
The Brisbane River is the longest river in South East Queensland, Australia, and flows through the city of Brisbane, before emptying into Moreton Bay on the Coral Sea. John Oxley, the first European to explore the river, named it after the Governor of New South Wales, Sir Thomas Brisbane in 1823. The penal colony of Moreton Bay later adopted the same name, eventually becoming the present city of Brisbane. The river is a tidal estuary and the water is brackish from its mouth through the majority of the Brisbane metropolitan area westward to the Mount Crosby Weir. The river is wide and navigable throughout the Brisbane metropolitan area.

Moreton Bay is a bay located on the eastern coast of Australia 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) from central Brisbane, Queensland. It is one of Queensland's most important coastal resources. The waters of Moreton Bay are a popular destination for recreational anglers and are used by commercial operators who provide seafood to market.

The Logan River is a perennial river in the Scenic Rim, Logan and Gold Coast local government areas of the South East region of Queensland, Australia. The 184-kilometre (114 mi)-long river is one of the dominant waterways in South East Queensland that drains the southern ranges of the Scenic Rim and empties into Moreton Bay after navigating the City of Logan, a major suburban centre located south of Brisbane. The catchment is dominated by urban and agricultural land use. Near the river mouth are mangrove forests and a number of aquaculture farms.

The Shire of Pine Rivers was a local government area about 20 kilometres (12 mi) north of Brisbane in the Moreton Bay region of South East Queensland, Australia. The shire covered an area of 771 square kilometres (297.7 sq mi), and existed as a local government entity from 1888 until 2008, when it amalgamated with councils further north and east to form the Moreton Bay Region.

The Bremer River is a river that is a tributary of the Brisbane River, located in the Scenic Rim and Brisbane regions of South East Queensland, Australia. The 100-kilometre (62 mi)-long Bremer River drains several Scenic Rim valleys in south-east Queensland, including the Fassifern Valley, with its catchment area covering approximately 2,032 square kilometres (785 sq mi). Most valleys within the catchment have extensive river terraces. The Bremer River system is extremely degraded.

The South Pine River is a minor river in South East Queensland, Australia. It rises on the D'Aguilar Range and passes through the Samford Valley in the Moreton Bay Region local government area.

The Oxley Creek is a creek that is a tributary of the Brisbane River, located in suburban Brisbane in the South East region of Queensland, Australia.

The Lockyer Creek is a creek in South East Queensland, Australia. A tributary of the Brisbane River, the creek is a major drainage system in the Lockyer Valley. Rising on the eastern slopes of the Great Dividing Range, the creek flows generally north-easterly for more than 100 kilometres (62 mi) before it reaches its confluence with the Brisbane River north-northeast of Lowood, and downstream from the Wivenhoe Dam. The creek is named after Edmund Lockyer.

The Mary River is a major river system in the South East and Wide Bay–Burnett regions of Queensland, Australia.

Bramble Bay is an embayment of Moreton Bay in South East Queensland, Australia. The Brisway map reference is 12 H5, or see page 91 G19 in Refidex.

The North Pine River is a minor river in South East Queensland, Australia.

The City of Redcliffe is a former local government area in South East Queensland, Australia. In 2008 it was amalgamated with the Shires of Pine Rivers and Caboolture to create Moreton Bay Region. It is in the northern part of the County of Stanley, with a total area of 38.1 km² and a population of 51,174.

The Kedron Brook is a creek that flows through the northern suburbs of Brisbane in the south-east region of Queensland, Australia.

The Moreton Bay Region is a local government area in the north of the Brisbane metropolitan city in South East Queensland, Australia. Established in 2008, it replaced three established local government areas, the City of Redcliffe and the Shires of Pine Rivers and Caboolture.
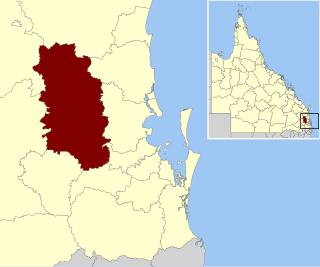
The Somerset Region is a local government area located in the West Moreton region of South East Queensland, Australia, about 100 kilometres (62 mi) northwest of Brisbane and centred on the town of Esk. It was created in 2008 from a merger of the Shire of Esk and the Shire of Kilcoy. It is commonly known as the Brisbane Valley, due to the Brisbane River which courses through the region, although significant parts of the region lie outside the hydrological Brisbane Valley itself.
Lake Manchester Dam is a concrete gravity dam with an un-gated spillway across Cabbage Tree Creek. It is also known as Cabbage Tree Creek Dam. It is in the locality of Lake Manchester, City of Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. The main purpose of the dam is for potable water supply of Brisbane. The impounded reservoir is called Lake Manchester.

Norman Creek is a small tributary of the Brisbane River. The headwaters of the creek are located on the northern slopes of Toohey Mountain and Mount Gravatt in southern Brisbane, Queensland, Australia. The name derives from a corruption of Gorman's Creek, after Lieutenant Gorman, of H. M. 8th Foot - the last commandant at Moreton Bay.
Burpengary Creek is a tidal creek in Moreton Bay Region, Queensland, Australia. It has a total catchment area of 7,960 hectares. It is about 40 kilometres north of Brisbane,

Moodlu is a rural locality in the Moreton Bay Region, Queensland, Australia. In the 2016 census, Moodlu had a population of 318 people.

The Geography of Brisbane is characterised by its coastal location in the south eastern corner of the Queensland state of Australia. It is located precisely halfway up the Australian east coast with longitudinal and latitudinal coordinates of 27.5° south and 153° east. The city resides within the Moreton Bay Floodplain, stretching from Caboolture to the north, Beenleigh to the south and as far as Ipswich to the west whilst being bordered by the Pacific Ocean to the east.




















