Longreach is a town and a locality in the Longreach Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Longreach had a population of 2,970 people. It is the administrative centre of the Longreach Regional Council, which was established in 2008 as a merger of the former Longreach, Ilfracombe, and Isisford shires. Longreach is a well known tourist destination due to its aviation history and importance.

The Diamantina River is a major river located in Central West Queensland and the far north of South Australia.

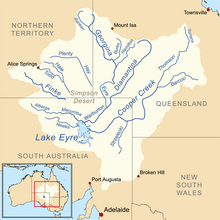
The Lake Eyre basin is a drainage basin that covers just under one-sixth of all Australia. It is the largest endorheic basin in Australia and amongst the largest in the world, covering about 1,200,000 square kilometres (463,323 sq mi), including much of inland Queensland, large portions of South Australia and the Northern Territory, and a part of western New South Wales. The basin is also one of the largest, least-developed arid zone basins with a high degree of variability anywhere. It supports only about 60,000 people and has no major irrigation, diversions or flood-plain developments. Low density grazing that sustains a large amount of wildlife is the major land use, occupying 82% of the total land within the basin. The Lake Eyre basin of precipitation to a great extent geographically overlaps the Great Artesian Basin underneath.

The Cooper Creek is one of the most famous rivers in Australia because it was the site of the death of the explorers Burke and Wills in 1861. It is sometimes known as the Barcoo River from one of its tributaries and is one of three major Queensland river systems that flow into the Lake Eyre basin. The flow of the creek depends on monsoonal rains falling months earlier and many hundreds of kilometres away in eastern Queensland. It is 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) in length.

The Channel Country is a region of outback Australia mostly in the state of Queensland but also in parts of South Australia, Northern Territory and New South Wales. The name comes from the numerous intertwined rivulets that cross the region, which cover 150,000 km². The Channel Country is over the Cooper and Eromanga geological basins and the Lake Eyre Basin drainage basin. Further to the east is the less arid Maranoa district.

Muttaburra is a town and locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Muttaburra had a population of 88 people. The undeveloped town of Scarrbury is within the locality.

The Stanley River is a perennial river located in the South East region of Queensland, Australia. A major tributary of the Brisbane River, the Stanley River valley extends roughly 35 kilometres (22 mi) westwards from the area south of Maleny, through Woodford to Kilcoy before veering southwards.

The Albert River is a perennial river located in the South East region of Queensland, Australia. Its catchment lies within the Gold Coast and Scenic Rim Region local government areas and covers an area of 782 square kilometres (302 sq mi). The river provides potable water for the town of Beaudesert.

The Georgina River is the north-westernmost of the three major rivers of the Channel Country in Central West Queensland, that also flows through a portion of the Northern Territory, in central Australia. Part of the Lake Eyre basin, the Georgina flows in extremely wet years into Lake Eyre.

The Barcaldine Region is a local government area in Central West Queensland, Australia. Established in 2008, it was preceded by three previous local government areas which had existed for over a century.

The Longreach Region is a local government area in Central West Queensland, Australia. Established in 2008, it superseded three previous local government areas that had existed for more than a century.

The Belyando River, including the Belyando River , is a river system located in Central Queensland, Australia. At 1,054 kilometres (655 mi) in length and with a catchment area of 35,000 square kilometres (14,000 sq mi), the Belyando River system is one of the longest rivers in Queensland.

The Alice River in central Queensland, Australia rises on the western slopes of the Great Dividing Range. The river bisects the Shire of Barcaldine, flowing in a south-westerly direction towards Isisford and its confluence with the Barcoo River. The town of Barcaldine is located on the Alice River. The Alice River's tributaries include Jordan Creek and Lagoon Creek. The Alice River is often dry, except after the annual summer rains.

Central West Queensland is a remote region in the Australian state of Queensland which covers 396 650.2 km2. The region lies to the north of South West Queensland and south of the Gulf Country. It has a population of approximately 12,387 people.

The Galilee Basin is a large inland geological basin in the western Queensland region of Australia. The Galilee Basin is part of a larger Carboniferous to Mid-Triassic basin system that contains the Cooper Basin, situated towards the south-west of the Galilee Basin, and the Bowen Basin to the east. The Galilee Basin covers a total area of approximately 247,000 square kilometres (95,000 sq mi). The basin is underlain by the Carboniferous Drummond Basin and overlain by the Cretaceous – Jurassic Eromanga Basin. The Triassic and younger sediments of the Galilee Basin form the basal sequence of the Great Artesian Basin drainage basin.

Bowen Downs Station is a pastoral lease that has operated both as a cattle station and a sheep station.

Cornish Creek is a former rural locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Cornish Creek had a population of 16 people.

The Wilson River, part of the Lake Eyre Basin, is an ephemeral river located in the Channel Country in western Queensland, Australia.
Bangall is a former rural locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Bangall had a population of 4 people.
Sardine is a former rural locality in the Barcaldine Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Sardine had a population of 5 people.