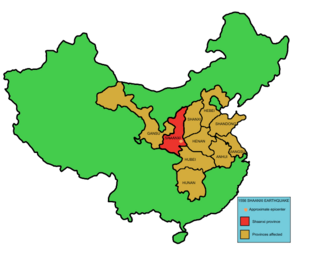
The 1556 Shaanxi earthquake, known in Chinese colloquially by its regnal year as the Jiajing Great Earthquake "嘉靖大地震" or officially by its epicenter as the Hua County Earthquake "华县地震", occurred in the early morning of 23 January 1556 in Huaxian, Shaanxi during the Ming dynasty.

The 2006 Yogyakarta earthquake occurred at with a moment magnitude of 6.4 and a maximum MSK intensity of VIII (Damaging). Several factors led to a disproportionate amount of damage and number of casualties for the size of the shock, with more than 5,700 dead, tens of thousands injured, and financial losses of Rp 29.1 trillion. With limited effects to public infrastructure and lifelines, housing and private businesses bore the majority of damage, and the United States' National Geophysical Data Center classified the total damage from the event as extreme.

An earthquake occurred at on 8 October 2005 in Azad Jammu and Kashmir, a territory under Pakistan. It was centred near the city of Muzaffarabad, and also affected nearby Balakot in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and some areas of Jammu and Kashmir, India. It registered a moment magnitude of 7.6 and had a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (Extreme). The earthquake was also felt in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, India and the Xinjiang region. The severity of the damage caused by the earthquake is attributed to severe upthrust. Over 86,000 people died, a similar number were injured, and millions were displaced. It is considered the deadliest earthquake in South Asia, surpassing the 1935 Quetta earthquake.
The 2003 Bachu earthquake occurred on 24 February at 10:03 local time in the Xinjiang Autonomous Region in northwest China. The epicentre was located near to the town of Jiashi and Bachu County, approximately 105 km east of Kashgar and 310 km west of Aksu.

