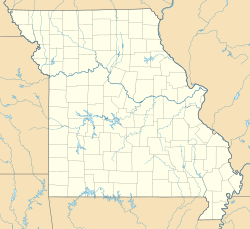
Arrow Rock is a village in Saline County, Missouri, United States, located near the Missouri River. The entire village is part of the National Historic Landmark Arrow Rock Historic District, designated by the Department of the Interior, National Park Service in 1963. It is significant in the history of Westward Expansion, the Santa Fe Trail, and 19th-century artist George Caleb Bingham. The town is well known for the Arrow Rock Lyceum Theatre, hosting over 33,000 patrons every year.

George Caleb Bingham was an American artist, soldier and politician known in his lifetime as "the Missouri Artist". Initially a Whig, he was elected as a delegate to the Missouri legislature before the American Civil War where he fought against the extension of slavery westward. During that war, although born in Virginia, Bingham was dedicated to the Union cause and became captain of a volunteer company which helped keep the state from joining the Confederacy, and then served four years as Missouri's Treasurer. During his final years, Bingham held several offices in Kansas City, while also serving as Missouri's Adjutant General. His paintings of American frontier life along the Missouri River exemplify the Luminist style.

Nicodemus National Historic Site, located in Nicodemus, Kansas, United States, preserves, protects and interprets the only remaining western town established by African Americans during the Reconstruction Period following the American Civil War. The town of Nicodemus is symbolic of the pioneer spirit of African Americans who dared to leave the only region they had been familiar with to seek personal freedom and the opportunity to develop their talents and capabilities. The site was named, at least in part, for a legendary African-American slave featured in abolitionist Henry Clay Work's "Wake, Nicodemus (1864)." It is a mystical story of an old slave died away and buried in a hollow tree who had asked to be awakened on the Day of Jubilee.

Fredericksburg and Spotsylvania National Military Park is a unit of the National Park Service in Fredericksburg, Virginia, and elsewhere in Spotsylvania County, commemorating four major battles in the American Civil War: Fredericksburg, Chancellorsville, The Wilderness, and Spotsylvania.

Arrow Rock State Historic Site is an open-air museum encompassing a geographic formation and a portion of the village of Arrow Rock, Missouri. The park is part of the Arrow Rock Historic District, a National Historic Landmark, and commemorates the history of the area as a key stop on the Santa Fe Trail.

The Rabideau CCC Camp was a Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) camp in the Chippewa National Forest in northern Minnesota, United States. It is located off Beltrami County Highway 39, in Taylor Township, and is one of the best-preserved of the nation's many CCC camps. A National Historic Landmark, it now serves as an educational center.

Litchfield Historic District, in Litchfield, Connecticut, is a National Historic Landmark District designated in 1968 as a notable and well-preserved example of a typical late 18th century New England village. As a National Historic Landmark, it is listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP). It is the core area of a larger NRHP-listed historic district that includes the entire borough of Litchfield and was designated a state historic district in 1959.

Borough House Plantation, also known as Borough House, Hillcrest Plantation and Anderson Place, is an historic plantation on South Carolina Highway 261, 0.8 miles (1.3 km) north of its intersection with U.S. Route 76/US Route 378 in Stateburg, in the High Hills of Santee near Sumter, South Carolina. A National Historic Landmark, the plantation is noted as the largest assemblage of high-style pisé structures in the United States. The main house and six buildings on the plantation were built using this technique, beginning in 1821. The plantation is also notable as the home of Confederate Army General Richard H. Anderson.

San Juan Bautista State Historic Park is a California state park encompassing the historic center of San Juan Bautista, California, United States. It preserves a significant concentration of buildings dating to California's period of Spanish and Mexican control. It includes the Plaza Hotel, the José Castro House, and several other buildings facing the historic plaza. It became a state park in 1933.

Chestertown Historic District is a historic district in Chestertown, Maryland. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places and designated a National Historic Landmark in 1970, and its area was increased in 1984. The town on the Chester River, became the chief port for tobacco and wheat on the Eastern Shore of Maryland between 1750 and 1790. The port declined thereafter, as Baltimore became the major port for such activity. In consequence, Chestertown acquired a collection of more than fifty Georgian style town houses. The 18th-century residential area survived without harm a 1910 fire that destroyed the central business district of Chestertown.

