
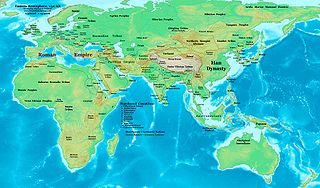
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 through AD 100 (C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the 1st century AD or 1st century CE to distinguish it from the 1st century BC which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. The Roman Empire, Han China and the Parthian Persia were the most powerful and hegemonic states.
The 50s decade ran from January 1, 50, to December 31, 59. It was the sixth decade in the Anno Domini/Common Era, if the nine-year period from 1 AD to 9 AD is considered as a "decade".

The 60s decade ran from January 1, AD 60, to December 31, AD 69.

The 70s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 70, to December 31, AD 79.

The 80s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 80, to December 31, AD 89.

The 90s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 90, to December 31, AD 99.

The 100s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 100, to December 31, AD 109.

The 110s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 110, to December 31, AD 119.

The 120s was a decade that ran from January 1, AD 120, to December 31, AD 129.
AD 18 (XVIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Caesar. The denomination AD 18 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 0s BC were the period between 9 BC and 1 BC, the last nine years of the before Christ era. It is one of two "0-to-9" decade-like timespans that contain nine years, along with the 0s.
Year 101 (CI) was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Traianus and Paetus. The denomination 101 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 160s decade ran from January 1, 160, to December 31, 169.
Year 113 (CXIII) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Celsus and Crispinus. The denomination 113 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 115 (CXV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Vergilianus. The denomination 115 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 100 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marius and Flaccus and the First Year of Tianhan. The denomination 100 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 165 (CLXV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Orfitus and Pudens. The denomination 165 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
80s BC is the time period from 89 BC – 80 BC.
Year 190 (CXC) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Sura. The denomination 190 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Parthian Empire, also known as the Arsacid Empire, was a major Iranian political and cultural power centered in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conquering the region of Parthia in Iran's northeast, then a satrapy (province) under Andragoras, who was rebelling against the Seleucid Empire. Mithridates I greatly expanded the empire by seizing Media and Mesopotamia from the Seleucids. At its height, the Parthian Empire stretched from the northern reaches of the Euphrates, in what is now central-eastern Turkey, to present-day Afghanistan and western Pakistan. The empire, located on the Silk Road trade route between the Roman Empire in the Mediterranean Basin and the Han dynasty of China, became a center of trade and commerce.












