Marcus Antonius, commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the autocratic Roman Empire.
Year 43 BC was either a common year starting on Sunday, Monday or Tuesday or a leap year starting on Sunday or Monday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Monday of the Proleptic Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pansa and Hirtius. The denomination 43 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

This article concerns the period 49 BC – 40 BC.

Marcus Junius Brutus was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Servilius Caepio Brutus, which was retained as his legal name. He is often referred to simply as Brutus.

Marcus Aemilius Lepidus was a Roman general and statesman who formed the Second Triumvirate alongside Octavian and Mark Antony during the final years of the Roman Republic. Lepidus had previously been a close ally of Julius Caesar. He was also the last pontifex maximus before the Roman Empire, and (presumably) the last interrex and magister equitum to hold military command.
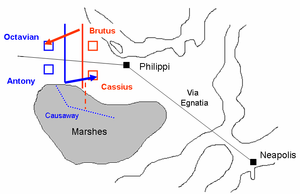
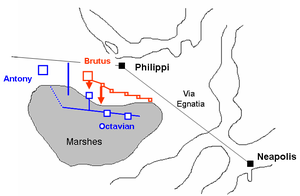
The Battle of Philippi was the final battle in the Liberators' civil war between the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian and the leaders of Julius Caesar's assassination, Brutus and Cassius, in 42 BC, at Philippi in Macedonia. The Second Triumvirate declared the civil war ostensibly to avenge Julius Caesar's assassination in 44 BC, but the underlying cause was a long-brewing conflict between the Optimates and the Populares.

Gaius Cassius Longinus was a Roman senator and general best known as a leading instigator of the plot to assassinate Julius Caesar on 15 March 44 BC. He was the brother-in-law of Brutus, another leader of the conspiracy. He commanded troops with Brutus during the Battle of Philippi against the combined forces of Mark Antony and Octavian, Caesar's former supporters, and committed suicide after being defeated by Mark Antony.

Sextus Pompeius Magnus Pius, also known in English as Sextus Pompey, was a Roman military leader who, throughout his life, upheld the cause of his father, Pompey the Great, against Julius Caesar and his supporters during the last civil wars of the Roman Republic.
Decimus Junius Brutus Albinus was a Roman general and politician of the late republican period and one of the leading instigators of Julius Caesar's assassination. He had previously been an important supporter of Caesar in the Gallic Wars and in the civil war against Pompey. Decimus Brutus is often confused with his distant cousin and fellow conspirator, Marcus Junius Brutus.

Publius Servilius Casca Longus was one of the assassins of Julius Caesar and plebeian tribune in 43 BC. He and several other senators conspired to kill him, a plan which they carried out on 15 March 44 BC. Afterward, Casca fought with the liberators during the Liberators' civil war. He is believed to have died at the Battle of Phillipi either by suicide or at the hands of Octavian's forces.

Gaius Antonius was the second son of Marcus Antonius Creticus and Julia, and thus, younger brother of the Triumvir Mark Antony.

The Battle of Mutina took place on 21 April 43 BC between the forces loyal to the Senate under consuls Gaius Vibius Pansa and Aulus Hirtius, supported by the forces of Caesar Octavian, versus the forces of Mark Antony which were besieging the troops of Decimus Brutus. The latter, one of Caesar's assassins, held the city of Mutina in Cisalpine Gaul.
Junia Tertia, also called Tertulla, was the third daughter of Servilia and her second husband Decimus Junius Silanus, and later the wife of Gaius Cassius Longinus.
Gaius Norbanus Flaccus was a Roman politician and general during the 1st century BC.

The Liberators' civil war was started by the Second Triumvirate to avenge Julius Caesar's assassination. The war was fought by the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian against the forces of Caesar's assassins, led by Marcus Junius Brutus and Gaius Cassius Longinus, referred to as the Liberatores. The latter were defeated by the Triumvirs at the Battle of Philippi in October 42 BC, and committed suicide. Brutus committed suicide after the second part of the battle.

The October Horse is the sixth novel in Colleen McCullough's Masters of Rome series. It was first published in November 2002 by Century in UK and Simon & Schuster in USA.

The Philippics are a series of 14 speeches composed by Cicero in 44 and 43 BC, condemning Mark Antony. Cicero likened these speeches to those of Demosthenes against Philip II of Macedon; both Demosthenes' and Cicero's speeches became known as Philippics. Cicero's Second Philippic is styled after Demosthenes' On the Crown.
Lucius Decidius Saxa was a Roman general in the 1st century BC.
Gaius Cassius Parmensis was a Roman politician and a Latin writer of the late Roman Republic, who belonged to the circle of conspirators against Gaius Julius Caesar.