An earthquake occurred in the province of Sichuan, China at 14:28:01 China Standard Time on May 12, 2008. Measuring at 8.0 , the earthquake's epicenter was located 80 kilometres (50 mi) west-northwest of Chengdu, the provincial capital, with a focal depth of 19 km (12 mi). The earthquake ruptured the fault for over 240 km (150 mi), with surface displacements of several meters. The earthquake was also felt as far away as both Beijing and Shanghai—1,500 and 1,700 km away, respectively—where office buildings swayed with the tremor, as well as Bangkok, Thailand and Hanoi, Vietnam. Strong aftershocks, some exceeding 6 , continued to hit the area up to several months after the main shock, causing further casualties and damage. The earthquake also caused the largest number of geohazards ever recorded, including about 200,000 landslides and more than 800 quake lakes distributed over an area of 110,000 km2 (42,000 sq mi).
The 2003 Bingöl earthquake hit eastern Turkey with a moment magnitude of 6.4 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent) on 1 May at . The epicenter of this strike-slip earthquake was in Bingöl Province, 15 km north of Bingöl. At least 177 people were killed, and 625 buildings collapsed or suffered heavy damage in the affected region. Eighty-four of the fatalities occurred when a dormitory block collapsed in a boarding school in Celtiksuyu.
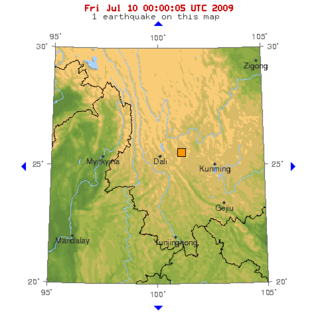
The 2009 Yunnan earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 5.7 in Yao'an County, Yunnan province, People's Republic of China on 9 July. At least one person died and over 300 were injured, with over 50 of these sustaining serious injuries.
The 2011 Yunnan earthquake was a 5.4 magnitude earthquake that occurred on 10 March 2011 at 12:58 CST, with its epicenter in Yingjiang County, Yunnan, People's Republic of China, near the Burmese border. A total of 26 people died and 313 were injured with 133 in serious condition. China's Xinhua reports that up to seven aftershocks, measuring up to a magnitude of 4.7, followed the initial quake, which caused a total of 127,000 people to be evacuated to nearby shelters. It joined over 1,000 other minor tremors that affected the region in the two preceding months. Following damage surveys, officials reported that 1,039 buildings were destroyed and 4,994 more were seriously damaged. The earthquake occurred one day before a much larger earthquake struck Japan that triggered a tsunami.
The 2011 Tarlay earthquake occurred on 24 March in Shan State, Myanmar. The earthquake measured 6.8 and had an epicenter northwest of the border between Myanmar, Thailand and Laos. It occurred in a region accommodating tectonic deformation brought by the collision between the Indo-Australian and Eurasian plates. Strike-slip faulting along the Nan Ma Fault was identified as the cause. There were between 75 and 151 fatalities; including one death in Thailand. An additional 212 people were injured. Hundreds of buildings and some transport infrastructure were damaged in Myanmar and Thailand. In the aftermath of the disaster, the Burmese government provided aid and relief supplies to the affected region. Neighbouring countries China, India and Thailand provided monetary assistance. Several international humanitarian organizations also supported in the relief and recovery.
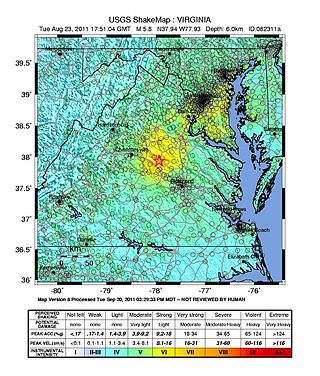
On August 23, 2011, a magnitude 5.8 earthquake hit the Piedmont region of the U.S. state of Virginia at 1:51:04 p.m. EDT. The epicenter, in Louisa County, was 38 mi (61 km) northwest of Richmond and 5 mi (8 km) south-southwest of the town of Mineral. It was an intraplate earthquake with a maximum perceived intensity of VIII (Severe) on the Mercalli intensity scale. Several aftershocks, ranging up to 4.5 in magnitude, occurred after the main tremor.
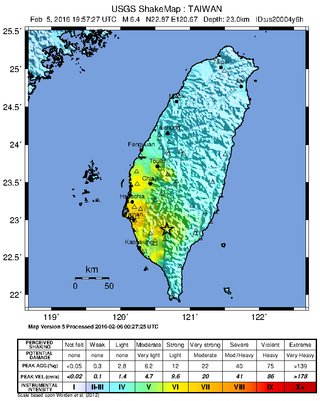
At 03:57 local time on 6 February 2016, an earthquake with a moment magnitude of 6.4 struck 28 km (17 mi) northeast of Pingtung City in southern Taiwan, in the Meinong District of Kaohsiung. The earthquake struck at a depth of around 23 km (14 mi). Its comparatively shallow depth caused more intense reverberations on the surface. The earthquake had a maximum intensity of VII on the Mercalli intensity scale, causing widespread damage and 116 deaths. Almost all of the deaths were caused by a collapsed residential building, named Weiguan Jinlong in Yongkang District, while two other people were killed in Gueiren District. Sixty-eight aftershocks have occurred. The earthquake was the deadliest earthquake in Taiwan since the 1999 Jiji earthquake.
The 1988 Lancang–Gengma earthquakes, also known as the 11.6 earthquakes by the Chinese media were a pair of devastating seismic events that struck Lancang and Gengma counties, Yunnan, near the border with Shan State, Burma. The earthquake measured moment magnitude (Mw ) 7.0 and was followed 13 minutes later by a 6.9 Mw shock. These earthquakes were assigned a maximum China seismic intensity of IX and X, respectively. Between 748 and 939 people were killed; more than 7,700 were injured. Both earthquakes resulted in US$270 million in damage and economic losses. Moderately large aftershocks continued to rock the region, causing additional casualties and damage.
The 1902 Turkestan earthquake devastated Xinjiang, China, near the Kyrgyzstan border. It occurred on August 22, 1902, at 03:00:22 with an epicenter in the Tien Shan mountains. The thrust earthquake measured 7.7 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ) and had a depth of 18 km (11 mi).
The 2020 Kashgar earthquake, also known as the Jiashi earthquake occurred on 19 January 2020 at 21:27:56 China Standard Time in Xinjiang Province, China. According to the United States Geological Survey, the earthquake had a moment magnitude of 6.0 and a surface wave magnitude of 6.4 according to the China Earthquake Network Center. It struck at a shallow depth of 5.6 km according to the USGS while the CENC has the figure at 16 km. Local emergency management agencies said the earthquake damaged more than 1,000 homes and businesses in the nearby populated towns and villages. One person is known to have died while two other children were injured.
The 1995 Menglian earthquake or 1995 Myanmar–China earthquake occurred on 12 July at 05:46:43 local time in the Myanmar–China border region. The earthquake had an epicenter on the Myanmar side of the border, located in the mountainous region of Shan State. It registered 7.3 on the Chinese surface wave magnitude scale (Ms ) and 6.8 on the moment magnitude scale (Mw ). With a maximum Mercalli intensity assigned at VIII, the quake killed eleven people and left another 136 injured. Over 100,000 homes in both countries were destroyed and 42,000 seriously damaged. Some damage to structures were also reported in Chiang Mai and Chiang Rai, Thailand. The low death toll from this earthquake was attributed to an early warning issued prior to it happening. Precursor events including foreshocks and some seismic anomalies led to an evacuation of the area before the mainshock struck. It is thought to be one of the few successfully predicted earthquakes in history.
The 2021 Luxian earthquake was a damaging seismic event occurring in the early hours of September 16 at 04:33 China Standard Time. The surface wave magnitude (Ms ) 6.0 or moment magnitude (Mw ) 5.4 earthquake struck at a shallow depth of 7.5 km and severe shaking in an area of 4,000 square kilometers was assigned a maximum intensity of VIII on the China seismic intensity scale. Three people were killed and 146 injured when the earthquake struck Lu County, Luzhou, Sichuan Province. At least 36,800 buildings were affected, 7,800 of them seriously damaged or completely destroyed, causing about a quarter of a billion dollars worth of damage.

