A palindromic number is a number that remains the same when its digits are reversed. In other words, it has reflectional symmetry across a vertical axis. The term palindromic is derived from palindrome, which refers to a word whose spelling is unchanged when its letters are reversed. The first 30 palindromic numbers are:
In recreational mathematics, a repunit is a number like 11, 111, or 1111 that contains only the digit 1 — a more specific type of repdigit. The term stands for "repeated unit" and was coined in 1966 by Albert H. Beiler in his book Recreations in the Theory of Numbers.
In recreational mathematics, a repdigit or sometimes monodigit is a natural number composed of repeated instances of the same digit in a positional number system. The word is a portmanteau of "repeated" and "digit". Examples are 11, 666, 4444, and 999999. All repdigits are palindromic numbers and are multiples of repunits. Other well-known repdigits include the repunit primes and in particular the Mersenne primes.
23 (twenty-three) is the natural number following 22 and preceding 24.
61 (sixty-one) is the natural number following 60 and preceding 62.
62 (sixty-two) is the natural number following 61 and preceding 63.
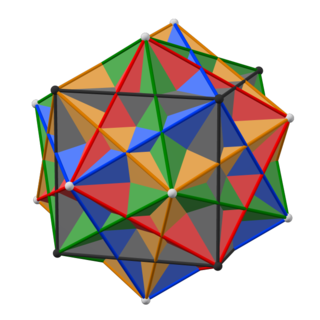
360 is the natural number following 359 and preceding 361.
127 is the natural number following 126 and preceding 128. It is also a prime number.
500 is the natural number following 499 and preceding 501.
2520 is the natural number following 2519 and preceding 2521.
10,000 is the natural number following 9,999 and preceding 10,001.
A Friedman number is an integer, which represented in a given numeral system, is the result of a non-trivial expression using all its own digits in combination with any of the four basic arithmetic operators (+, −, ×, ÷), additive inverses, parentheses, exponentiation, and concatenation. Here, non-trivial means that at least one operation besides concatenation is used. Leading zeros cannot be used, since that would also result in trivial Friedman numbers, such as 024 = 20 + 4. For example, 347 is a Friedman number in the decimal numeral system, since 347 = 73 + 4. The decimal Friedman numbers are:
999 is a natural number following 998 and preceding 1000. It is the largest 3-digit decimal integer.

1,000,000, or one thousand thousand, is the natural number following 999,999 and preceding 1,000,001. The word is derived from the early Italian millione, from mille, "thousand", plus the augmentative suffix -one.

1,000,000,000 is the natural number following 999,999,999 and preceding 1,000,000,001. With a number, "billion" can be abbreviated as b, bil or bn.
An undulating number is a number that has the digit form ABABAB... when in the base 10 number system. It is sometimes restricted to non-trivial undulating numbers which are required to have at least three digits and A ≠ B. The first few such numbers are:
10,000,000 is the natural number following 9,999,999 and preceding 10,000,001.
100,000,000 is the natural number following 99,999,999 and preceding 100,000,001.
In mathematics, a pandigital number is an integer that in a given base has among its significant digits each digit used in the base at least once. For example, 1234567890 is a pandigital number in base 10.
230 is the natural number following 229 and preceding 231.





