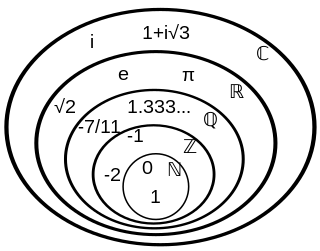
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called numerals; for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the number five. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number. The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any non-negative integer using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called digits. In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels, for ordering, and for codes. In common usage, a numeral is not clearly distinguished from the number that it represents.

Benford's law, also known as the Newcomb–Benford law, the law of anomalous numbers, or the first-digit law, is an observation that in many real-life sets of numerical data, the leading digit is likely to be small. In sets that obey the law, the number 1 appears as the leading significant digit about 30% of the time, while 9 appears as the leading significant digit less than 5% of the time. Uniformly distributed digits would each occur about 11.1% of the time. Benford's law also makes predictions about the distribution of second digits, third digits, digit combinations, and so on.

Subtraction is one of the four arithmetic operations along with addition, multiplication and division. Subtraction is an operation that represents removal of objects from a collection. For example, in the adjacent picture, there are 5 − 2 peaches—meaning 5 peaches with 2 taken away, resulting in a total of 3 peaches. Therefore, the difference of 5 and 2 is 3; that is, 5 − 2 = 3. While primarily associated with natural numbers in arithmetic, subtraction can also represent removing or decreasing physical and abstract quantities using different kinds of objects including negative numbers, fractions, irrational numbers, vectors, decimals, functions, and matrices.
In computer science, subnormal numbers are the subset of denormalized numbers that fill the underflow gap around zero in floating-point arithmetic. Any non-zero number with magnitude smaller than the smallest positive normal number is subnormal, while denormal can also refer to numbers outside that range.
English number words include numerals and various words derived from them, as well as a large number of words borrowed from other languages.
In recreational mathematics, a repunit is a number like 11, 111, or 1111 that contains only the digit 1 — a more specific type of repdigit. The term stands for "repeated unit" and was coined in 1966 by Albert H. Beiler in his book Recreations in the Theory of Numbers.
In mathematics, an automorphic number is a natural number in a given number base whose square "ends" in the same digits as the number itself.
Significant figures, also referred to as significant digits or sig figs, are specific digits within a number written in positional notation that carry both reliability and necessity in conveying a particular quantity. When presenting the outcome of a measurement, if the number of digits exceeds what the measurement instrument can resolve, only the number of digits within the resolution's capability are dependable and therefore considered significant.

A power of two is a number of the form 2n where n is an integer, that is, the result of exponentiation with number two as the base and integer n as the exponent.
142,857 is the natural number following 142,856 and preceding 142,858. It is a Kaprekar number.

In mathematics and computer science, the middle-square method is a method of generating pseudorandom numbers. In practice it is a highly flawed method for many practical purposes, since its period is usually very short and it has some severe weaknesses; repeated enough times, the middle-square method will either begin repeatedly generating the same number or cycle to a previous number in the sequence and loop indefinitely.
In number theory, a self number or Devlali number in a given number base is a natural number that cannot be written as the sum of any other natural number and the individual digits of . 20 is a self number, because no such combination can be found. 21 is not, because it can be written as 15 + 1 + 5 using n = 15. These numbers were first described in 1949 by the Indian mathematician D. R. Kaprekar.
A Lychrel number is a natural number that cannot form a palindrome through the iterative process of repeatedly reversing its digits and adding the resulting numbers. This process is sometimes called the 196-algorithm, after the most famous number associated with the process. In base ten, no Lychrel numbers have been yet proven to exist, but many, including 196, are suspected on heuristic and statistical grounds. The name "Lychrel" was coined by Wade Van Landingham as a rough anagram of "Cheryl", his girlfriend's first name.
100,000 (one hundred thousand) is the natural number following 99,999 and preceding 100,001. In scientific notation, it is written as 105.
In number theory, Kaprekar's routine is an iterative algorithm named after its inventor, Indian mathematician D. R. Kaprekar. Each iteration starts with a number, sorts the digits into descending and ascending order, and calculates the difference between the two new numbers.
In mathematics, the digit sum of a natural number in a given number base is the sum of all its digits. For example, the digit sum of the decimal number would be

Dattatreya Ramchandra Kaprekar was an Indian recreational mathematician who described several classes of natural numbers including the Kaprekar, harshad and self numbers and discovered the Kaprekar's constant, named after him. Despite having no formal postgraduate training and working as a schoolteacher, he published extensively and became well known in recreational mathematics circles.

In mathematics, zero is an even number. In other words, its parity—the quality of an integer being even or odd—is even. This can be easily verified based on the definition of "even": zero is an integer multiple of 2, specifically 0 × 2. As a result, zero shares all the properties that characterize even numbers: for example, 0 is neighbored on both sides by odd numbers, any decimal integer has the same parity as its last digit—so, since 10 is even, 0 will be even, and if y is even then y + x has the same parity as x—indeed, 0 + x and x always have the same parity.
The Kempner series is a modification of the harmonic series, formed by omitting all terms whose denominator expressed in base 10 contains the digit 9. That is, it is the sum
6174 is the natural number following 6173 and preceding 6175.






