| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Virgo |
| Right ascension | 13h 26m 01.9928s [2] |
| Declination | −03° 22′ 43.4299″ [2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 9.46 [3] (9.46 - 10.75 [4] ) |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | F0Ib-G0Ib [4] |
| B−V color index | +0.40 [5] (+0.43 - +0.99 [6] ) |
| Variable type | W Virginis [4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | −65.5 [7] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −3.944±0.094 [2] mas/yr Dec.: 1.027±0.102 [2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.3986 ± 0.0663 mas [2] |
| Distance | approx. 8,000 ly (approx. 2,500 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −3.0 [8] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 0.4 [9] M☉ |
| Radius | 35 [8] (22 - 52 [6] ) R☉ |
| Luminosity | 851 [9] (474 - 1,247 [6] ) L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 0.0 [10] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,280 - 6,550 [6] K |
| Metallicity | −1.0 [10] |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
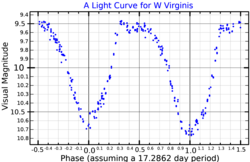
W Virginis is the prototype W Virginis variable, a subclass of the Cepheid variable stars. It is located in the constellation Virgo, and varies between magnitudes 9.46 and 10.75 over a period of approximately 17 days. [4]
There are variations in the light curve apparently due to multiple pulsation periods rather than inherent instabilities in the pulsation. The dominant pulsation mode has a period of 17.27134 days with a period decrease detected over a 75-year period. [12]
The pulsations cause changes in both temperature and size, leading to large changes in the luminosity and brightness. The maximum temperature occurs when the star is at its brightest visually, when the star is also at its smallest. The minimum temperature and maximum radius occur at around phase 0.5 when the brightness is decreasing and nearly at minimum. Because relatively more infrared radiation is produced when the star is cooler, the maximum brightness in the infrared occurs when the visual brightness is already decreasing, and the maximum bolometric luminosity occurs at around phase 0.25 around halfway from maximum to minimum visual brightness. [6]
W Virginis stars are old helium shell burning stars with masses less than the sun. They have supergiant spectral luminosity classes despite their modest masses and actual luminosities, because they are highly inflated evolved stars with very low surface gravities. W Virginis itself is typical, with a mass less than half the sun, pulsating between 20 and 50 times the sun's radius, and a luminosity that varies from less than 500 L☉ to over a thousand L☉.