Related Research Articles
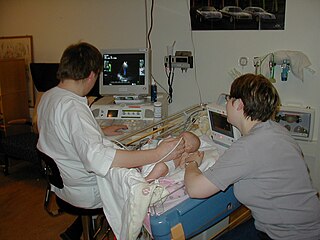
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics or to generate an informative audible sound. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography, or echography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. The machine used is called an ultrasound machine, a sonograph or an echograph. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ultrasonogram, a sonogram or an echogram.
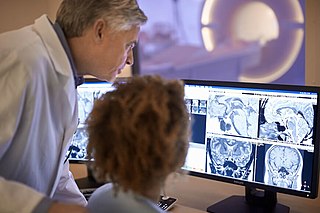
Radiology is the medical specialty that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography, but today it includes all imaging modalities, including those that use no ionizing electromagnetic radiation, as well as others that do, such as computed tomography (CT), fluoroscopy, and nuclear medicine including positron emission tomography (PET). Interventional radiology is the performance of usually minimally invasive medical procedures with the guidance of imaging technologies such as those mentioned above.

Mammography is the process of using low-energy X-rays to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through detection of characteristic masses or microcalcifications.

Gynecologic ultrasonography or gynecologic sonography refers to the application of medical ultrasonography to the female pelvic organs as well as the bladder, the adnexa, and the recto-uterine pouch. The procedure may lead to other medically relevant findings in the pelvis.This technique is useful to detect myomas or mullerian malformations.

Fibroadenomas are benign breast tumours characterized by an admixture of stromal and epithelial tissue. Breasts are made of lobules and ducts. These are surrounded by glandular, fibrous and fatty tissues. Fibroadenomas develop from the lobules. The glandular tissue and ducts grow over the lobule to form a solid lump.
Computed tomography laser mammography (CTLM) is the trademark of Imaging Diagnostic Systems, Inc. for its optical tomographic technique for female breast imaging.

Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) or echo-endoscopy is a medical procedure in which endoscopy is combined with ultrasound to obtain images of the internal organs in the chest, abdomen and colon. It can be used to visualize the walls of these organs, or to look at adjacent structures. Combined with Doppler imaging, nearby blood vessels can also be evaluated.

3D ultrasound is a medical ultrasound technique, often used in fetal, cardiac, trans-rectal and intra-vascular applications. 3D ultrasound refers specifically to the volume rendering of ultrasound data. When involving a series of 3D volumes collected over time, it can also be referred to as 4D ultrasound or real-time 3D ultrasound.
The Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) is a quality assurance tool originally designed for use with mammography. The system is a collaborative effort of many health groups but is published and trademarked by the American College of Radiology (ACR).

Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of medical images. Imaging techniques in X-ray, MRI, Endoscopy, and ultrasound diagnostics yield a great deal of information that the radiologist or other medical professional has to analyze and evaluate comprehensively in a short time. CAD systems process digital images or videos for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases, in order to offer input to support a decision taken by the professional.
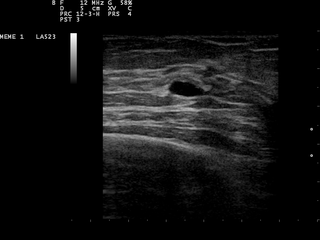
A breast cyst is a cyst, a fluid-filled sac, within the breast. One breast can have one or more cysts. They are often described as round or oval lumps with distinct edges. In texture, a breast cyst usually feels like a soft grape or a water-filled balloon, but sometimes a breast cyst feels firm.

Breast cancer screening is the medical screening of asymptomatic, apparently healthy women for breast cancer in an attempt to achieve an earlier diagnosis. The assumption is that early detection will improve outcomes. A number of screening tests have been employed, including clinical and self breast exams, mammography, genetic screening, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging.

Molecular breast imaging (MBI), also known as scintimammography, is a type of breast imaging test that is used to detect cancer cells in breast tissue of individuals who have had abnormal mammograms, especially for those who have dense breast tissue, post-operative scar tissue or breast implants.
Daniel B. Kopans, MD, FACR is a radiologist specializing in mammography and other forms of breast imaging.
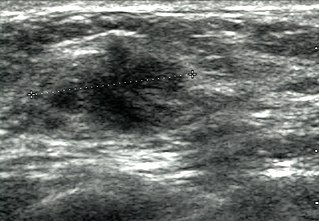
Breast ultrasound is a medical imaging technique that uses medical ultrasonography to perform imaging of the breast. It can be performed for either diagnostic or screening purposes and can be used with or without a mammogram. In particular, breast ultrasound may be useful for younger women who have denser fibrous breast tissue that may make mammograms more challenging to interpret.