The George Caleb Bingham House is a historic house, part of Arrow Rock State Historic Site in Arrow Rock, Missouri, United States. Built in 1837, it was the principal residence of portraitist and landscape painter George Caleb Bingham (1811–79) from 1837 to 1845. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1965.

The Geraldine Lucas–Fabian Place Historic District in Jackson Hole, Wyoming is significant as the 1913 home of Geraldine Lucas, a single woman pioneer in a harsh environment. It later became the home of Harold Fabian, vice president of the Snake River Land Company, which assembled much of the land that became Jackson Hole National Monument for John D. Rockefeller Jr.

Gen. John J. Pershing Boyhood Home State Historic Site in Laclede, Missouri, is maintained by the Missouri Department of Natural Resources as a state historic site. General John Joseph "Jack" Pershing led the American Expeditionary Forces in World War I and attained the rank of General of the Armies. Pershing was born on a farm outside Laclede, but lived in the home from age six to adulthood. The historic site preserves and interprets the boyhood home and the one-room Prairie Mound School at which he taught for a year before attending West Point Military Academy. The home has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places since 1969, and was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1976.

Mill City Museum is located in the ruins of the Washburn "A" Mill next to Mill Ruins Park on the banks of the Mississippi River in Minneapolis. The museum, an entity of the Minnesota Historical Society that opened in 2003, focuses on the founding and growth of Minneapolis, especially flour milling and the other industries that used hydropower from Saint Anthony Falls. The mill complex that the museum is within, dates from the 1870s and is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. It is also part of the St. Anthony Falls Historic District and within the Mississippi National River and Recreation Area.

Wheeling Island Historic District is a national historic district located on Wheeling Island in Wheeling, Ohio County, West Virginia. The district includes 1,110 contributing buildings, 5 contributing sites, 2 contributing structures, and 3 contributing objects. It is a largely residential district consisting of two-story, frame detached dwellings built in the mid- to late-19th and early-20th century, including the Irwin-Brues House (1853) and a number of houses on Zane Street. The houses are representative of a number of popular architectural styles including Bungalow, Italianate, Queen Anne, and Colonial Revival. Notable non-residential contributing properties include the Exposition Building (1924), Thompson United Methodist Church (1913-1915), Madison School (1916), firehouse (1930-1931), the Bridgeport Bridge (1893), the Aetnaville Bridge (1891), "The Marina," Wheeling Island Baseball Park, and "Belle Island Park." It includes the separately listed Wheeling Suspension Bridge, Harry C. and Jessie F. Franzheim House, and John McLure House.

Hawkwood is an Italianate-villa style country house near Gordonsville, Virginia, United States. It was designed by architect Alexander Jackson Davis of New York in 1851 for Richard Overton Morris of the locally prominent Morris family, and was completed in 1855. The house, which has also been described as being in the Italian Villa style, is one of only two Davis designs in that style which have not been substantially altered.

Chester Springs Historic District, also known as The Old Art School, Orphan's School, Yellow Springs Spa, and Good News Buildings, is a national historic district located in West Pikeland Township, Chester County, Pennsylvania. The district includes 7 contributing buildings, 1 contributing site, and 1 contributing structure in the spa community of Chester Springs. The district includes the old hotel and inn, two large residences, a bath house at one end of the springs, and a studio. It also includes a wooden summer house that enclosed the iron springs. The property was the site of a hospital commissioned by the Continental Congress and built in 1777. The three-story, 106 feet by 36 feet wide building burned in 1902, was reconstructed, then burned again in the 1960s. The Yellow Springs resort operated in the early-mid 19th century and many of the buildings date from that period.

Yates Tavern, also known as Yancy Cabin, is a historic tavern located near Gretna, Pittsylvania County, Virginia. The building dates to the late-18th or early-19th century, and is a two-story, frame building sheathed in weatherboard. It measures approximately 18 feet by 24 feet and has eight-inch jetty on each long side at the second-floor level. It is representative of a traditional hall-and-parlor Tidewater house. The building was occupied by a tavern in the early-19th century. It was restored in the 1970s.

J. Huston Tavern, also known as the Arrow Rock Tavern and The Old Tavern, is a historic tavern building located at Arrow Rock, Saline County, Missouri. It was built in 1834 by Judge Joseph Huston, and is a 2 1/2-story, Federal style brick building. A store with a second-floor ballroom was added in 1840. The tavern is the oldest continuously serving restaurant west of the Mississippi River.