Pope Stephen II was born a Roman aristocrat and member of the Orsini family. Stephen was the bishop of Rome from 26 March 752 to his death. Stephen II marks the historical delineation between the Byzantine Papacy and the Frankish Papacy. During Stephen's pontificate, Rome was facing invasion by the Lombards when Stephen II went to Paris to seek assistance from Pepin the Short. Pepin defeated the Lombards and made a gift of land to the pope, eventually leading to the establishment of the Papal States.

Pope Zachary was the bishop of Rome from 28 November 741 to his death in March 752. He was the last pope of the Byzantine Papacy. Zachary built the original church of Santa Maria sopra Minerva, forbade the traffic of slaves in Rome, negotiated peace with the Lombards, and sanctioned Pepin the Short's usurpation of the Frankish throne from Childeric III. Zachary is regarded as a capable administrator and a skillful and subtle diplomat in a dangerous time.
The 760s decade ran from January 1, 760, to December 31, 769.
The 750s decade ran from January 1, 750, to December 31, 759.
The 740s decade ran from January 1, 740, to December 31, 749.

Year 742 (DCCXLII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar, the 742nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 742nd year of the 1st millennium, the 42nd year of the 8th century, and the 3rd year of the 740s decade. The denomination 742 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 757 (DCCLVII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 757 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 754 (DCCLIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 754th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 754th year of the 1st millennium, the 54th year of the 8th century, and the 5th year of the 750s decade. The denomination 754 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 741 (DCCXLI) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 741 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 635 (DCXXXV) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 635 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 740 (DCCXL) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar, the 740th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 740th year of the 1st millennium, the 40th year of the 8th century, and the 1st year of the 740s decade. The denomination 740 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
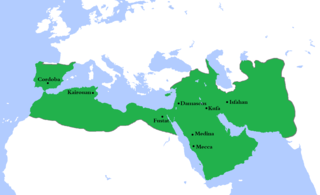
Year 744 (DCCXLIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 744 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 751 (DCCLI) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 751 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 756 (DCCLVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 756th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 756th year of the 1st millennium, the 56th year of the 8th century, and the 7th year of the 750s decade. The denomination 756 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 770 (DCCLXX) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 770 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
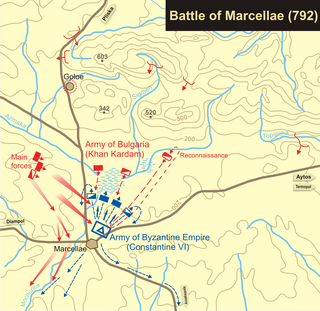
Year 792 (DCCXCII) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar, the 792nd year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 792nd year of the 1st millennium, the 92nd year of the 8th century, and the 3rd year of the 790s decade. The denomination 792 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 715 (DCCXV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 715 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 687 (DCLXXXVII) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 687 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

700 (DCC) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar, the 700th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 700th year of the 1st millennium, the 100th and last year of the 7th century, and the 1st year of the 700s decade. As of the start of 700, the Gregorian calendar was 3 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which was the dominant calendar of the time.

The siege of Narbonne took place in France between 752 and 759, led by the Frankish king Pepin the Short against the Umayyad stronghold defended by an garrison of Arab and Berber Muslim troops who had invaded Septimania and occupied the Visigothic Kingdom and its Gallo-Roman inhabitants since 719. The siege remained as a key battlefield in the context of the Carolingian expedition south to Provence and Septimania starting in 752.
















