Related Research Articles

A tokamak is a device which uses a powerful magnetic field to confine plasma in the shape of a torus. The tokamak is one of several types of magnetic confinement devices being developed to produce controlled thermonuclear fusion power. As of 2016, it was the leading candidate for a practical fusion reactor. The word "tokamak" is derived from a Russian acronym meaning "toroidal chamber with magnetic coils".

A reversed-field pinch (RFP) is a device used to produce and contain near-thermonuclear plasmas. It is a toroidal pinch which uses a unique magnetic field configuration as a scheme to magnetically confine a plasma, primarily to study magnetic confinement fusion. Its magnetic geometry is somewhat different from that of the more common tokamak. As one moves out radially, the portion of the magnetic field pointing toroidally reverses its direction, giving rise to the term reversed field. This configuration can be sustained with comparatively lower fields than that of a tokamak of similar power density. One of the disadvantages of this configuration is that it tends to be more susceptible to non-linear effects and turbulence. This makes it a useful system for studying non-ideal (resistive) magnetohydrodynamics. RFPs are also used in studying astrophysical plasmas, which share many common features.
JT-60 is a large research tokamak, the flagship of Japan's magnetic fusion program, previously run by the Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute (JAERI) and currently run by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency's (JAEA) Naka Fusion Institute in Ibaraki Prefecture. It is properly an advanced tokamak, including a D-shaped plasma cross-section and active feedback control.

The T-15 is a Russian nuclear fusion research reactor located at the Kurchatov Institute, which is based on the (Soviet-invented) tokamak design. It was the first industrial prototype fusion reactor to use superconducting magnets to control the plasma. These enormous superconducting magnets confined the plasma the reactor produced, but failed to sustain it for more than just a few seconds. Despite not being immediately applicable, this new technological advancement proved to the USSR that they were on the right path. In the original shape, a toroidal chamber design, it had a major radius of 2.43 m and minor radius 0.7 m.

Magnetic confinement fusion (MCF) is an approach to generate thermonuclear fusion power that uses magnetic fields to confine fusion fuel in the form of a plasma. Magnetic confinement is one of two major branches of controlled fusion research, along with inertial confinement fusion.
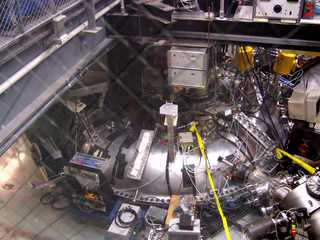
The Madison Symmetric Torus (MST) is a reversed field pinch (RFP) physics experiment with applications to both fusion energy research and astrophysical plasmas.

Alcator C-Mod was a tokamak that operated between 1991 and 2016 at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Plasma Science and Fusion Center (PSFC). Notable for its high toroidal magnetic field, Alcator C-Mod holds the world record for volume averaged plasma pressure in a magnetically confined fusion device. Until its shutdown in 2016, it was one of the major fusion research facilities in the United States.

The National Spherical Torus Experiment (NSTX) is a magnetic fusion device based on the spherical tokamak concept. It was constructed by the Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) in collaboration with the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Columbia University, and the University of Washington at Seattle. It entered service in 1999. In 2012 it was shut down as part of an upgrade program and became NSTX-U, for Upgrade.

The KSTAR is a magnetic fusion device at the Korea Institute of Fusion Energy in Daejeon, South Korea. It is intended to study aspects of magnetic fusion energy that will be pertinent to the ITER fusion project as part of that country's contribution to the ITER effort. The project was approved in 1995, but construction was delayed by the East Asian financial crisis, which weakened the South Korean economy considerably; however, the project's construction phase was completed on September 14, 2007. The first plasma was achieved in June 2008.
The Enormous Toroidal Plasma Device (ETPD) is an experimental physics device housed at the Basic Plasma Science Facility at University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA). It previously operated as the Electric Tokamak (ET) between 1999 and 2006 and was noted for being the world's largest tokamak before being decommissioned due to the lack of support and funding. The machine was renamed to ETPD in 2009. At present, the machine is undergoing upgrades to be re-purposed into a general laboratory for experimental plasma physics research.

ASDEX Upgrade is a divertor tokamak at the Max-Planck-Institut für Plasmaphysik, Garching that went into operation in 1991. At present, it is Germany's second largest fusion experiment after stellarator Wendelstein 7-X.


The Helically Symmetric Experiment, is an experimental plasma confinement device at the University of Wisconsin–Madison, with design principles that are intended to be incorporated into a fusion reactor. The HSX is a modular coil stellarator which is a toroid-shaped pressure vessel with external electromagnets which generate a magnetic field for the purpose of containing a plasma. It began operation in 1999.

The Pegasus Toroidal Experiment is a plasma confinement experiment relevant to fusion power production, run by the Department of Engineering Physics of the University of Wisconsin–Madison. It is a spherical tokamak, a very low-aspect-ratio version of the tokamak configuration, i.e. the minor radius of the torus is comparable to the major radius.
SST-1 is a plasma confinement experimental device in the Institute for Plasma Research (IPR), an autonomous research institute under Department of Atomic Energy, India. It belongs to a new generation of tokamaks with the major objective being steady state operation of an advanced configuration plasma. It has been designed as a medium-sized tokamak with superconducting magnets.
The ISTTOK Tokamak is a research fusion reactor (tokamak) of the Instituto Superior Técnico. It has a circular cross-section due to a poloidal graphite limiter and an iron core transformer. Its particularity is that it is one of the few tokamaks operating in AC regime, as well in DC regime. In 2013, the AC operation allowed the standard discharges to extend from 35 ms to more than 1s.
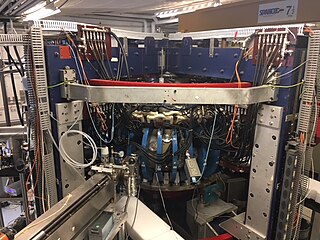
The Hybrid Illinois Device for Research and Applications (HIDRA) is a medium-sized toroidal magnetic fusion device housed in the Nuclear Radiation Laboratory and operated by the Center for Plasma-Material Interactions (CPMI) within the Department of Nuclear, Plasma and Radiological Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign, United States. HIDRA had its first plasma at the end of April 2016 and started experimental campaigns by December of that year. HIDRA is the former WEGA classical stellarator that was operated at the Max Planck Institute for Plasma Physics in Greifswald Germany from 2001 to 2013.

The Compact Toroidal Hybrid (CTH) is an experimental device at Auburn University that uses magnetic fields to confine high-temperature plasmas. CTH is a torsatron type of stellarator with an external, continuously wound helical coil that generates the bulk of the magnetic field for containing a plasma.

The Tokamak Chauffage Alfvén Brésilien (TCABR) is a tokamak situated at the University of Sao Paulo (USP), Brazil. TCABR is the largest tokamak in the southern hemisphere and one of the magnetic-confinement devices committed to advancing scientific knowledge in fusion power.
References
- ↑ "The Indian programme". Frontline. 2006-01-26. Retrieved 2023-10-22.
- ↑ Jha, Saurav (2022-04-21). "India's activities in nuclear fusion". Nuclear Engineering International. Retrieved 2023-10-22.
- ↑ World Survey of Fusion Devices 2022. Vienna: IAEA. 2022. p. 37. ISBN 9789201431226.