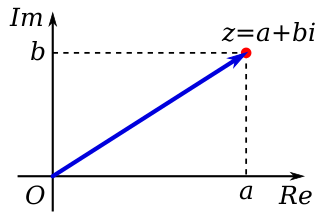
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted i, called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation ; every complex number can be expressed in the form , where a and b are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, i was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number ,a is called the real part, and b is called the imaginary part. The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols or C. Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world.

In mathematics, the Fibonacci sequence is a sequence in which each number is the sum of the two numbers that precede it. Numbers that are part of the Fibonacci sequence are known as Fibonacci numbers, commonly denoted Fn . Many writers begin the sequence with 0 and 1, although some authors start it from 1 and 1 and some from 1 and 2. Starting from 0 and 1, the sequence begins
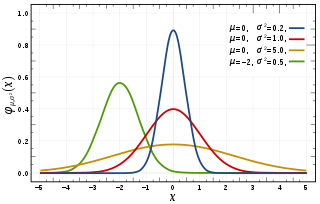
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is The parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution, while the parameter is the variance. The standard deviation of the distribution is (sigma). A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate.
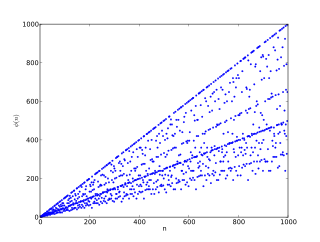
In number theory, Euler's totient function counts the positive integers up to a given integer n that are relatively prime to n. It is written using the Greek letter phi as or , and may also be called Euler's phi function. In other words, it is the number of integers k in the range 1 ≤ k ≤ n for which the greatest common divisor gcd(n, k) is equal to 1. The integers k of this form are sometimes referred to as totatives of n.

In probability theory, a log-normal (or lognormal) distribution is a continuous probability distribution of a random variable whose logarithm is normally distributed. Thus, if the random variable X is log-normally distributed, then Y = ln(X) has a normal distribution. Equivalently, if Y has a normal distribution, then the exponential function of Y, X = exp(Y), has a log-normal distribution. A random variable which is log-normally distributed takes only positive real values. It is a convenient and useful model for measurements in exact and engineering sciences, as well as medicine, economics and other topics (e.g., energies, concentrations, lengths, prices of financial instruments, and other metrics).

In mathematics, the prime-counting function is the function counting the number of prime numbers less than or equal to some real number x. It is denoted by π(x) (unrelated to the number π).

In mathematics, the inverse trigonometric functions are the inverse functions of the trigonometric functions, under suitably restricted domains. Specifically, they are the inverses of the sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant functions, and are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle's trigonometric ratios. Inverse trigonometric functions are widely used in engineering, navigation, physics, and geometry.

The Lucas sequence is an integer sequence named after the mathematician François Édouard Anatole Lucas (1842–1891), who studied both that sequence and the closely related Fibonacci sequence. Individual numbers in the Lucas sequence are known as Lucas numbers. Lucas numbers and Fibonacci numbers form complementary instances of Lucas sequences.

In mathematics, theta functions are special functions of several complex variables. They show up in many topics, including Abelian varieties, moduli spaces, quadratic forms, and solitons. Theta functions are parametrized by points in a tube domain inside a complex Lagrangian Grassmannian, namely the Siegel upper half space.

A hexagonal number is a figurate number. The nth hexagonal number hn is the number of distinct dots in a pattern of dots consisting of the outlines of regular hexagons with sides up to n dots, when the hexagons are overlaid so that they share one vertex.

In mathematics and combinatorics, a centered hexagonal number, or hex number, is a centered figurate number that represents a hexagon with a dot in the center and all other dots surrounding the center dot in a hexagonal lattice. The following figures illustrate this arrangement for the first four centered hexagonal numbers:
In mathematics, an octagonal number is a figurate number that gives the number of points in a certain octagonal arrangement. The octagonal number for n is given by the formula 3n2 − 2n, with n > 0. The first few octagonal numbers are
In mathematics, subadditivity is a property of a function that states, roughly, that evaluating the function for the sum of two elements of the domain always returns something less than or equal to the sum of the function's values at each element. There are numerous examples of subadditive functions in various areas of mathematics, particularly norms and square roots. Additive maps are special cases of subadditive functions.

In mathematics, the plastic ratio is a geometrical proportion close to 53/40. Its true value is the real solution of the equation x3 = x + 1.
In mathematics, the explicit formulae for L-functions are relations between sums over the complex number zeroes of an L-function and sums over prime powers, introduced by Riemann (1859) for the Riemann zeta function. Such explicit formulae have been applied also to questions on bounding the discriminant of an algebraic number field, and the conductor of a number field.
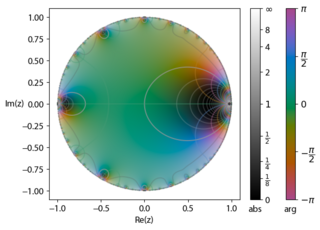
In mathematics, the Euler function is given by

In algebra, the Bring radical or ultraradical of a real number a is the unique real root of the polynomial
The square root of 5 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the prime number 5. It is more precisely called the principal square root of 5, to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property. This number appears in the fractional expression for the golden ratio. It can be denoted in surd form as .

The Rogers–Ramanujan continued fraction is a continued fraction discovered by Rogers (1894) and independently by Srinivasa Ramanujan, and closely related to the Rogers–Ramanujan identities. It can be evaluated explicitly for a broad class of values of its argument.
In mathematics, for a sequence of complex numbers a1, a2, a3, ... the infinite product