The 1695 Linfen earthquake struck Shanxi Province in North China, Qing dynasty on May 18. Occurring at a shallow depth within the continental crust, the surface-wave magnitude 7.8 earthquake had a maximum intensity of XI on the China seismic intensity scale and Mercalli intensity scale. This devastating earthquake affected over 120 counties across eight provinces of modern-day China. An estimated 52,600 people died in the earthquake, although the death toll may have been 176,365.
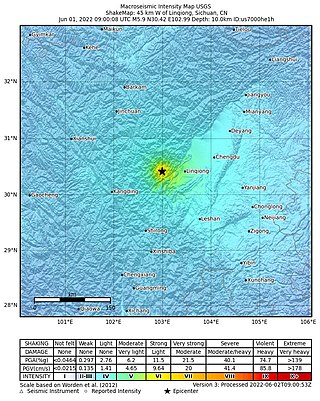
On June 1, 2022, a moment magnitude (Mw ) 5.8 or surface-wave magnitude (Ms ) 6.1 earthquake struck Lushan County in Ya'an, Sichuan Province, China. At least four people were killed and 42 were injured. The earthquake had a maximum intensity of VIII on the China seismic intensity scale, causing damage to many homes and triggering rockslides.

A 6.7 earthquake struck Luding County in Sichuan province, China on 5 September 2022 at 12:52:19 local time. The epicenter was located 226 km (140 mi) from Chengdu, or 43 km (27 mi) southeast of Kangding. Ninety-three people died, 424 were injured and 24 remained missing. More than 13,000 homes and other infrastructure were damaged or destroyed. It was the largest earthquake to strike the province since 2017.
On 23 January 2024, at 02:09 CST, a Ms 7.1 or Mw 7.0 earthquake occurred in Uqturpan County, also known as Wushi County, in Xinjiang, China, near the border with Kyrgyzstan.










