Related Research Articles
(152680) 1998 KJ9 is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. Based on absolute magnitude, it is the third largest asteroid known to have passed closer than the Moon.
(101869) 1999 MM is a sub-kilometer asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It was discovered on 20 June 1999, by the Lowell Observatory Near-Earth-Object Search (LONEOS) at its U.S. Anderson Mesa Station in Flagstaff, Arizona. The first observation was made by Catalina Sky Survey just 8 days before its official discovery.
(456938) 2007 YV56, provisional designation 2007 YV56, is a sub-kilometer asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as a near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 190–360 meters (620–1,200 ft) in diameter. It was discovered on 31 December 2007, by astronomers of the Catalina Sky Survey conducted at the Catalina Station in Arizona, United States.
2013 TX68 is an Apollo asteroid and near-Earth object discovered on 6 October 2013 by the Catalina Sky Survey, during which it was near a close approach of 5.4 Lunar distances (LD) from the Earth. The asteroid only has a 10-day observation arc which makes long-term predictions of its position less certain. It was observed for three days as it approached Earth in the night sky starting with the sixth of October, 2013. Then it became unobservable by being between the Earth and the Sun, then not recovered due to its small size and dimness. Precovery images by Pan-STARRS from 29 September 2013 were announced on 11 February 2016 that extended the observation arc to 10 days. It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 11 February 2016, so there is no risk of impact from this object for the next hundred years or more. The asteroid was last observed on 9 October 2013.
2017 SX17 is a very small asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 6–12 meters (20–40 feet) in diameter. It was first observed by astronomers of the Mount Lemmon Survey at Mount Lemmon Observatory on 29 September 2017, three days prior to its sub-lunar close encounter with Earth at 0.23 lunar distances on 2 October 2017.

2017 OO1 is a small asteroid, classified as near-Earth object of the Aten group, approximately 35–76 meters (115–249 feet) in diameter. It was first observed on 23 July 2017, by the robotic ATLAS survey at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, two days after the object had approached Earth at 0.33 lunar distances on 21 July 2017.

2017 XO2, also written 2017 XO2, is a sub-kilometer asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group approximately 110 meters (360 feet) in diameter. The asteroid was discovered by Pan-STARRS in December 2017, after it already had approached Earth at 0.051 AU (7,600,000 km) or 20 lunar distances (LD) on 6 November 2017. On 26 April 2057, it will pass Earth at a similar distance of 21 LD again.

2018 CN2 is a very small asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 5 to 16 meters in diameter. It was first observed by astronomers of the Mount Lemmon Survey at Mount Lemmon Observatory, Arizona, on 8 February 2018, one day prior its close encounter with Earth at 0.18 lunar distances.

2018 CY2 is an asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, with an estimated diameter of 59–190 metres (190–620 ft). It was first observed on 9 February 2018, by astronomers of the Catalina Sky Survey at Mount Lemmon Observatory, Arizona, during its close approach to Earth.

2018 CF2 is a micro-asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group on an eccentric orbit with has an estimated 4–15 meters (10–50 ft). It was first observed on 7 February 2018, by astronomers of the Mount Lemmon Survey at Mount Lemmon Observatory, Arizona, United States. The discovery occurred the day after its sub-lunar passage as it approached the Earth from a sunward direction, and this flyby altered the asteroid's orbit slightly.

2018 CC is a micro-asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 20 meters (70 ft) in diameter. Its official first observation was made by the Catalina Sky Survey at Mount Lemmon Observatory, Arizona, United States, on 4 February 2018. Two days later, the asteroid crossed the orbit of the Moon and made a very close approach to Earth.