A breast biopsy is usually done after a suspicious lesion is discovered on either mammography or ultrasound to get tissue for pathological diagnosis. Several methods for a breast biopsy now exist. The most appropriate method of biopsy for a patient depends upon a variety of factors, including the size, location, appearance and characteristics of the abnormality. The different types of breast biopsies include fine-needle aspiration (FNA), vacuum-assisted biopsy, core needle biopsy, and surgical excision biopsy. Breast biopsies can be done utilizing ultrasound, MRI or a stereotactic biopsy imaging guidance. Vacuum assisted biopsies are typically done using stereotactic techniques when the suspicious lesion can only be seen on mammography. On average, 5–10 biopsies of a suspicious breast lesion will lead to the diagnosis of one case of breast cancer. Needle biopsies have largely replaced open surgical biopsies in the initial assessment of imaging as well as palpable abnormalities in the breast.

The triple test score is a diagnostic tool for examining potentially cancerous breasts. Diagnostic accuracy of the triple test score is nearly 100%. Scoring includes using the procedures of physical examination, mammography and needle biopsy. If the results of a triple test score are greater than five, an excisional biopsy is indicated.
Dynamic angiothermography (DATG) is a technique for the diagnosis of breast cancer. This technique, though springing from the previous conception of thermography, is based on a completely different principle. DATG records the temperature variations linked to the vascular changes in the breast due to angiogenesis. The presence, change, and growth of tumors and lesions in breast tissue change the vascular network in the breast. Consequently, through measuring the vascular structure over time, DATG effectively monitors the change in breast tissue due to tumors and lesions. It is currently used in combination with other techniques for diagnosis of breast cancer. This diagnostic method is a low-cost one compared with other techniques.
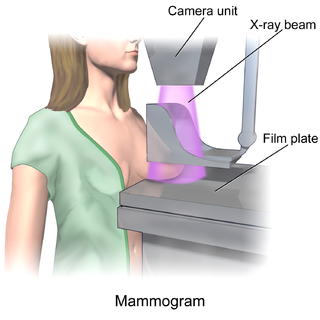
In medicine, breast imaging is a sub-speciality of diagnostic radiology that involves imaging of the breasts for screening or diagnostic purposes. There are various methods of breast imaging using a variety of technologies as described in detail below. Traditional screening and diagnostic mammography uses x-ray technology and has been the mainstay of breast imaging for many decades. Breast tomosynthesis is a relatively new digital x-ray mammography technique that produces multiple image slices of the breast similar to, but distinct from, computed tomography (CT). Xeromammography and galactography are somewhat outdated technologies that also use x-ray technology and are now used infrequently in the detection of breast cancer. Breast ultrasound is another technology employed in diagnosis and screening that can help differentiate between fluid filled and solid lesions, an important factor to determine if a lesion may be cancerous. Breast MRI is a technology typically reserved for high-risk patients and patients recently diagnosed with breast cancer. Lastly, scintimammography is used in a subgroup of patients who have abnormal mammograms or whose screening is not reliable on the basis of using traditional mammography or ultrasound.
Ultrasound computer tomography (USCT), sometimes also Ultrasound computed tomography, Ultrasound computerized tomography or just Ultrasound tomography, is a form of medical ultrasound tomography utilizing ultrasound waves as physical phenomenon for imaging. It is mostly in use for soft tissue medical imaging, especially breast imaging.
References
- 1 2 Mahesh K. Shetty (15 March 2013). Breast and Gynecological Cancers: An Integrated Approach for Screening and Early Diagnosis in Developing Countries. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 309–311. ISBN 978-1-4614-1876-4.
- 1 2 Kelly KM, Richwald GA (2011). "Automated whole-breast ultrasound: advancing the performance of breast cancer screening". Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI (review). 32 (4): 273–80. doi:10.1053/j.sult.2011.02.004. PMID 21782117.
- ↑ Marie Tartar; Christopher E. Comstock; Michael S. Kipper (2008). Breast Cancer Imaging: A Multidisciplinary, Multimodality Approach. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 4. ISBN 978-0-323-04677-0.
- ↑ S. S. Kaplan (May 2014). "Automated whole breast ultrasound". Radiologic Clinics of North America. 52 (3): 539–46. doi:10.1016/j.rcl.2014.01.002. PMID 24792655.
- ↑ Denise Thigpen; Amanda Kappler; Rachel Brem (March 2018). "The Role of Ultrasound in Screening Dense Breasts – A Review of the Literature and Practical Solutions for Implementation". Diagnostics. 8 (1): 20. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics8010020 . PMC 5872003 . PMID 29547532.
- 1 2 Matejka Rebolj; Valentina Assi; Adam Brentnall; Dharmishta Parmar; Stephen W. Duffy (June 2018). "Addition of ultrasound to mammography in the case of dense breast tissue: Systematic review and meta-analysis". British Journal of Cancer. 118 (12): 1559–1570. doi:10.1038/s41416-018-0080-3. PMC 6008336 . PMID 29736009.
- ↑ A. Thomas Stavros (2004). Breast Ultrasound. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 151. ISBN 978-0-397-51624-7.
- ↑ Sylvia Helen Heywang-Koebrunner; Ingrid Schreer (15 January 2014). Diagnostic Breast Imaging: Mammography, Sonography, Magnetic Resonance Imaging, and Interventional Procedures. Thieme. p. 349. ISBN 978-3-13-150411-1.