle fought from late summer to fall between American frontiersmen and the Chickamauga Cherokee. This Cherokee band had resisted the increasing American encroachment into their territory and raided American settlements in the region.

The Treaty of New Echota was a treaty signed on December 29, 1835, in New Echota, Georgia, by officials of the United States government and representatives of a minority Cherokee political faction, the Treaty Party.
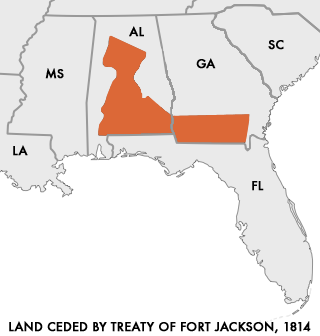
The Treaty of Fort Jackson was signed on August 9, 1814 at Fort Jackson near Wetumpka, Alabama following the defeat of the Red Stick resistance by United States allied forces at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend.

Three agreements, each known as a Treaty of Hopewell, were signed between representatives of the Congress of the United States and the Cherokee, Choctaw, and Chickasaw peoples. They were negotiated and signed at the Hopewell plantation in South Carolina over 45 days during the winter of 1785–86.

The Treaty of Holston was a treaty between the United States government and the Cherokee signed on July 2, 1791, and proclaimed on February 7, 1792. It was negotiated and signed by William Blount, governor of the Southwest Territory and superintendent of Indian affairs for the southern district for the United States, and various representatives of the Cherokee peoples, most notably John Watts. The treaty established terms of relations between the United States and the Cherokee, and established that the Cherokee tribes were to fall under the protection of the United States, with the United States managing all future foreign affairs for all the loosely affiliated Cherokee tribes.

The Cherokee–American wars, also known as the Chickamauga Wars, were a series of raids, campaigns, ambushes, minor skirmishes, and several full-scale frontier battles in the Old Southwest from 1776 to 1794 between the Cherokee and American settlers on the frontier. Most of the events took place in the Upper South region. While the fighting stretched across the entire period, there were extended periods with little or no action.

The Treaty of Fort Clark was signed at Fort Osage on November 10, 1808, in which the Osage Nation ceded all the land east of the fort in Missouri and Arkansas north of the Arkansas River to the United States. The Fort Clark treaty and the Treaty of St. Louis in which the Sac (tribe) and Fox (tribe) ceded northeastern Missouri along with northern Illinois and southern Wisconsin were the first two major treaties in the newly acquired Louisiana Purchase. The affected tribes, upset with the terms, were to side with the British in the War of 1812. Following the settlement of that war, John C. Sullivan for the United States was to survey the ceded land in 1816 (adjusting it 23 miles westward to the mouth of the Kansas River to create the Indian Boundary Line west of which and south of which virtually all tribes were to be removed in the Indian Removal Act in 1830.

The Treaty of Doak's Stand was signed on October 18, 1820 between the United States and the Choctaw Indian tribe. Based on the terms of the accord, the Choctaw agreed to give up approximately one-half of their remaining Choctaw homeland. In October 1820, Andrew Jackson and Thomas Hinds were sent as commissioners who represented the United States to negotiate a treaty to surrender a large portion of Choctaw country in Mississippi. They met with tribal representatives at Doak's Stand on the Natchez Trace. They met with the chiefs Pushmataha, Mushulatubbee, and Apuckshunubbee, who represented the three major regional divisions of the Choctaw. Chiefs of the towns and other prominent men accompanied them, such as Colonel Silas Dinsmoor.

The Tellico Blockhouse was an early American outpost located along the Little Tennessee River in what developed as Vonore, Monroe County, Tennessee. Completed in 1794, the blockhouse was a US military outpost that operated until 1807; the garrison was intended to keep peace between the nearby Overhill Cherokee towns and encroaching early Euro-American pioneers in the area in the wake of the Cherokee–American wars.
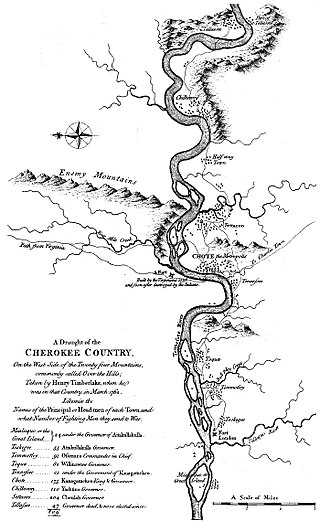
Overhill Cherokee was the term for the Cherokee people located in their historic settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Tennessee in the Southeastern United States, on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. This name was used by 18th-century European traders and explorers from British colonies along the Atlantic coast, as they had to cross the mountains to reach these settlements.

Fort Southwest Point was a federal frontier outpost at what is now Kingston, Tennessee, in the Southeastern United States. Constructed in 1797 and garrisoned by federal soldiers until 1811, the fort served as a major point of interaction between the Cherokee and the United States government as well as a way station for early migrants travelling between Knoxville and Nashville.

The Treaty of Washington City was a treaty signed on January 20, 1825 between the Choctaw and the United States Government.
The Cherokee have participated in over forty treaties in the past three hundred years.

The Cherokee Nation was a legal, autonomous, tribal government in North America recognized from 1794 to 1907. It was often referred to simply as "The Nation" by its inhabitants. The government was effectively disbanded in 1907, after its land rights had been extinguished, prior to the admission of Oklahoma as a state. During the late 20th century, the Cherokee people reorganized, instituting a government with sovereign jurisdiction known as the Cherokee Nation. On July 9, 2020, the United States Supreme Court ruled that the Muscogee (Creek) Nation had never been disestablished in the years before allotment and Oklahoma Statehood.

Silas Dinsmoor was an appointed U. S. Agent to the Cherokee (1794–1798) and to the Choctaw (1801–1813). He later served as a surveyor in Alabama before eventually retiring to Boone County, Kentucky, where he is buried at the Dinsmore Homestead.
The Jacob Brown Grant Deeds, also known more simply as the Nolichucky Grants, were transactions for the sale of land by the Cherokee Nation to Jacob Brown. The transaction occurred at Sycamore Shoals on the Watauga River on March 25, 1775. The Jacob Brown grants were for two large tracts along the Nolichucky River some of which had been previously leased from the Cherokee.

