2010 WC9, unofficially designated ZJ99C60, is a sub-kilometer near-Earth asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 100 meters (330 feet) in diameter. First observed for eleven days by the Catalina Sky Survey in 2010, the asteroid was recovered in May 2018 during its sub-lunar close encounter with Earth.
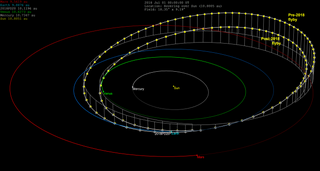
2018 PD20 is a small asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 9–20 meters (30–66 feet) in diameter. On 11 August 2018, it was first observed by ATLAS at the Mauna Loa Observatory on Hawaii (T08), when it passed 33,500 kilometers (20,800 miles) from the Earth. This is notable because it came within a tenth of the lunar distance, or 0.10 LD which is closer to Earth than satellites in a geostationary orbit. These have an altitude of 0.11 LD, about 36,000 km (22,000 mi), approximately 3 times the width of the Earth.
2017 SN16, is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 90 meters (300 feet) in diameter. The object was first observed on 24 September 2017, by cometary discoverer Alex Gibbs with the Mount Lemmon Survey at Mount Lemmon Observatory, Arizona, in the United States. It forms an asteroid pair with 2018 RY7 and is currently trapped in a 3:5 mean motion resonance with Venus.
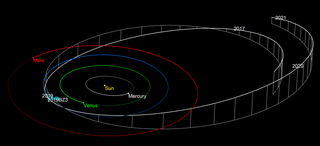
2019 BZ3 is a very small near-Earth asteroid of the Apollo group, approximately 6 meters (20 feet) in diameter. It was first observed by the Mount Lemmon Survey on 28 January 2019, just hours after the asteroid's sub-lunar flyby of Earth at less than 0.12 lunar distance.

(501647) 2014 SD224 is an Aten near-Earth asteroid around 150 meters (490 feet) in diameter. It was discovered on 22 September 2014 when the asteroid was 0.29 AU (43 million km; 110 LD) from Earth and had a solar elongation of 123 degrees. The glare of the Sun had masked the approach of the asteroid as it passed closest approach to Earth on 11 August 2014. The asteroid now has a 6-year observation arc and a well-determined orbit. It also makes close approaches to Venus.

2020 LD is an Apollo near-Earth asteroid roughly 140 meters in diameter. It was discovered on 7 June 2020 when the asteroid was about 0.03 AU from Earth and had a solar elongation of 154 degrees. The glare of the Sun had masked the approach of the asteroid since November 2019. The asteroid passed closest approach to Earth on 5 June 2020 at a distance of 0.002 AU. The close approach distance is now known with an accuracy of roughly ± 1000 km. This is the largest asteroid to pass closer than the Moon this year and possibly the largest since (308635) 2005 YU55 in November 2011. The asteroid makes close approaches to Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. It will be brighter than apparent magnitude 24 until 18 July 2020.
(458732) 2011 MD5 is an Apollo near-Earth asteroid around 1.2 kilometers (0.75 miles) in diameter. It is the largest asteroid known to have passed closer than the Moon. On 17 September 1918 the asteroid passed 0.00234 AU (350 thousand km; 0.91 LD) from Earth with a peak apparent magnitude of around 8.4. The 1918 close approach distance is known with an accuracy of roughly ±120 km. The asteroid had come to opposition (opposite the Sun in the sky) on 9 August 1918 at magnitude 16.
2020 AP1 is an Apollo near-Earth object roughly 5 meters (20 feet) in diameter. On 2 January 2020 it passed 0.00218 AU (326 thousand km; 0.85 LD) from Earth. With a short 1-day observation arc it was roughly expected to pass about 0.01 AU (1.5 million km; 3.9 LD) from Earth on 7 January 2022, but with an uncertainty of ±8 days for the close approach date it could have passed significantly closer or further.
2022 QX4 is a Tunguska event-sized asteroid, classified as a near-Earth object of the Aten group, approximately 40 meters (130 feet) in diameter. It was discovered by ATLAS on 24 August 2022, when it was 0.03 AU (4.5 million km) from Earth. On 4 September 2022 with an observation arc of 8 days, it was listed with a 1-in-109 chance of impacting Earth with a Torino scale of 1 for a virtual impactor on 4 September 2068 00:52 UTC. Five precovery images from August 2013 were published on 11 September 2022 extending the observation arc to 9 years and 2022 QX4 was removed from the Sentry Risk Table. The nominal approach is expected to occur 26 August 2068.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2017 TD6)" (2017-10-19 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- 1 2 "2017 TD6". Minor Planet Center . Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- 1 2 Steve Spaleta (19 October 2017). "Newfound Bus-Size Asteroid Will Zoom Safely By Earth Today". Space.com. Retrieved 25 January 2018.
- ↑ "Asteroid Size Estimator". CNEOS NASA/JPL. Retrieved 25 January 2018.


