
Amicable numbers are two different natural numbers related in such a way that the sum of the proper divisors of each is equal to the other number. That is, s(a)=b and s(b)=a, where s(n)=σ(n)-n is equal to the sum of positive divisors of n except n itself (see also divisor function).

In number theory, a perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its positive proper divisors, that is, divisors excluding the number itself. For instance, 6 has proper divisors 1, 2 and 3, and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6, so 6 is a perfect number. The next perfect number is 28, since 1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14 = 28.

Goldbach's conjecture is one of the oldest and best-known unsolved problems in number theory and all of mathematics. It states that every even natural number greater than 2 is the sum of two prime numbers.

In mathematics, a square number or perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 9 is a square number, since it equals 32 and can be written as 3 × 3.

In number theory, the partition functionp(n) represents the number of possible partitions of a non-negative integer n. For instance, p(4) = 5 because the integer 4 has the five partitions 1 + 1 + 1 + 1, 1 + 1 + 2, 1 + 3, 2 + 2, and 4.

In mathematics, a multiply perfect number is a generalization of a perfect number.
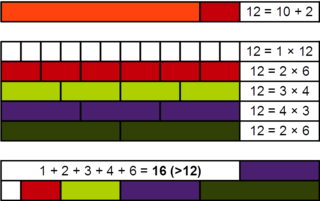
In number theory, an abundant number or excessive number is a positive integer for which the sum of its proper divisors is greater than the number. The integer 12 is the first abundant number. Its proper divisors are 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6 for a total of 16. The amount by which the sum exceeds the number is the abundance. The number 12 has an abundance of 4, for example.

In mathematics, an almost perfect number (sometimes also called slightly defective or least deficientnumber) is a natural number n such that the sum of all divisors of n (the sum-of-divisors function σ(n)) is equal to 2n − 1, the sum of all proper divisors of n, s(n) = σ(n) − n, then being equal to n − 1. The only known almost perfect numbers are powers of 2 with non-negative exponents (sequence A000079 in the OEIS). Therefore the only known odd almost perfect number is 20 = 1, and the only known even almost perfect numbers are those of the form 2k for some positive integer k; however, it has not been shown that all almost perfect numbers are of this form. It is known that an odd almost perfect number greater than 1 would have at least six prime factors.

An Egyptian fraction is a finite sum of distinct unit fractions, such as That is, each fraction in the expression has a numerator equal to 1 and a denominator that is a positive integer, and all the denominators differ from each other. The value of an expression of this type is a positive rational number ; for instance the Egyptian fraction above sums to . Every positive rational number can be represented by an Egyptian fraction. Sums of this type, and similar sums also including and as summands, were used as a serious notation for rational numbers by the ancient Egyptians, and continued to be used by other civilizations into medieval times. In modern mathematical notation, Egyptian fractions have been superseded by vulgar fractions and decimal notation. However, Egyptian fractions continue to be an object of study in modern number theory and recreational mathematics, as well as in modern historical studies of ancient mathematics.
1000 or one thousand is the natural number following 999 and preceding 1001. In most English-speaking countries, it can be written with or without a comma or sometimes a period separating the thousands digit: 1,000.

A powerful number is a positive integer m such that for every prime number p dividing m, p2 also divides m. Equivalently, a powerful number is the product of a square and a cube, that is, a number m of the form m = a2b3, where a and b are positive integers. Powerful numbers are also known as squareful, square-full, or 2-full. Paul Erdős and George Szekeres studied such numbers and Solomon W. Golomb named such numbers powerful.
In mathematics, an untouchable number is a positive integer that cannot be expressed as the sum of all the proper divisors of any positive integer. That is, these numbers are not in the image of the aliquot sum function. Their study goes back at least to Abu Mansur al-Baghdadi, who observed that both 2 and 5 are untouchable.

In number theory, a practical number or panarithmic number is a positive integer such that all smaller positive integers can be represented as sums of distinct divisors of . For example, 12 is a practical number because all the numbers from 1 to 11 can be expressed as sums of its divisors 1, 2, 3, 4, and 6: as well as these divisors themselves, we have 5 = 3 + 2, 7 = 6 + 1, 8 = 6 + 2, 9 = 6 + 3, 10 = 6 + 3 + 1, and 11 = 6 + 3 + 2.
In number theory, a positive integer k is said to be an Erdős–Woods number if it has the following property: there exists a positive integer a such that in the sequence (a, a + 1, …, a + k) of consecutive integers, each of the elements has a non-trivial common factor with one of the endpoints. In other words, k is an Erdős–Woods number if there exists a positive integer a such that for each integer i between 0 and k, at least one of the greatest common divisors gcd(a, a + i) or gcd(a + i, a + k) is greater than 1.
In number theory and enumerative combinatorics, the ordered Bell numbers or Fubini numbers count the weak orderings on a set of elements. Weak orderings arrange their elements into a sequence allowing ties, such as might arise as the outcome of a horse race.

In number theory, the Calkin–Wilf tree is a tree in which the vertices correspond one-to-one to the positive rational numbers. The tree is rooted at the number 1, and any rational number expressed in simplest terms as the fraction a/b has as its two children the numbers a/a + b and a + b/b. Every positive rational number appears exactly once in the tree. It is named after Neil Calkin and Herbert Wilf, but appears in other works including Kepler's Harmonices Mundi.

In number theory, the Moser–de Bruijn sequence is an integer sequence named after Leo Moser and Nicolaas Govert de Bruijn, consisting of the sums of distinct powers of 4. Equivalently, they are the numbers whose binary representations are nonzero only in even positions.
In mathematics, the fibbinary numbers are the numbers whose binary representation does not contain two consecutive ones. That is, they are sums of distinct and non-consecutive powers of two.
1105 is the natural number following 1104 and preceding 1106.




















